Structure
| InChI Key | VXBAJLGYBMTJCY-NSCUHMNNSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H24N4O |
| Molecular Weight | 372.47 |
| AlogP | 4.66 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 5.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 50.28 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 3.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 28.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed |
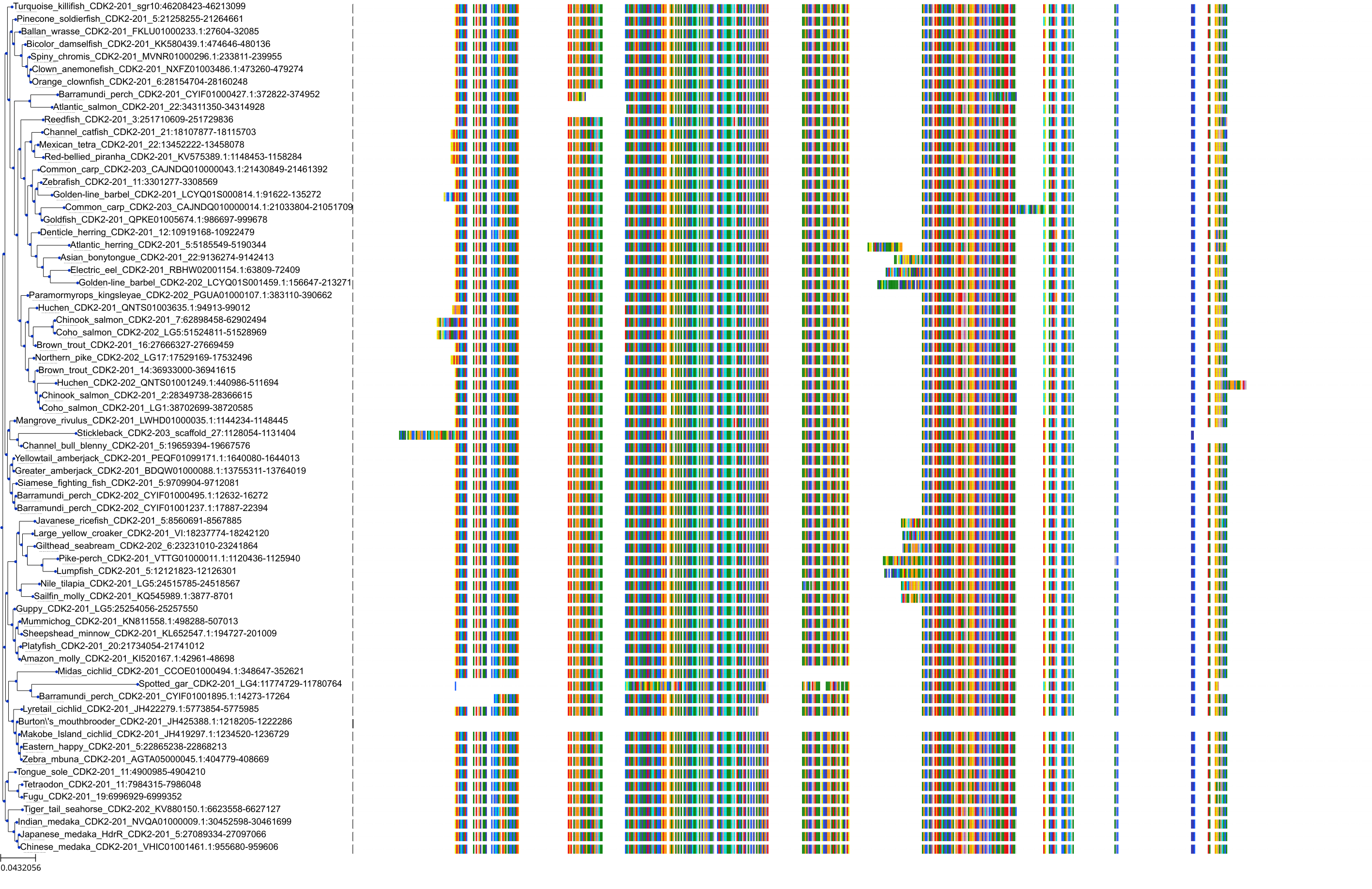
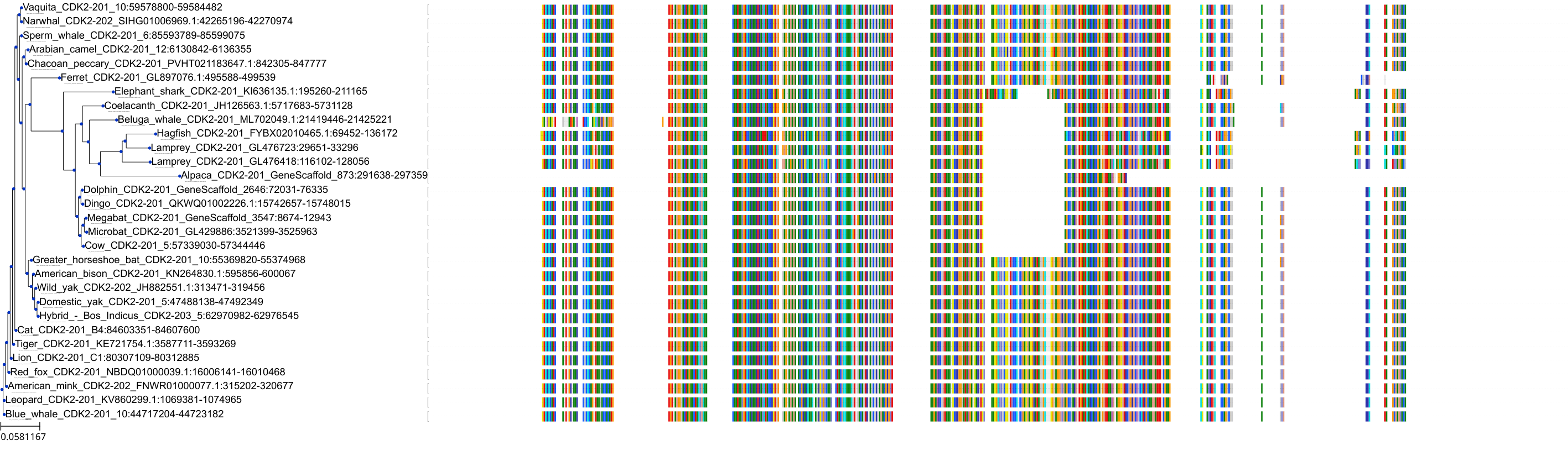
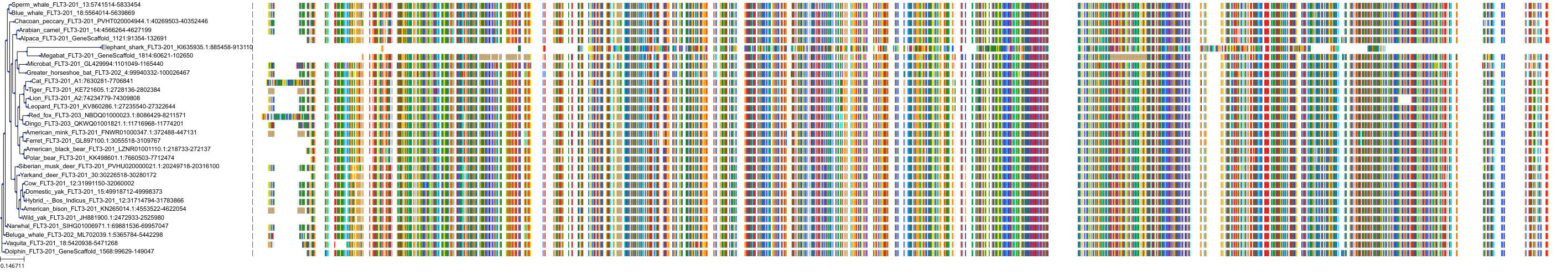
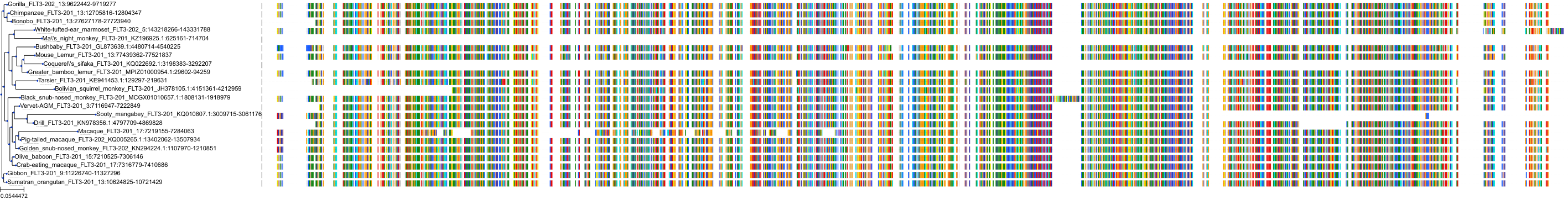
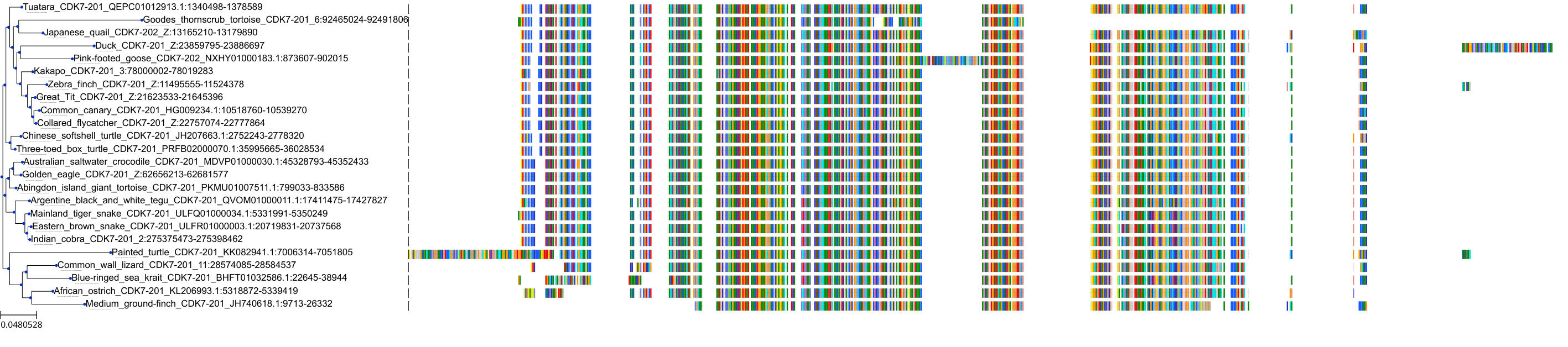
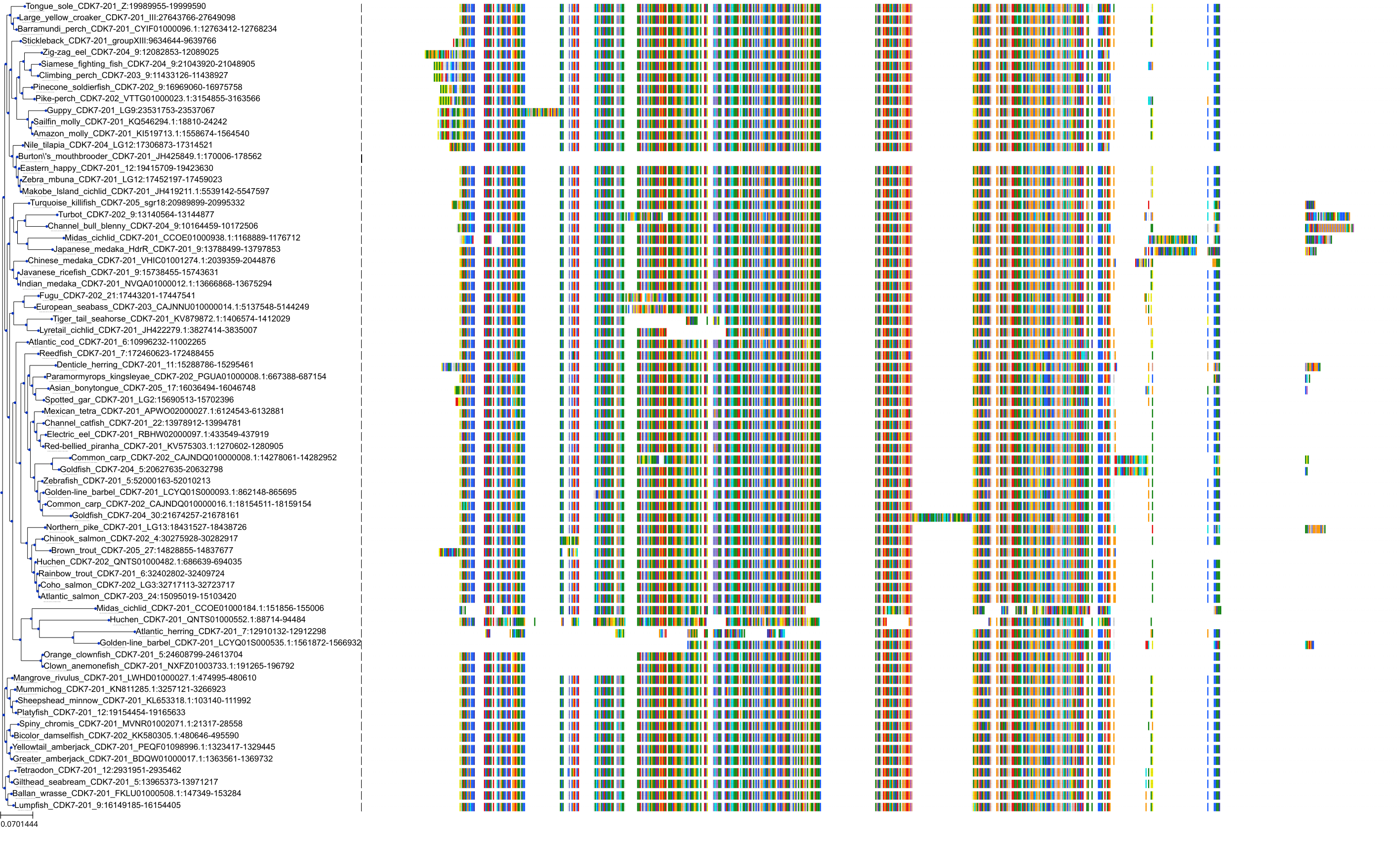
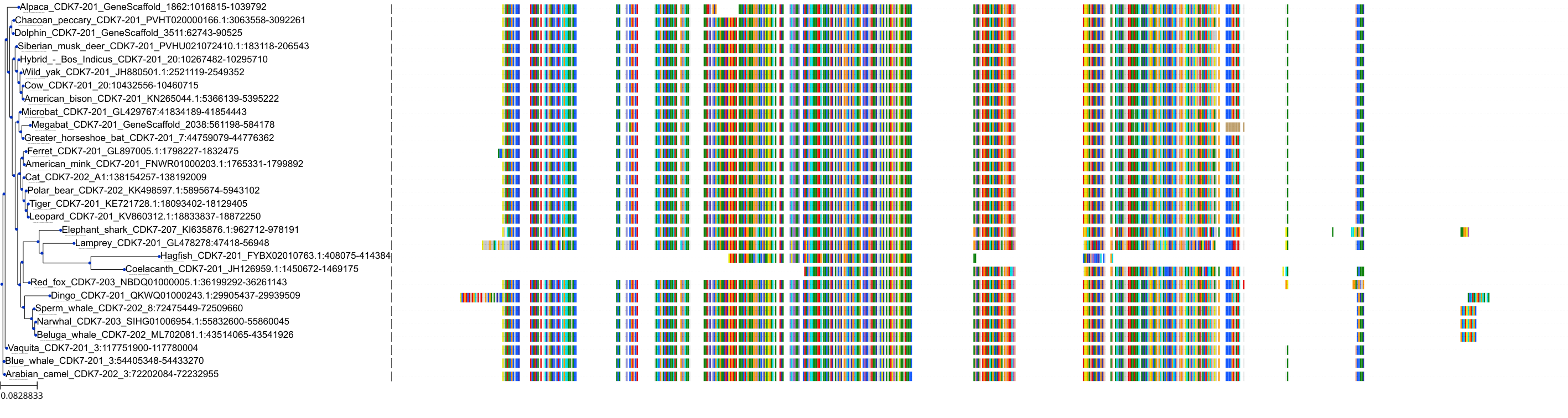
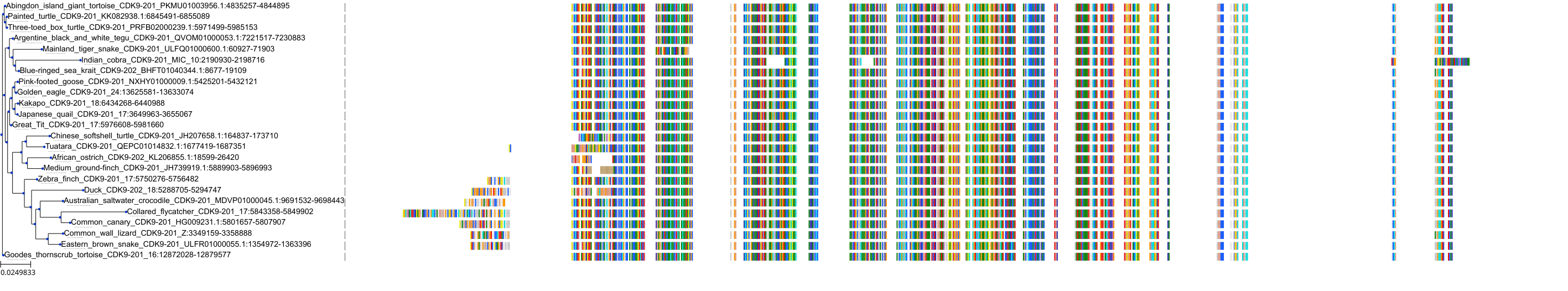
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 Description: Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 Organism : Homo sapiens O60674 ENSG00000096968 |
||||
|
Protein: Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 Description: Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 Organism : Homo sapiens P06493 ENSG00000170312 |
||||
|
Protein: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 Description: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 Organism : Homo sapiens P24941 ENSG00000123374 |
||||
|
Protein: Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor FLT3 Description: Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 Organism : Homo sapiens P36888 ENSG00000122025 |
||||
|
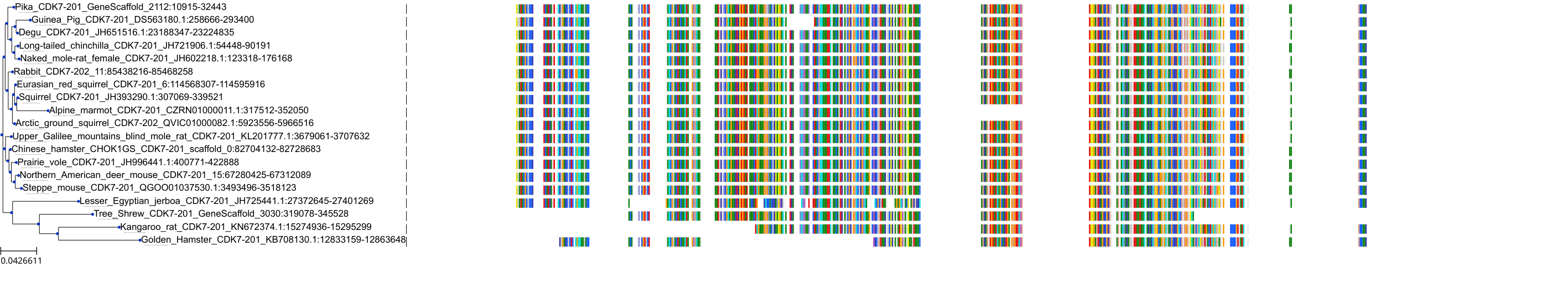
Protein: Cyclin-dependent kinase 7 Description: Cyclin-dependent kinase 7 Organism : Homo sapiens P50613 ENSG00000134058 |
||||
|
Protein: Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 Description: Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 Organism : Homo sapiens P50750 ENSG00000136807 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1944698 |
| FDA SRS | 40D08182TT |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 9095 |
| PubChem | 16739650 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL823947 |
| ZINC | ZINC000068251500 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens