| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| UNII | 78G6MP5PZ5 |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID00657619 |
Structure
| InChI Key | IRTDIKMSKMREGO-OAHLLOKOSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H24N4O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 408.46 |
| AlogP | 2.71 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 7.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 2.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 5.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 96.17 |
| Molecular species | ACID |
| Aromatic Rings | 3.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 30.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| PI3-kinase class I inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Transferase
|
- | 10-870 | - | - | - |
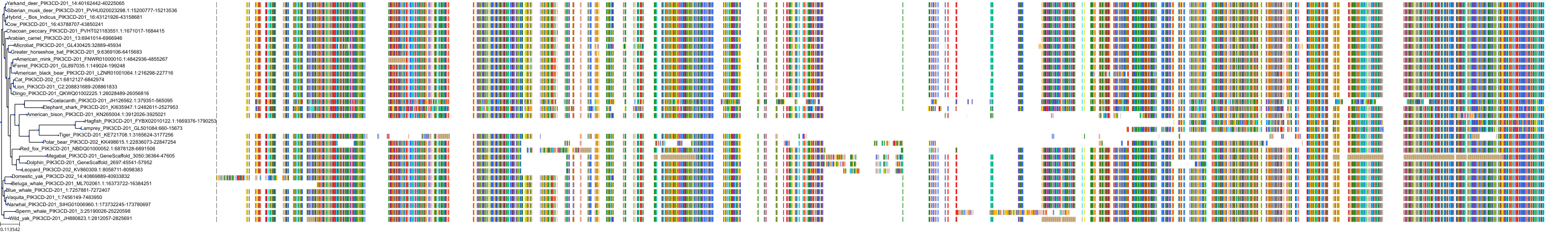
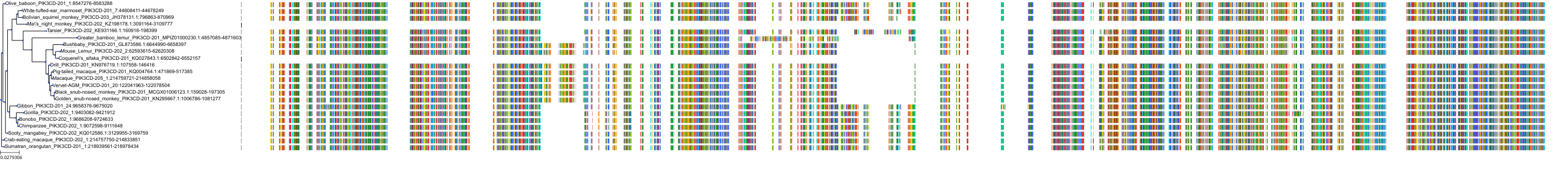
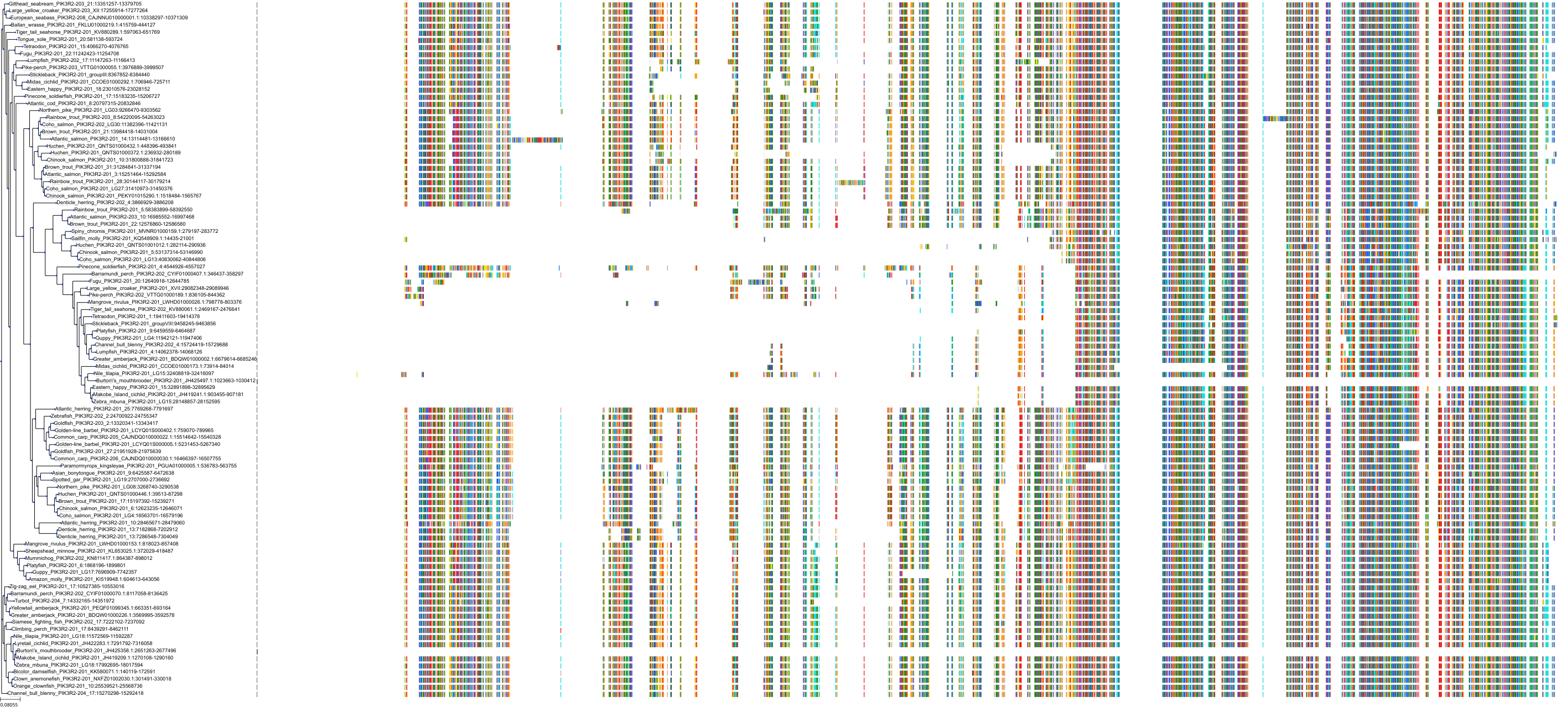
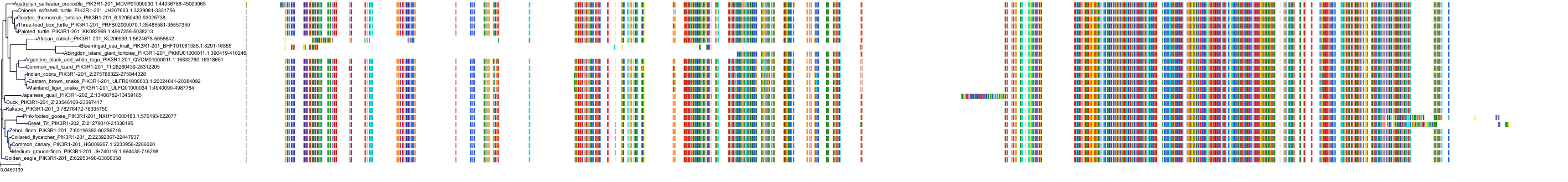
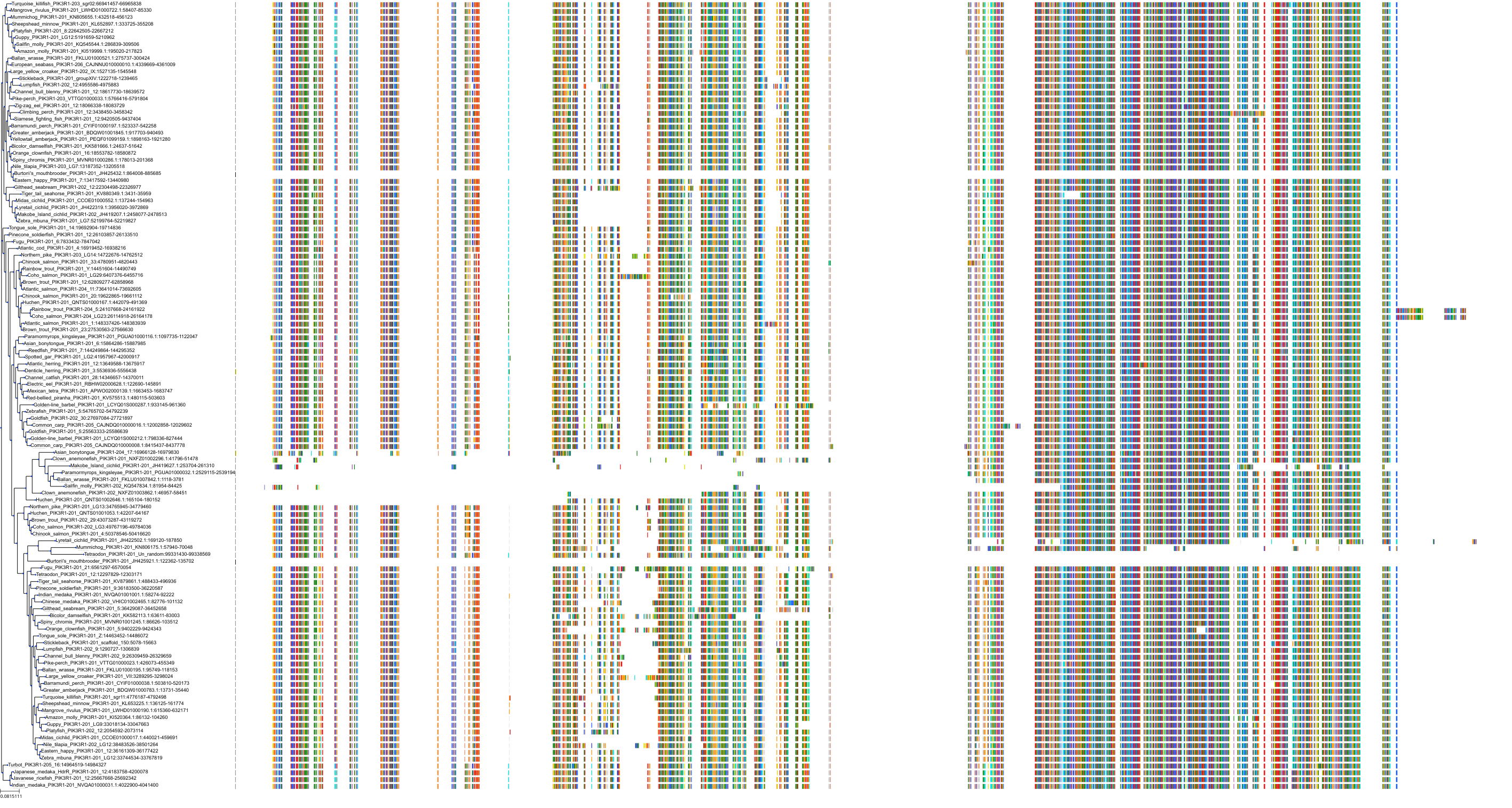
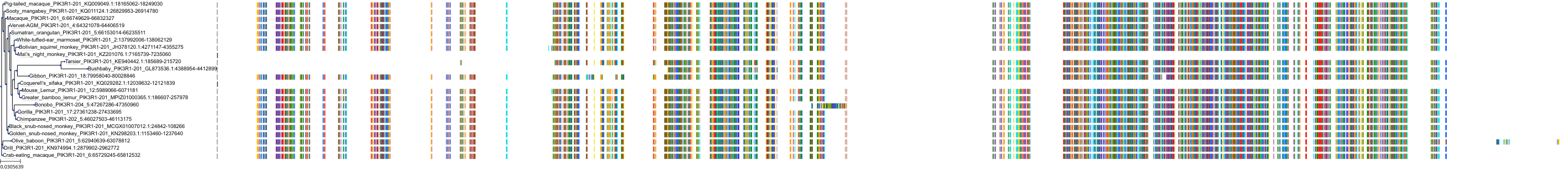
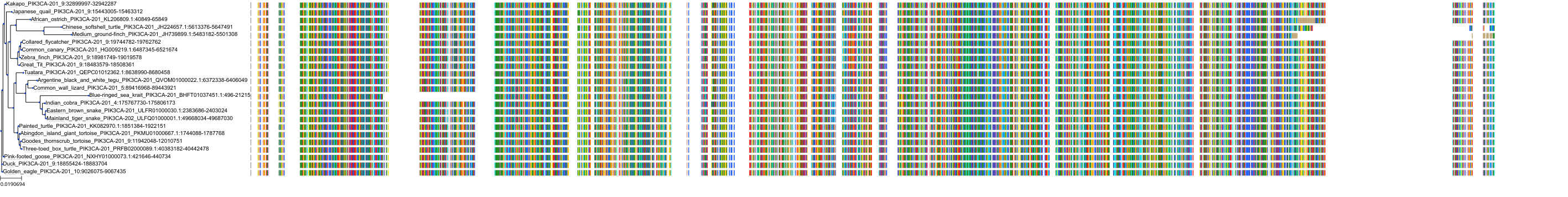
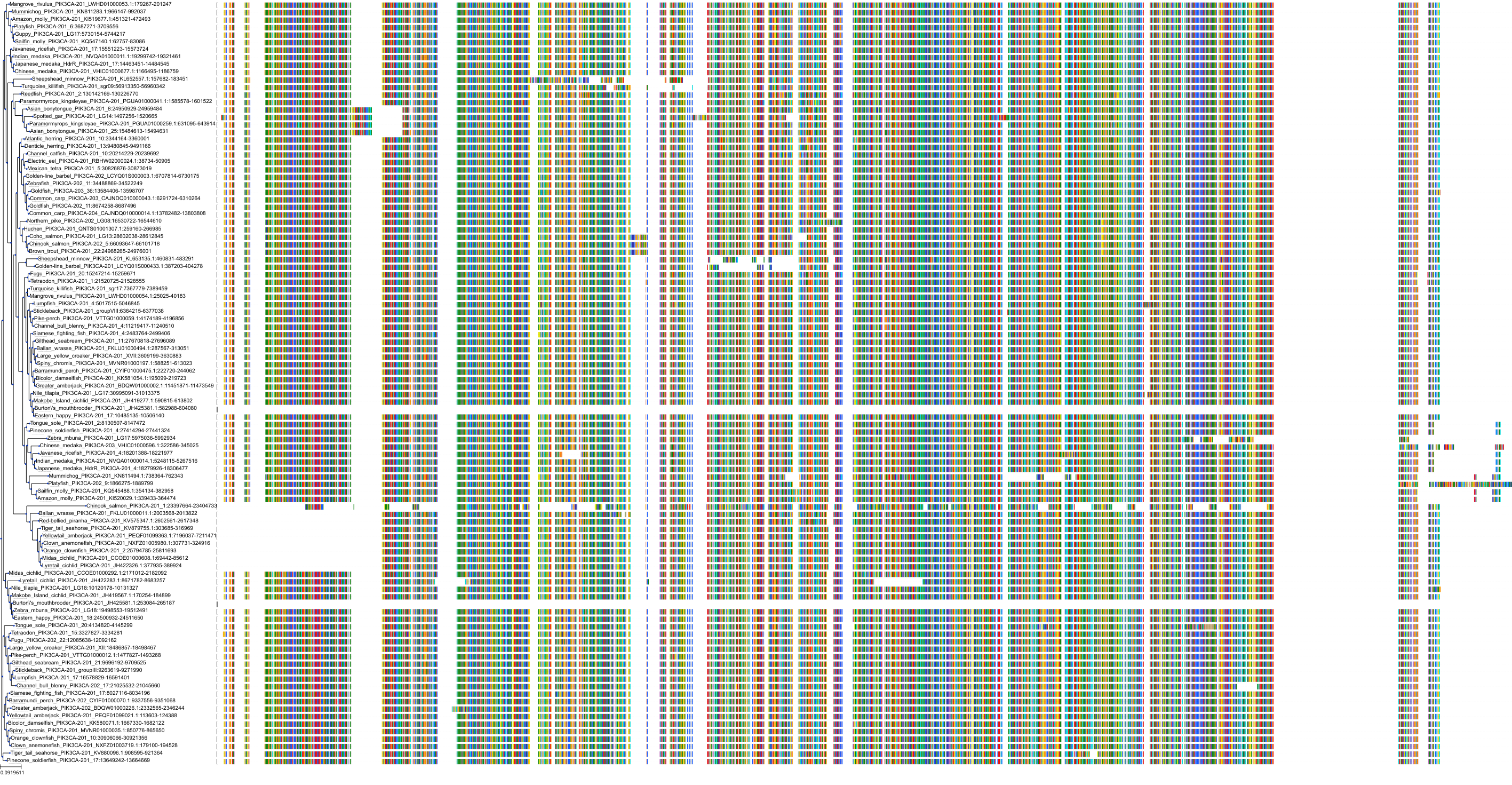
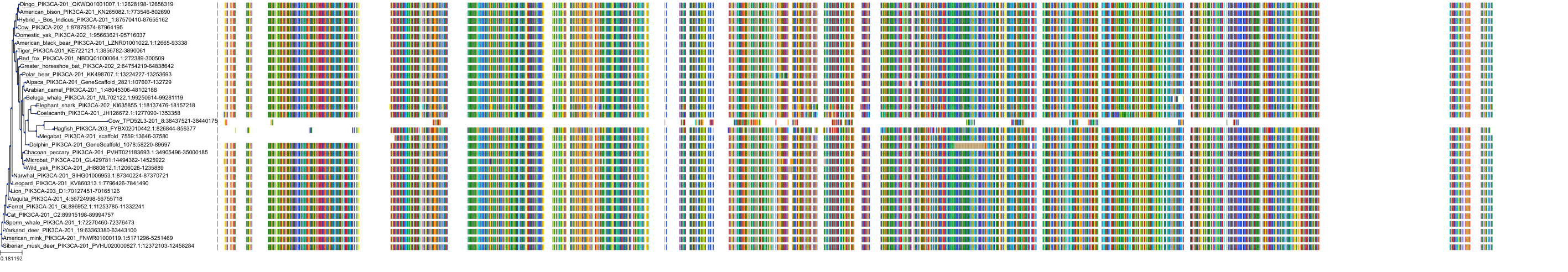
