Structure
| InChI Key | HGVNLRPZOWWDKD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H17NOS |
| Molecular Weight | 355.46 |
| AlogP | 6.25 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 3.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 1.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 32.59 |
| Molecular species | ACID |
| Aromatic Rings | 3.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 26.0 |
Pharmacology
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
Atypical protein kinase group
Atypical protein kinase PIKK family
Atypical protein kinase FRAP subfamily
|
- | 45-370 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Transferase
|
10-51 | 3-180 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
|
10-51 | 3-180 | - | - | - |
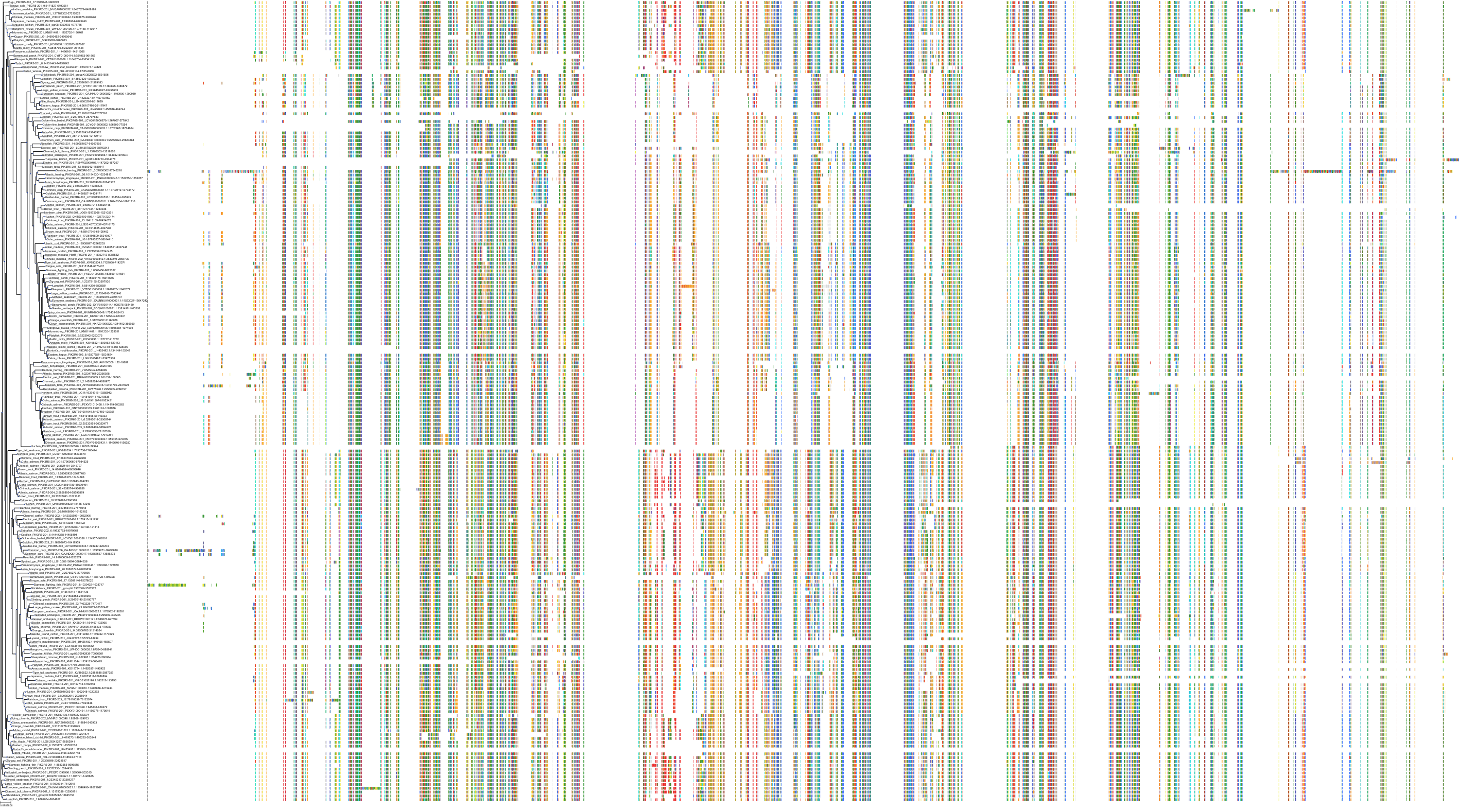
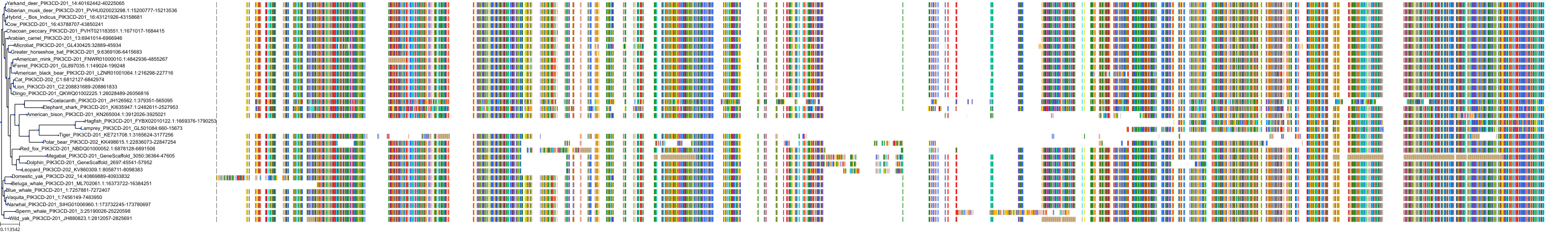
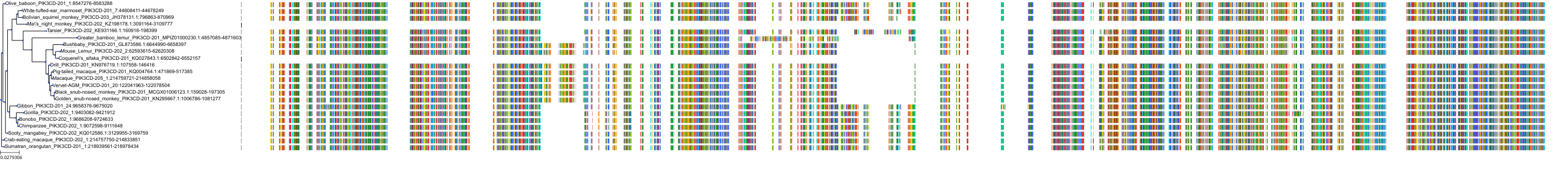
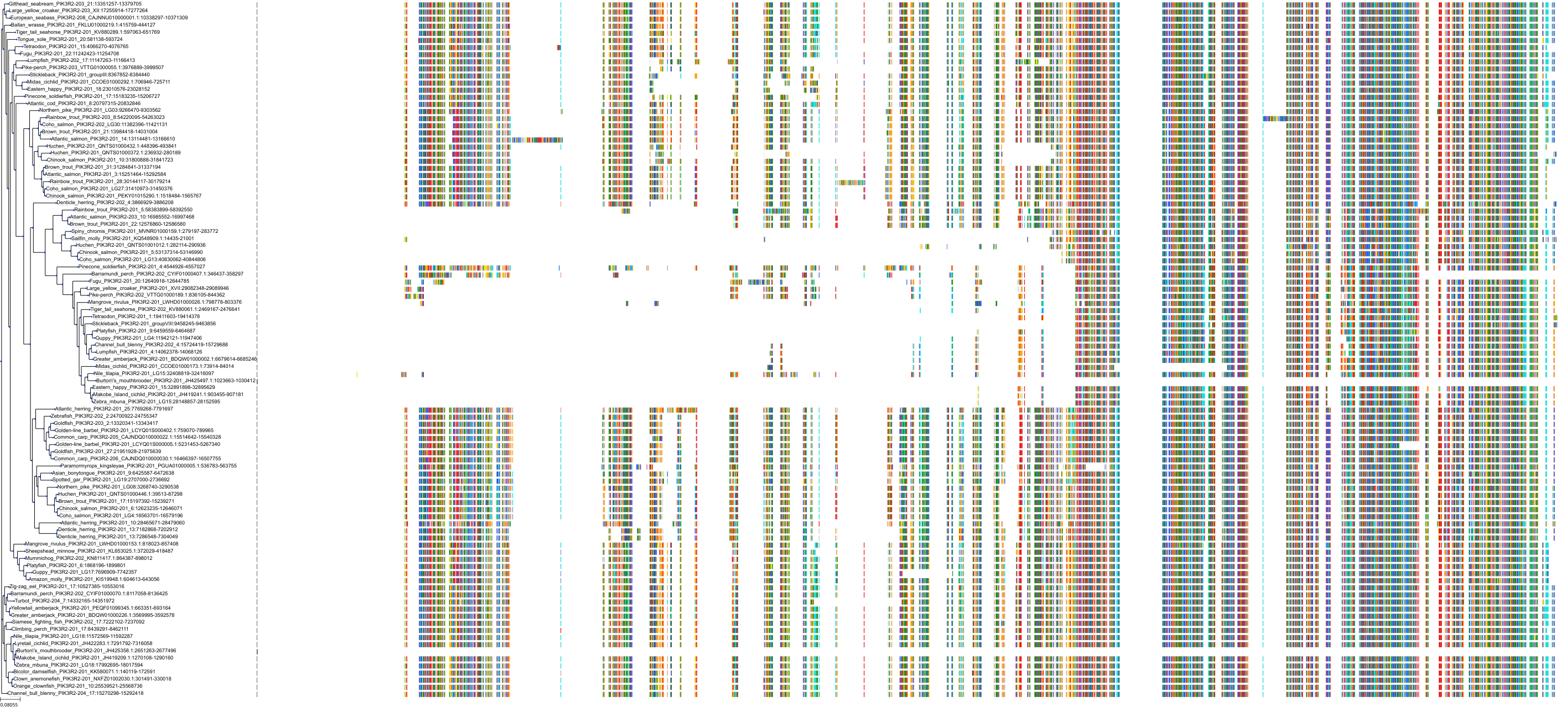
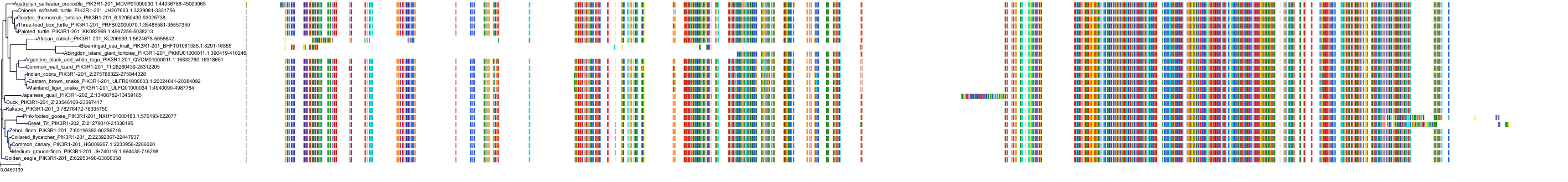
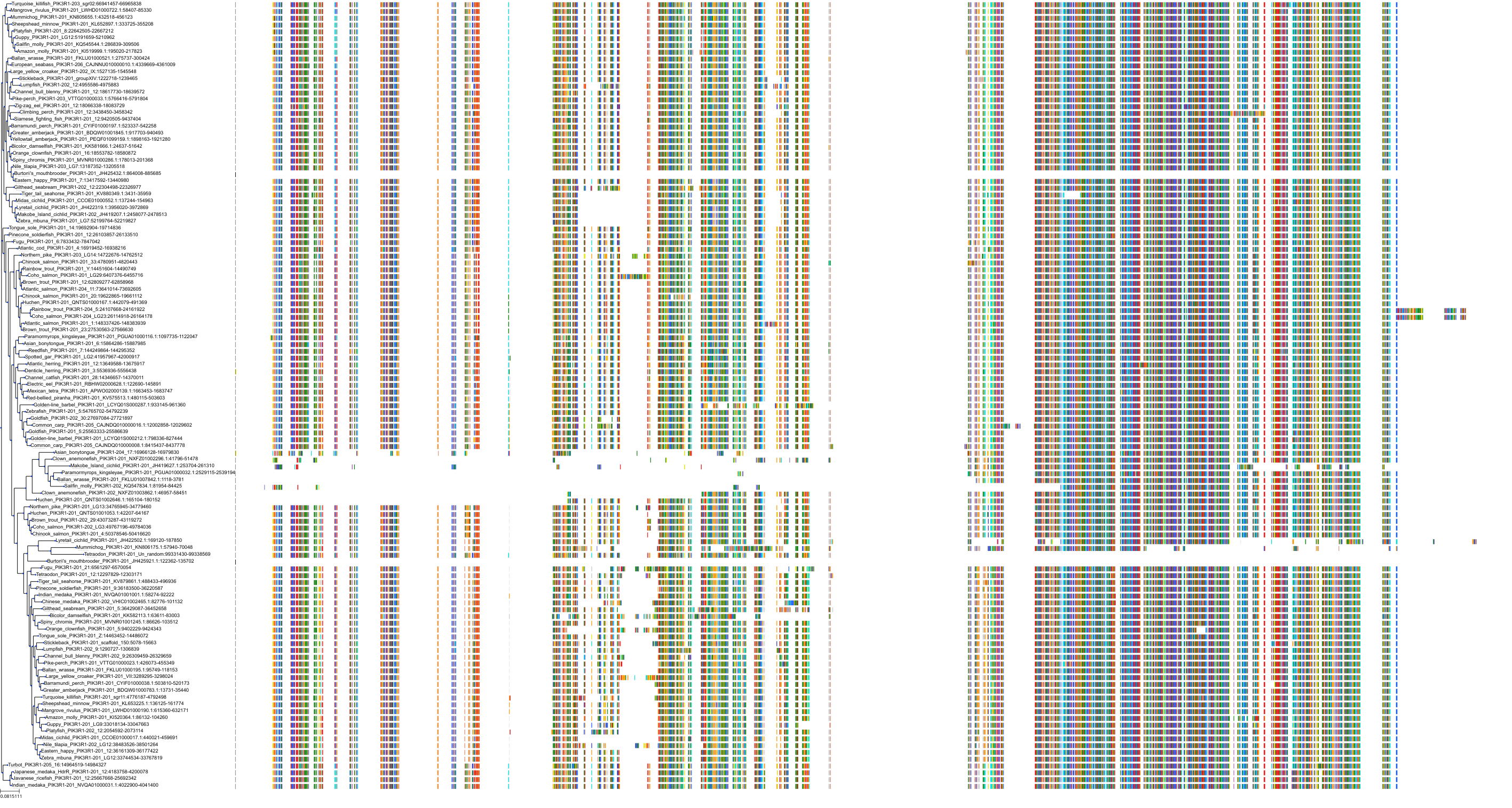
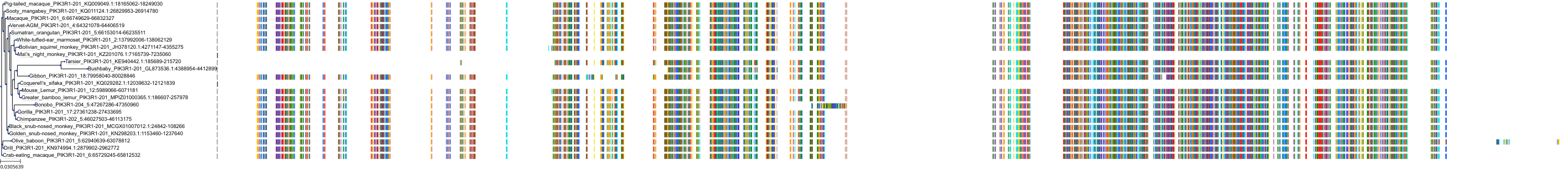
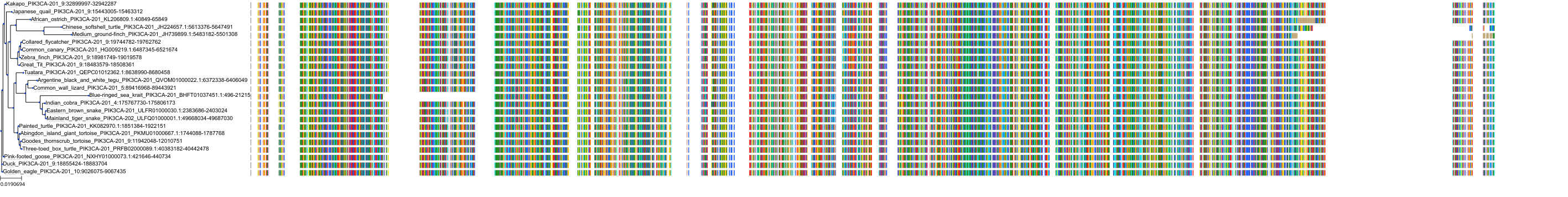
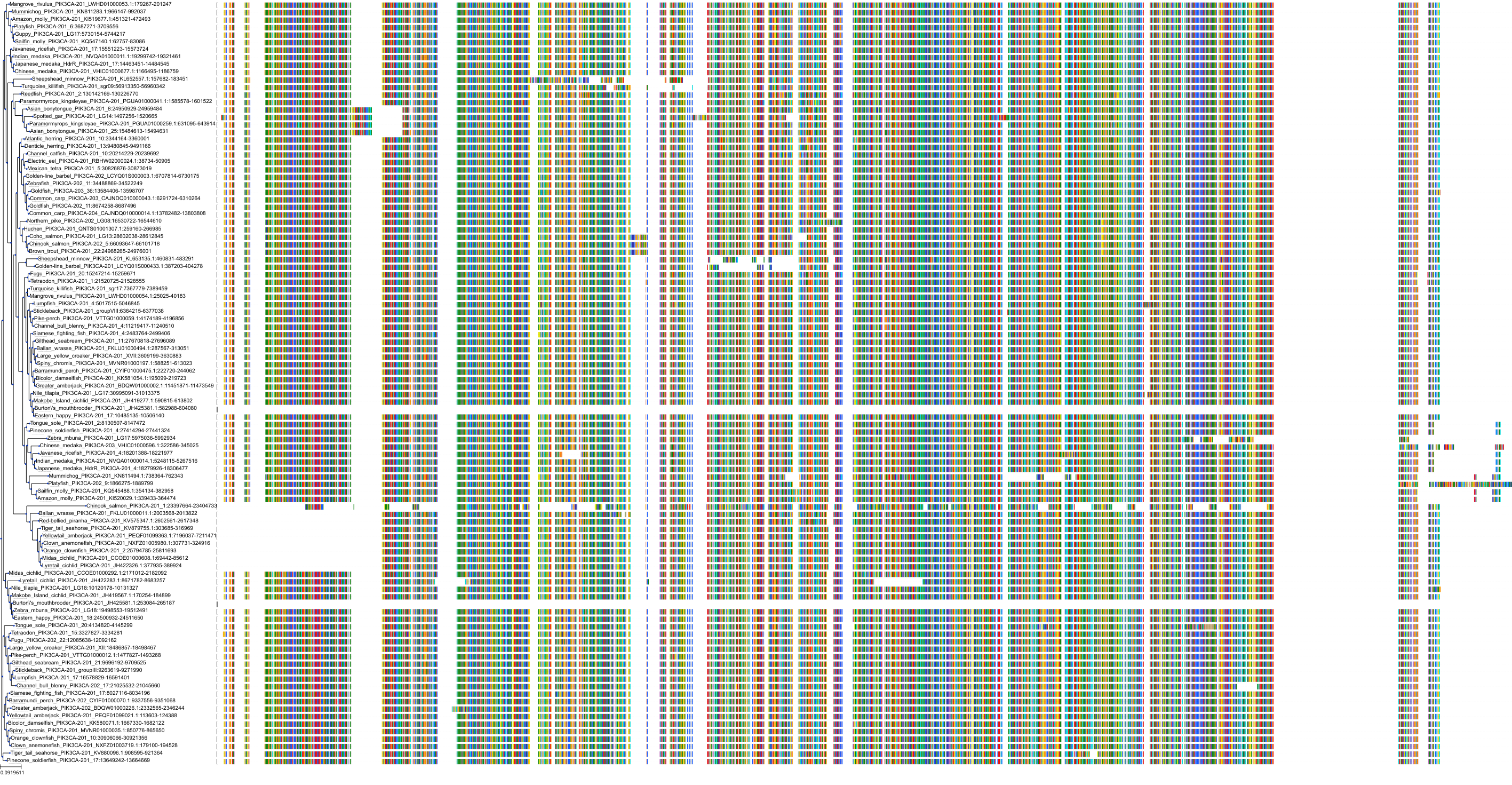
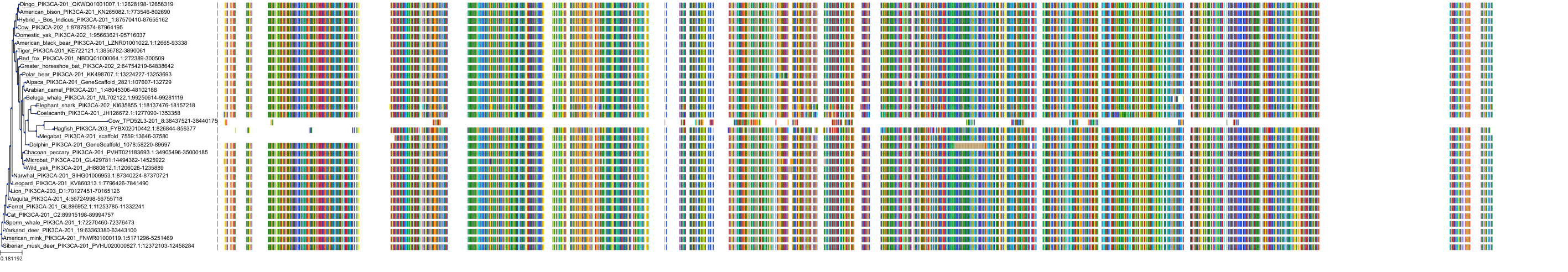
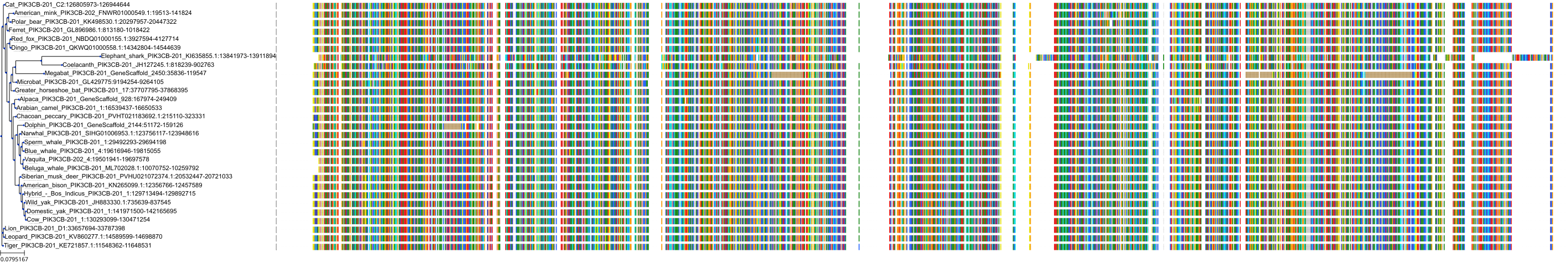
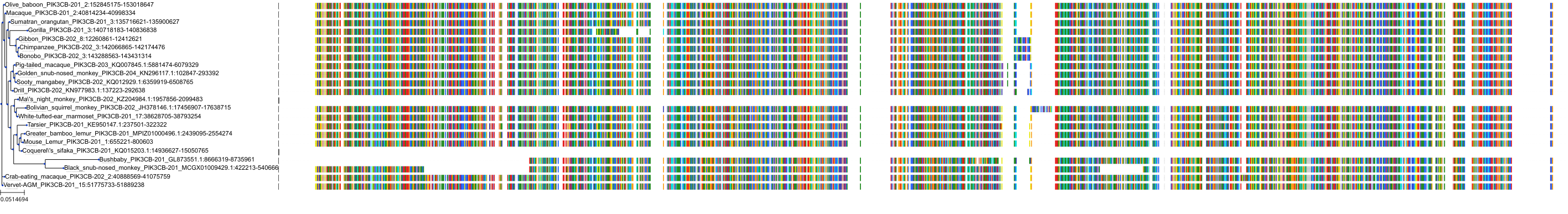
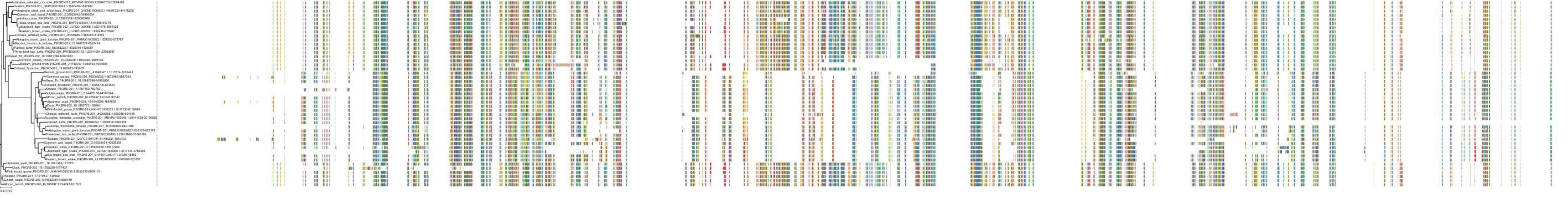
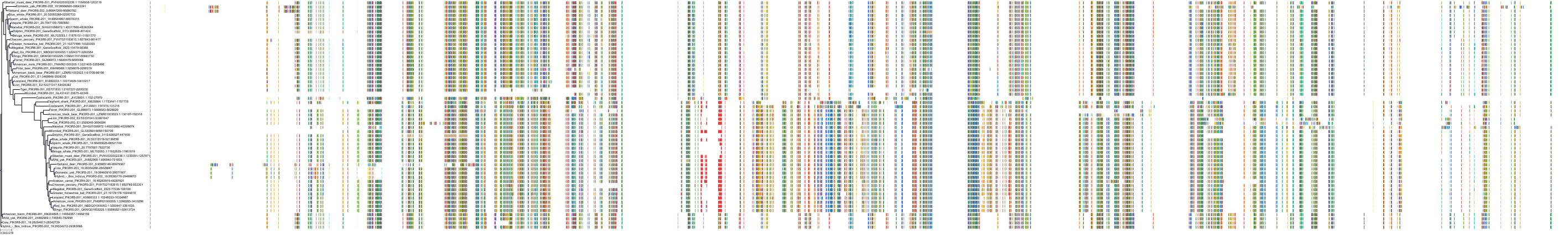
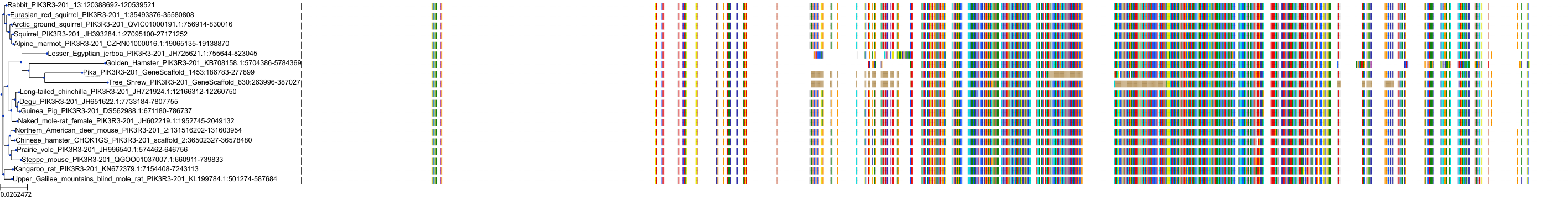
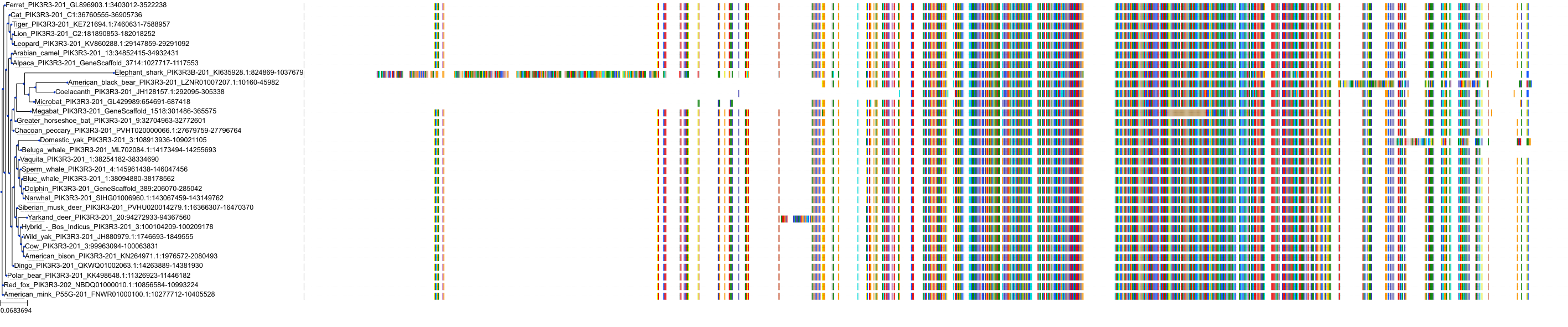
Target Conservation
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta isoform Organism : Homo sapiens O00329 ENSG00000171608 |
||||
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit beta Organism : Homo sapiens O00459 ENSG00000105647 |
||||
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha Organism : Homo sapiens P27986 ENSG00000145675 |
||||
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha isoform Organism : Homo sapiens P42336 ENSG00000121879 |
||||
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit beta isoform Organism : Homo sapiens P42338 ENSG00000051382 |
||||
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit gamma isoform Organism : Homo sapiens P48736 ENSG00000105851 |
||||
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulatory subunit 5 Organism : Homo sapiens Q8WYR1 ENSG00000141506 |
||||
|
Protein: PI3-kinase class I Description: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit gamma Organism : Homo sapiens Q92569 ENSG00000117461 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL586701 |
| FDA SRS | K0068GK39A |
| PubChem | 11647372 |
 Bos taurus
Bos taurus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus