Structure
| InChI Key | KPBNHDGDUADAGP-VAWYXSNFSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H29N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 391.52 |
| AlogP | 3.93 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 3.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 8.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 62.3 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 2.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 29.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Cytochrome P450
Cytochrome P450 family 3
Cytochrome P450 family 3A
Cytochrome P450 3A4
|
- | 540 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
|
- | 0.0301-61 | - | 0.2-6 | - |
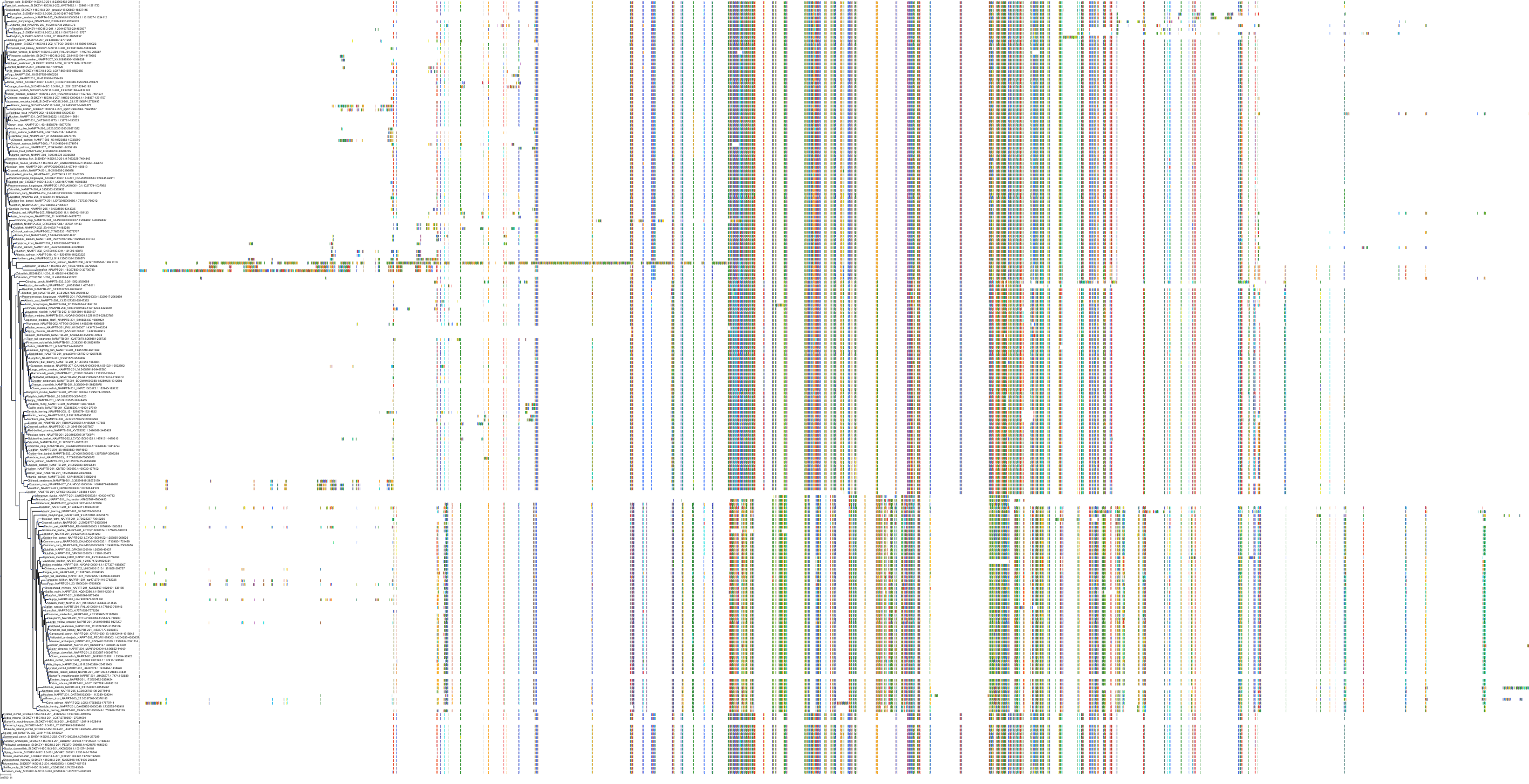
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase Description: Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase Organism : Homo sapiens P43490 ENSG00000105835 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL566757 |
| DrugBank | DB12731 |
| FDA SRS | V71TF6V9M7 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 7745 |
| PDB | DGB |
| PubChem | 6914657 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL82368 |
| ZINC | ZINC000003828115 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus