| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | R06AX11 |
| UNII | 7HU6337315 |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID9020110 |
Structure
| InChI Key | GXDALQBWZGODGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C28H31FN4O |
| Molecular Weight | 458.58 |
| AlogP | 5.35 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 5.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 8.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 42.32 |
| Molecular species | BASE |
| Aromatic Rings | 4.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 34.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Histamine H1 receptor antagonist | ANTAGONIST | PubMed |
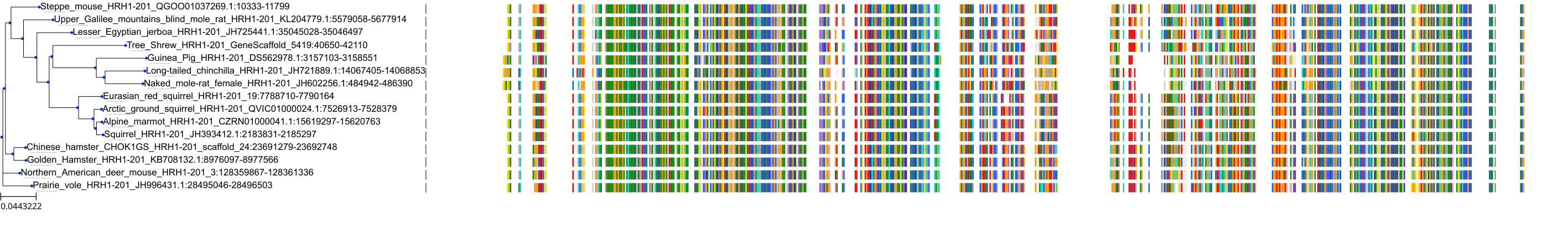
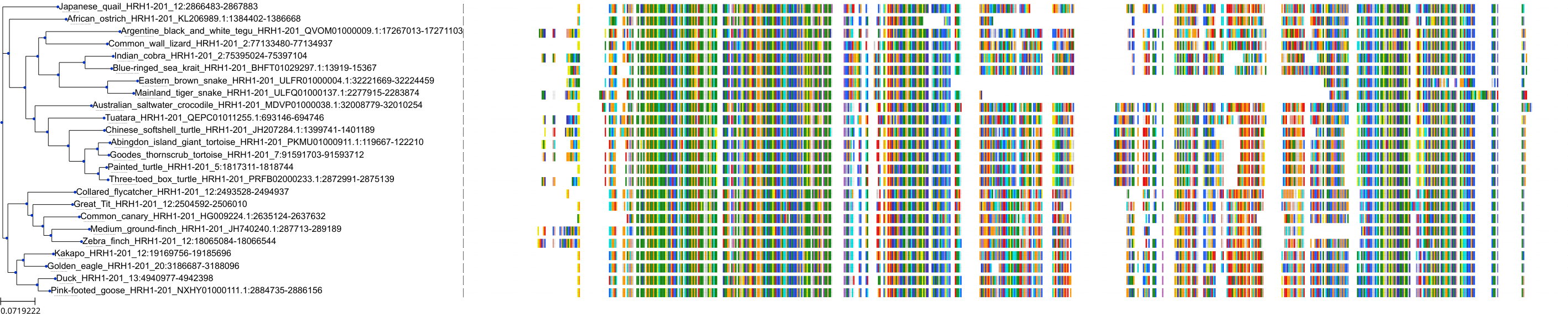
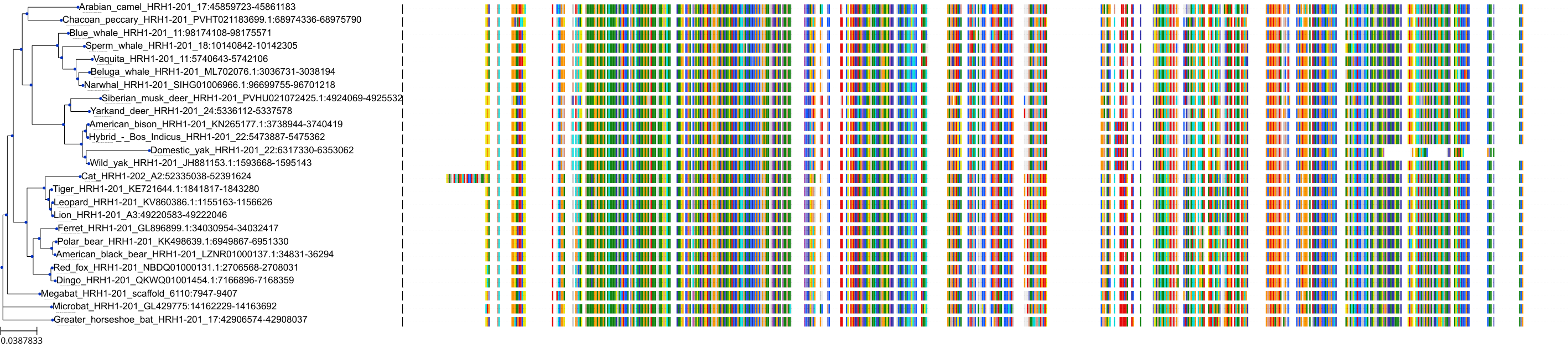
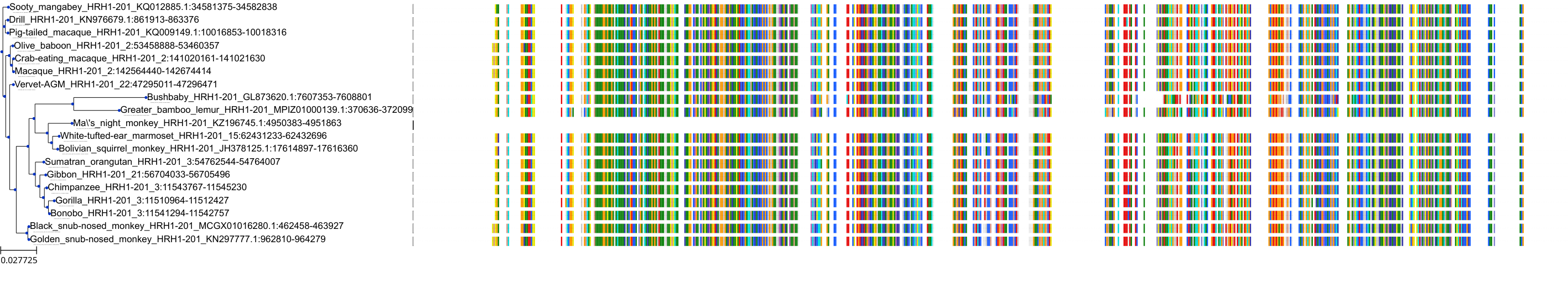
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Histamine H1 receptor Description: Histamine H1 receptor Organism : Homo sapiens P35367 ENSG00000196639 |
||||
Related Entries
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 2896 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL296419 |
| DrugBank | DB00637 |
| DrugCentral | 249 |
| FDA SRS | 7HU6337315 |
| Human Metabolome Database | HMDB0014775 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 2603 |
| KEGG | C06832 |
| PDB | XB7 |
| PharmGKB | PA448498 |
| PubChem | 2247 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL4385 |
| ZINC | ZINC000000601274 |
 Cavia porcellus
Cavia porcellus
 Cricetulus griseus
Cricetulus griseus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus
 Oryctolagus cuniculus
Oryctolagus cuniculus
 Plasmodium berghei
Plasmodium berghei
 Plasmodium falciparum
Plasmodium falciparum
 Plasmodium falciparum 3D7
Plasmodium falciparum 3D7
 Plasmodium vinckei
Plasmodium vinckei
 Plasmodium yoelii
Plasmodium yoelii
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus
 Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus