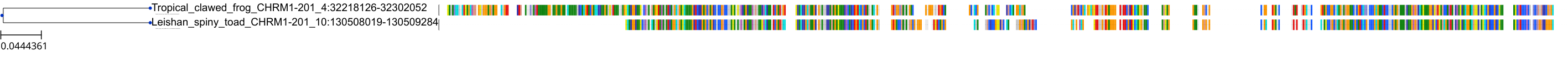| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| UNII | 9ORI6L73CJ |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID60157286 |
Structure
| InChI Key | JOLJIIDDOBNFHW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H23N3OS |
| Molecular Weight | 281.43 |
| AlogP | 3.22 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 5.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 7.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 38.25 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 1.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 19.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1 agonist | AGONIST | PubMed |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Membrane receptor
Family A G protein-coupled receptor
Small molecule receptor (family A GPCR)
Monoamine receptor
Acetylcholine receptor
|
1.6-630.96 | 0.008-954.99 | - | 7.762-724.44 | - |
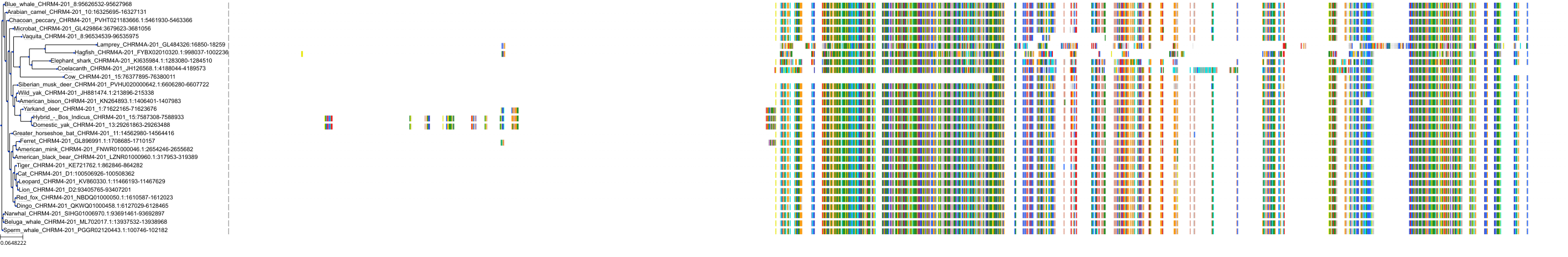
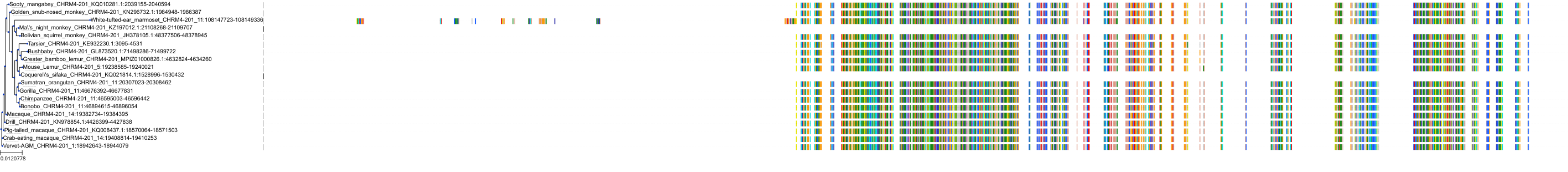
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4 Description: Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4 Organism : Homo sapiens P08173 ENSG00000180720 |
||||
|
Protein: Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1 Description: Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1 Organism : Homo sapiens P11229 ENSG00000168539 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 10056 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL21536 |
| DrugBank | DB15357 |
| DrugCentral | 3652 |
| FDA SRS | 9ORI6L73CJ |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 57 |
| KEGG | C11767 |
| PubChem | 60809 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL121046 |
| ZINC | ZINC000001532358 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus
 Oryctolagus cuniculus
Oryctolagus cuniculus
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus