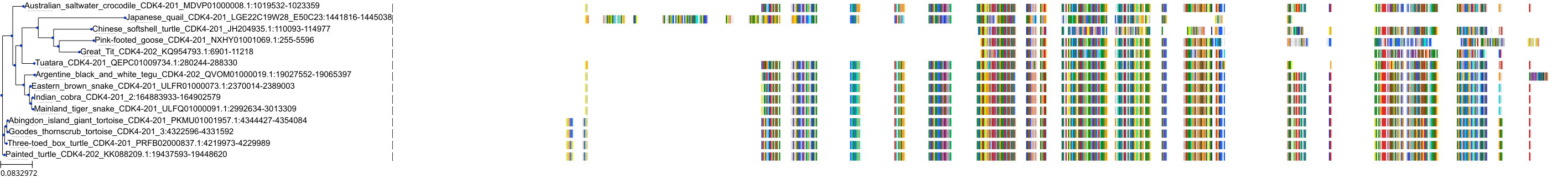| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| UNII | 688000M8S8 |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID80230186 |
Structure
| InChI Key | RXZMYLDMFYNEIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H32N8O |
| Molecular Weight | 460.59 |
| AlogP | 2.57 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 8.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 2.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 4.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 91.21 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 3.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 34.0 |
Pharmacology
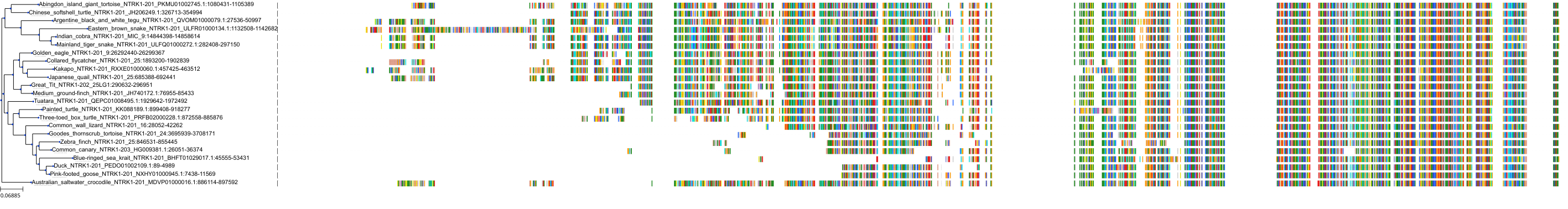
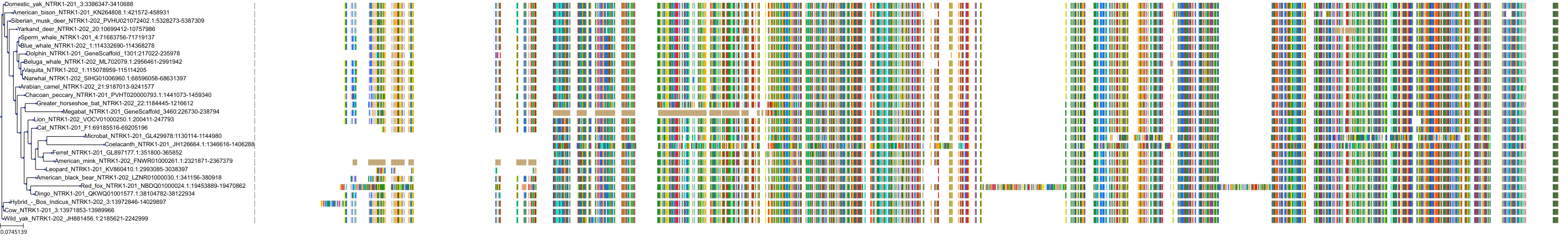
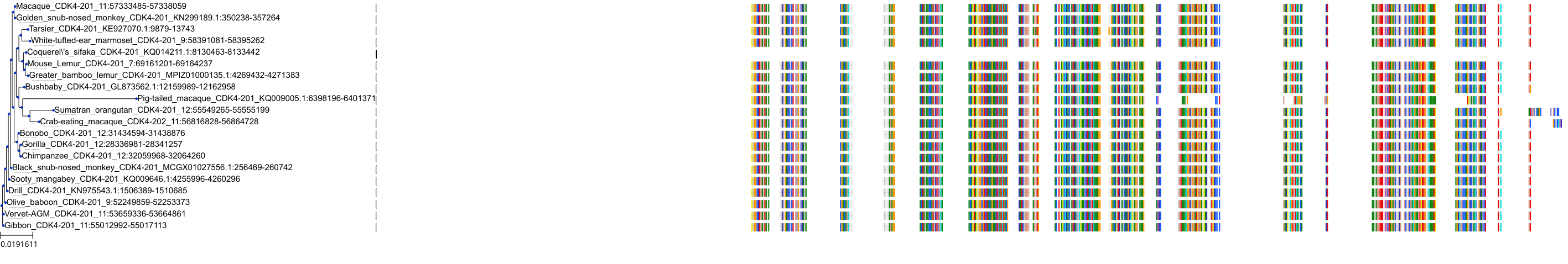
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Nerve growth factor receptor Trk-A Description: High affinity nerve growth factor receptor Organism : Homo sapiens P04629 ENSG00000198400 |
||||
|
Protein: Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 Description: Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 Organism : Homo sapiens P06493 ENSG00000170312 |
||||
|
Protein: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 Description: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 Organism : Homo sapiens P11802 ENSG00000135446 |
||||
|
Protein: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 Description: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 Organism : Homo sapiens P24941 ENSG00000123374 |
||||
Related Entries
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL564829 |
| DrugBank | DB16232 |
| FDA SRS | 688000M8S8 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 7938 |
| PDB | P48 |
| PubChem | 16718576 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL619139 |
| ZINC | ZINC000053119602 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Trypanosoma brucei
Trypanosoma brucei
 Trypanosoma brucei brucei
Trypanosoma brucei brucei