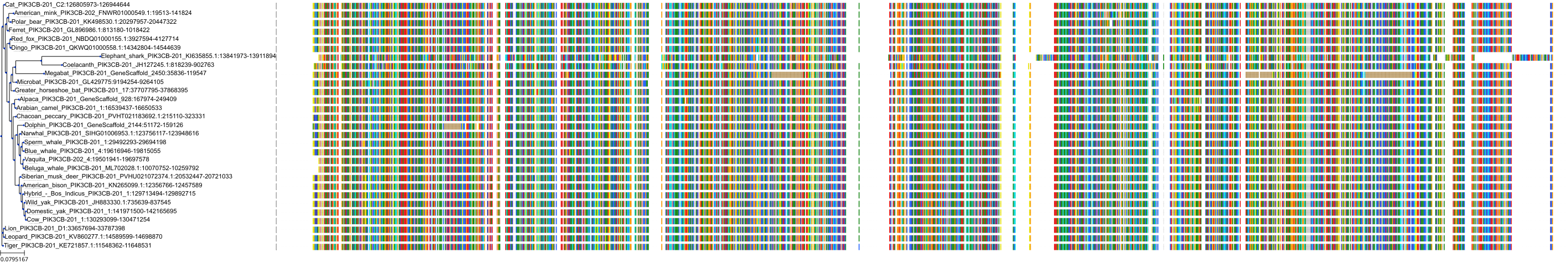
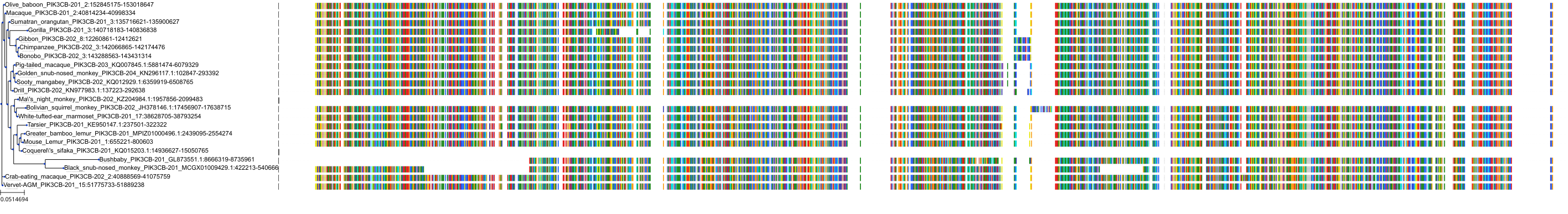
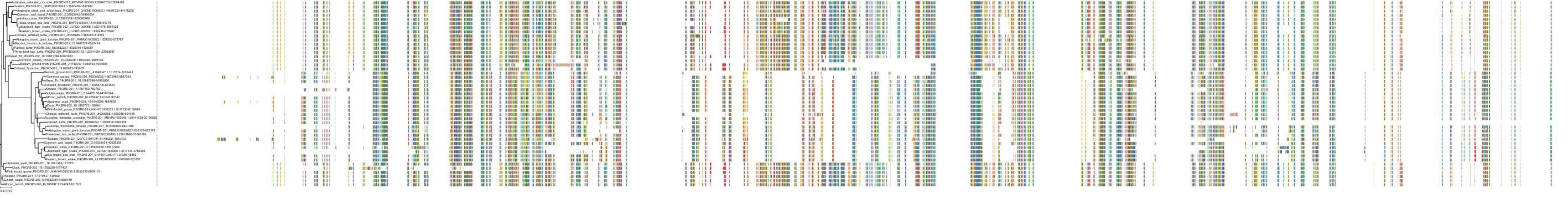
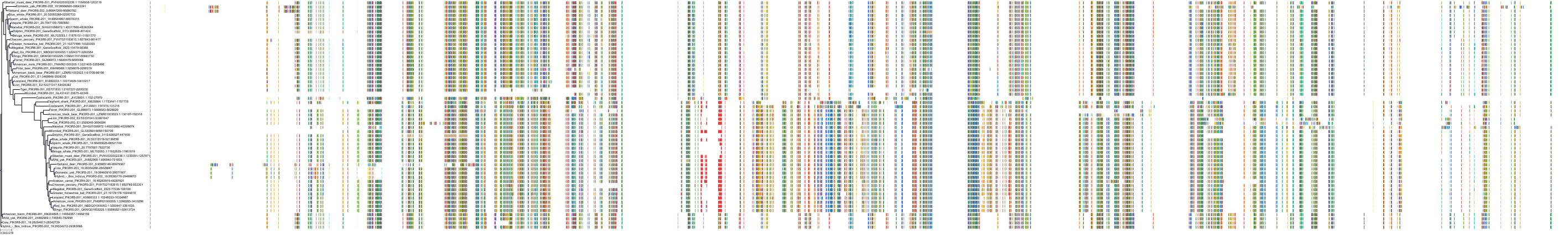
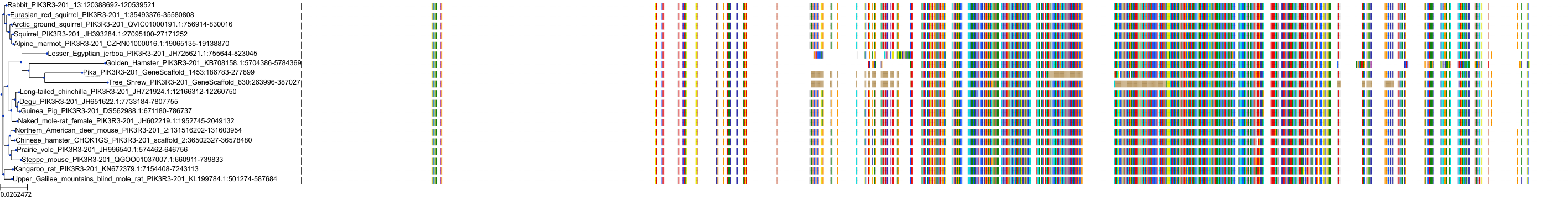
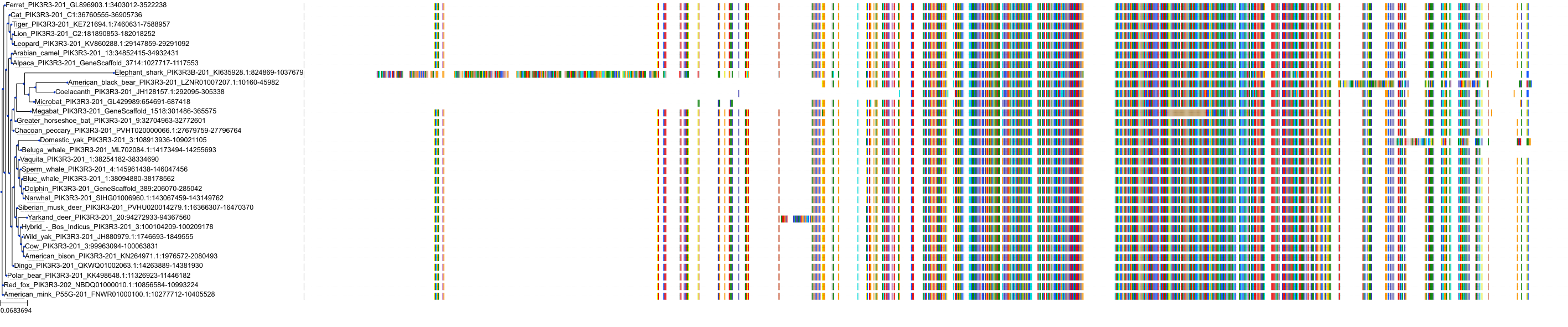
Target Conservation
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta isoform Organism : Homo sapiens O00329 ENSG00000171608 |
||||
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit beta Organism : Homo sapiens O00459 ENSG00000105647 |
||||
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha Organism : Homo sapiens P27986 ENSG00000145675 |
||||
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha isoform Organism : Homo sapiens P42336 ENSG00000121879 |
||||
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit beta isoform Organism : Homo sapiens P42338 ENSG00000051382 |
||||
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit gamma isoform Organism : Homo sapiens P48736 ENSG00000105851 |
||||
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulatory subunit 5 Organism : Homo sapiens Q8WYR1 ENSG00000141506 |
||||
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit gamma Organism : Homo sapiens Q92569 ENSG00000117461 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 91359 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2165191 |
| DrugBank | DB14980 |
| FDA SRS | 78G6MP5PZ5 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 8059 |
| PDB | A82 |
| PubChem | 44137675 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL1812377 |
| ZINC | ZINC000038628584 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens