| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | C09CA04 |
| UNII | J0E2756Z7N |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID0023169 |
Structure
| InChI Key | YOSHYTLCDANDAN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H28N6O |
| Molecular Weight | 428.54 |
| AlogP | 4.78 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 5.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 7.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 87.13 |
| Molecular species | ACID |
| Aromatic Rings | 3.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 32.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Type-1 angiotensin II receptor antagonist | ANTAGONIST | FDA |
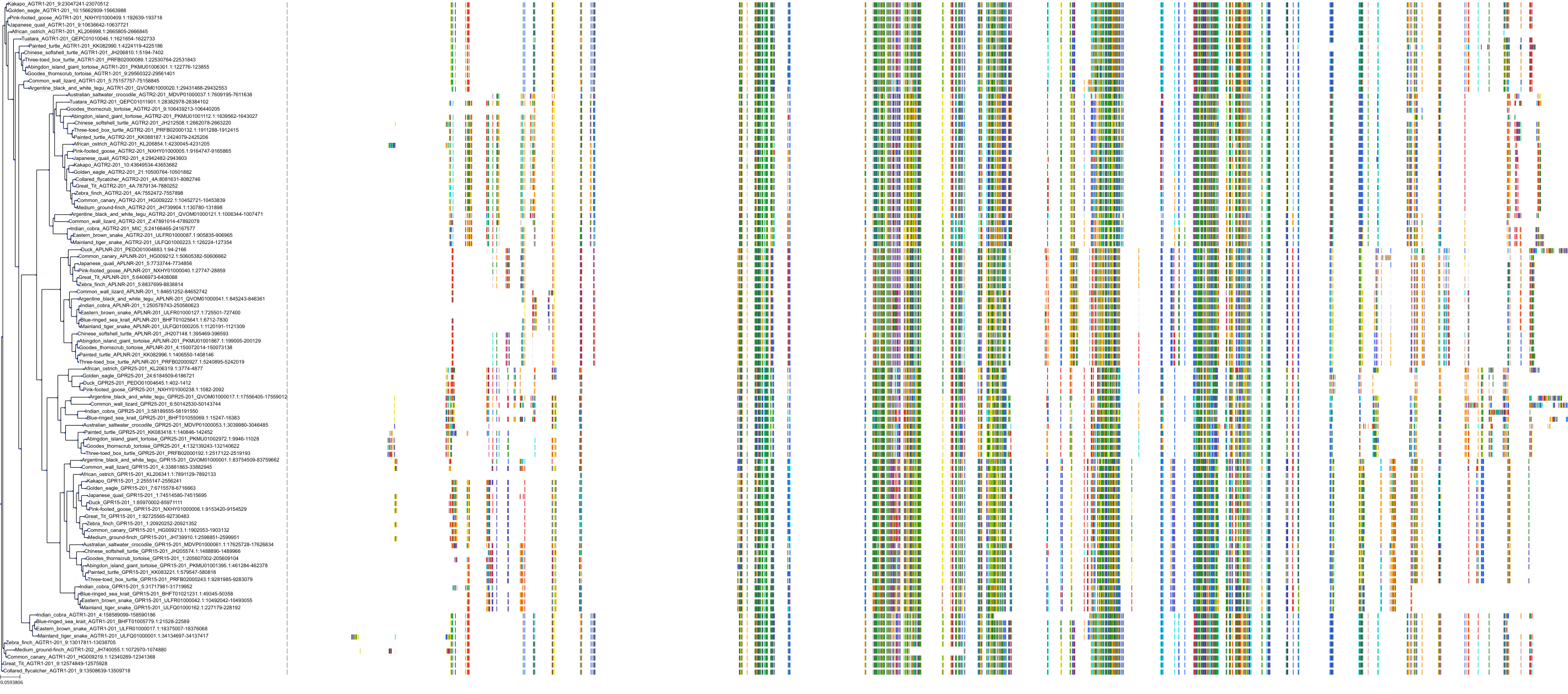
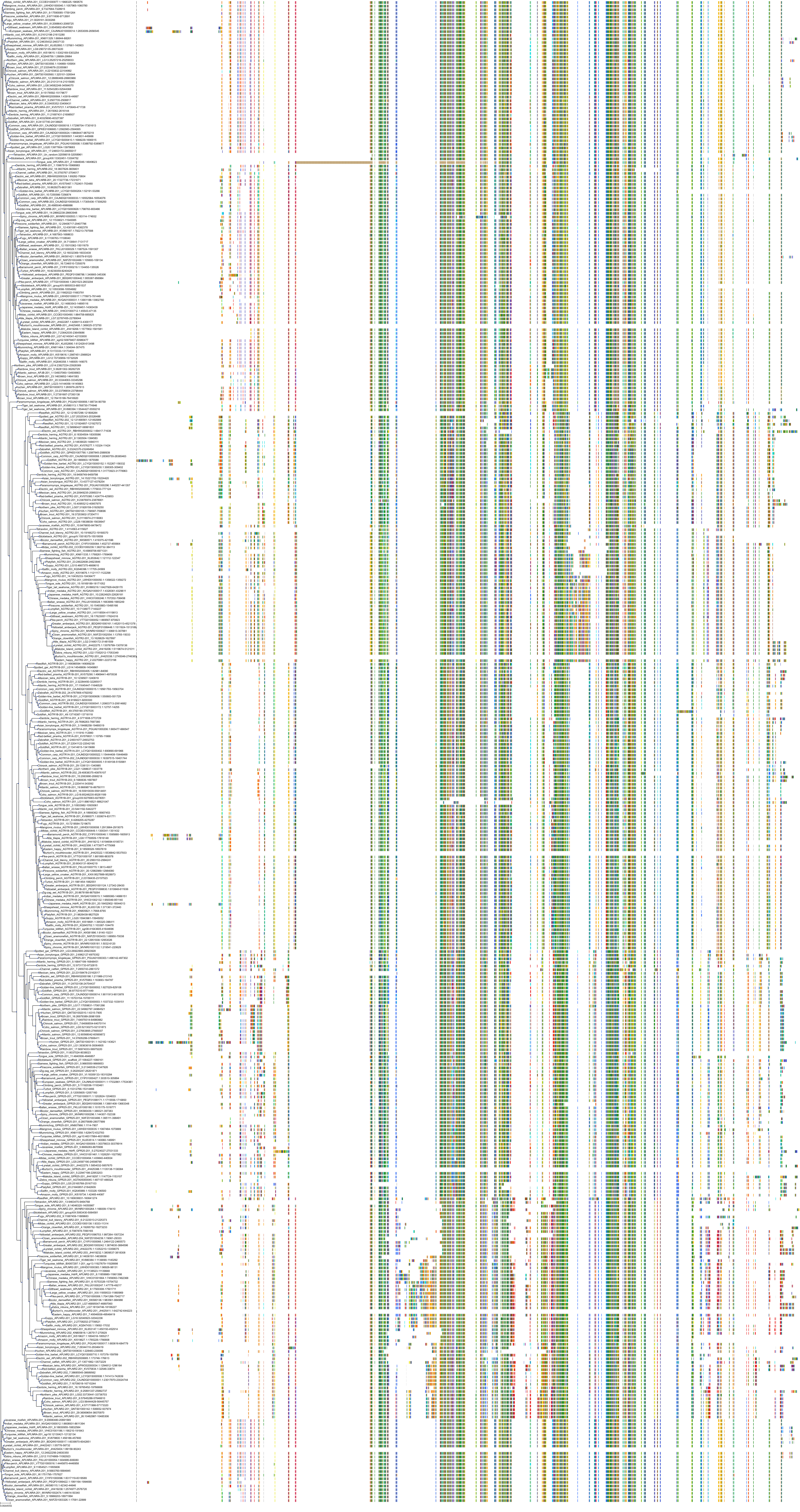
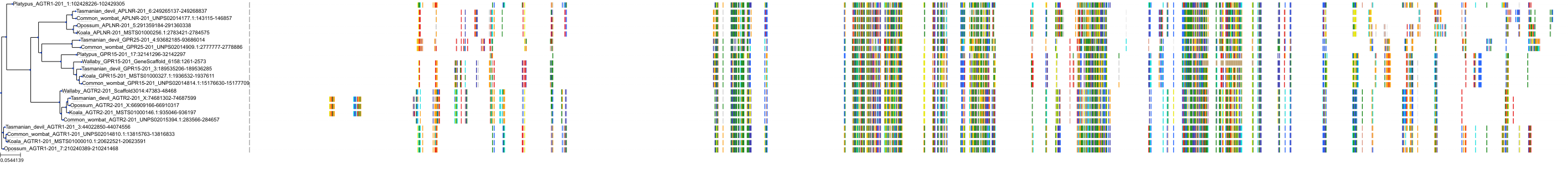
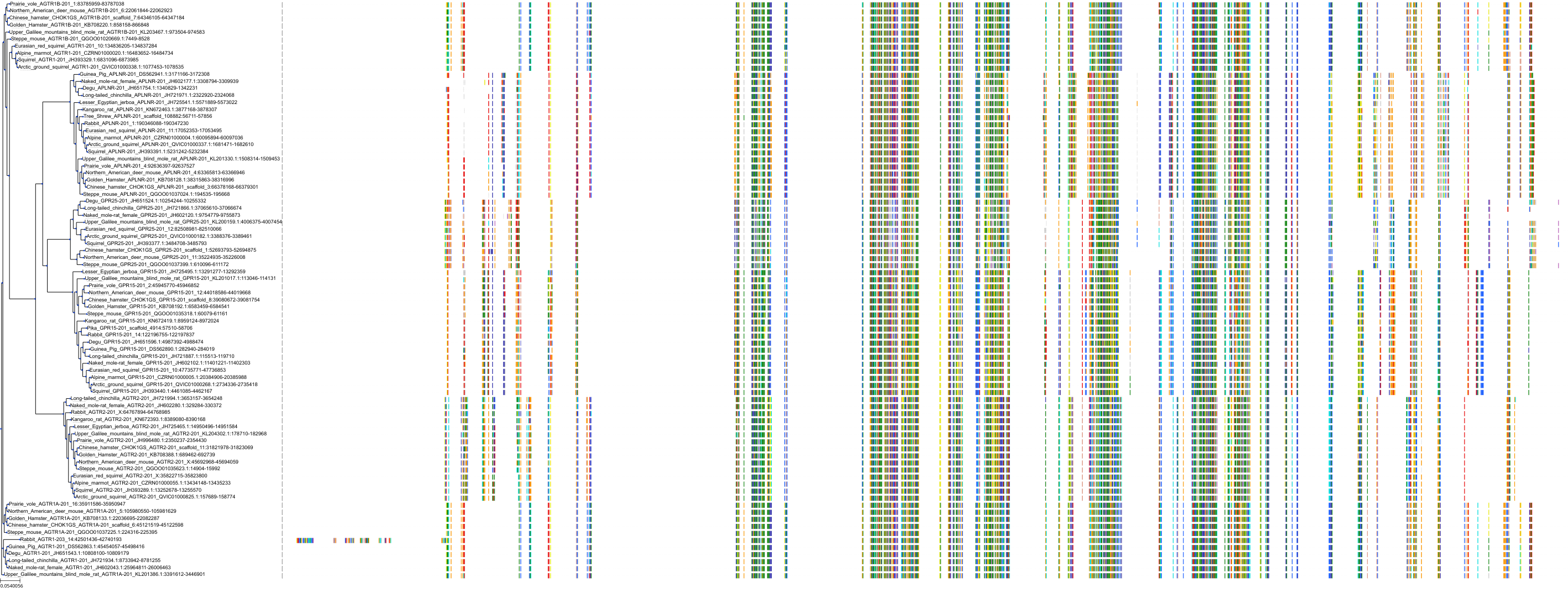
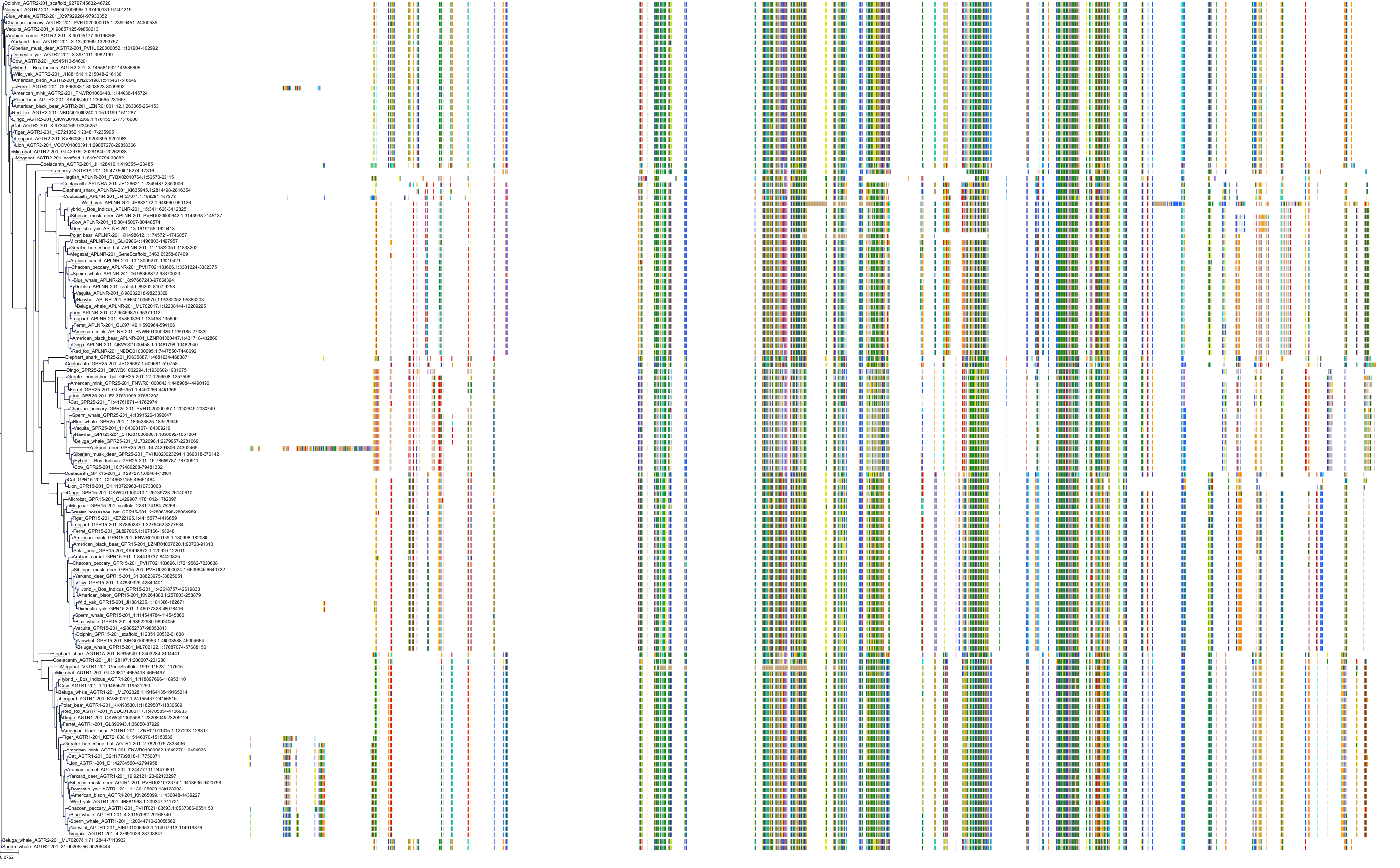
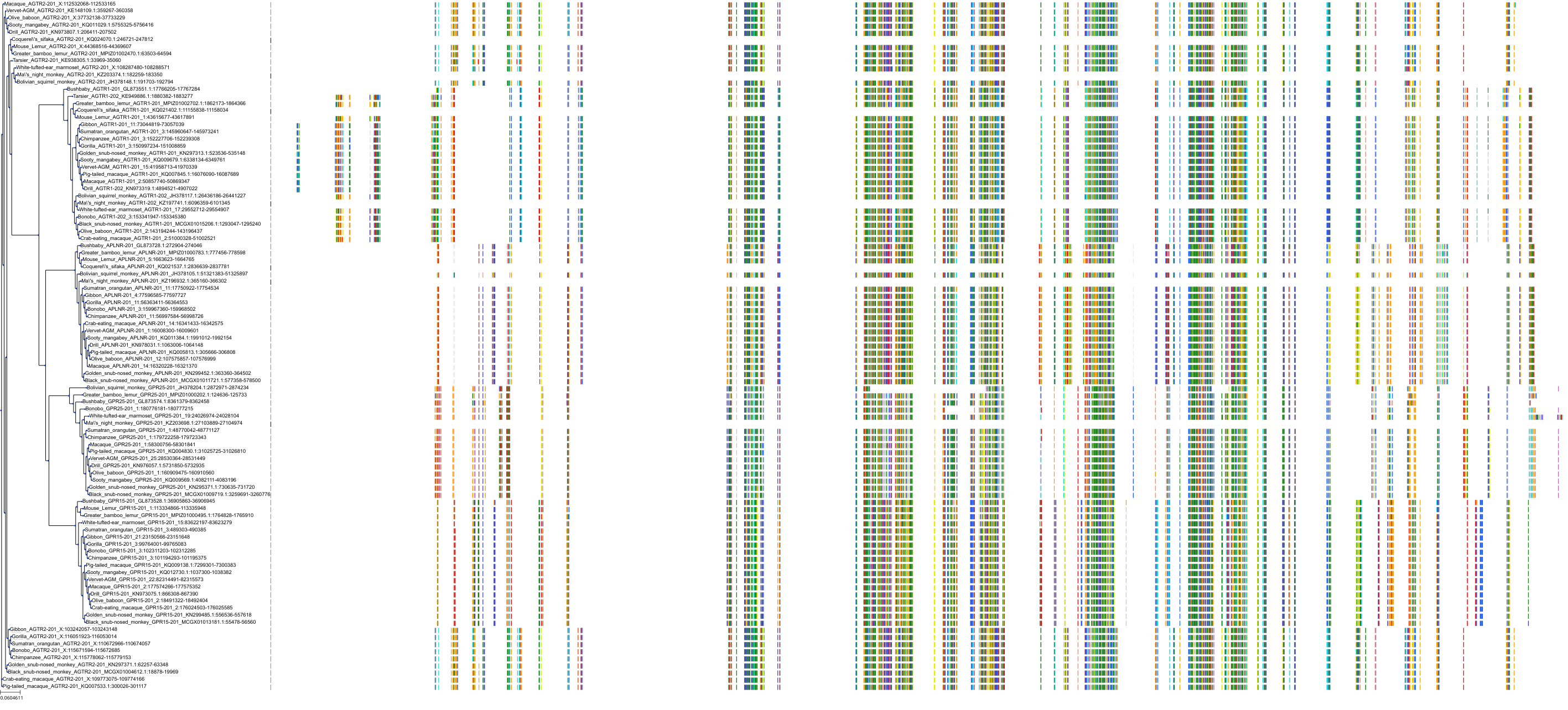
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Type-1 angiotensin II receptor Description: Type-1 angiotensin II receptor Organism : Homo sapiens P30556 ENSG00000144891 |
||||
Environmental Exposure
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 5959 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1513 |
| DrugBank | DB01029 |
| DrugCentral | 1481 |
| FDA SRS | J0E2756Z7N |
| Human Metabolome Database | HMDB0015163 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 589 |
| KEGG | C07469 |
| PharmGKB | PA450084 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL4246 |
| ZINC | ZINC000003872931 |
 Cricetulus griseus
Cricetulus griseus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Oryctolagus cuniculus
Oryctolagus cuniculus
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus