| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| UNII | 0H43101T0J |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID4040399 |
Structure
| InChI Key | FJHBVJOVLFPMQE-QFIPXVFZSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H20N2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 392.41 |
| AlogP | 2.35 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 7.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 2.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 2.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 101.65 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 3.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 29.0 |
Pharmacology
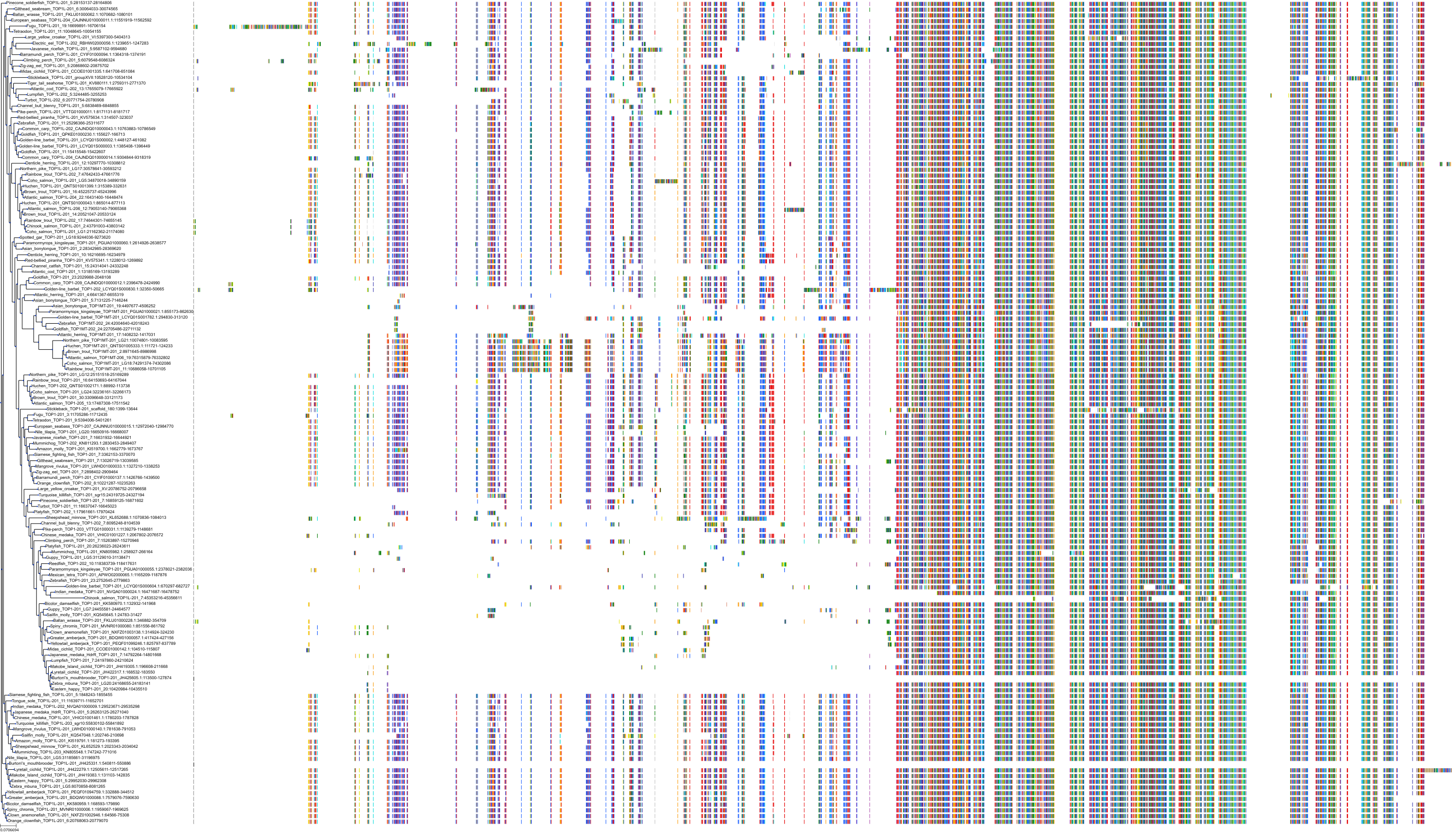
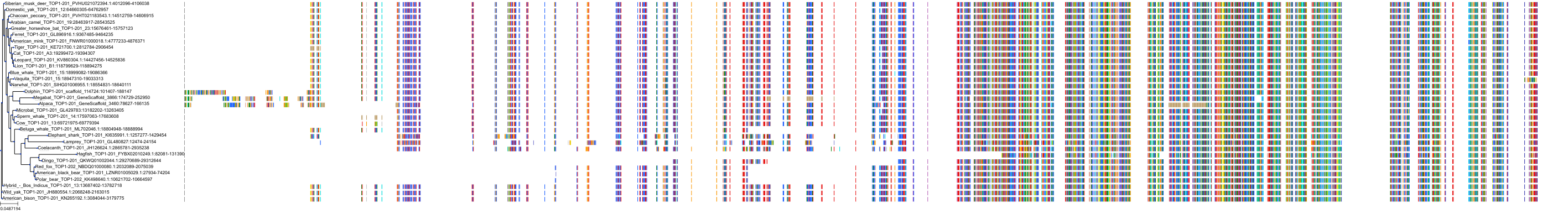
Target Conservation
|
Protein: DNA topoisomerase I Description: DNA topoisomerase 1 Organism : Homo sapiens P11387 ENSG00000198900 |
||||
Related Entries
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 8988 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL837 |
| DrugBank | DB05482 |
| FDA SRS | 0H43101T0J |
| Human Metabolome Database | HMDB0060510 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 6925 |
| KEGG | C11173 |
| PDB | RS4 |
| PubChem | 104842 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL34018 |
| ZINC | ZINC000004099013 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus