| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| UNII | A4055ME1VK |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID70236238 |
Structure
| InChI Key | QADPYRIHXKWUSV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H31Cl2N7O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 560.49 |
| AlogP | 5.35 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 8.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 2.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 8.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 95.09 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 3.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 38.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed Other |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase FGFR family
|
- | 0.59-581 | - | - | - | |
|
Membrane receptor
Frizzled family G protein-coupled receptor
Smoothened receptor (frizzled family GPCR)
|
- | - | - | 46.5 | - |
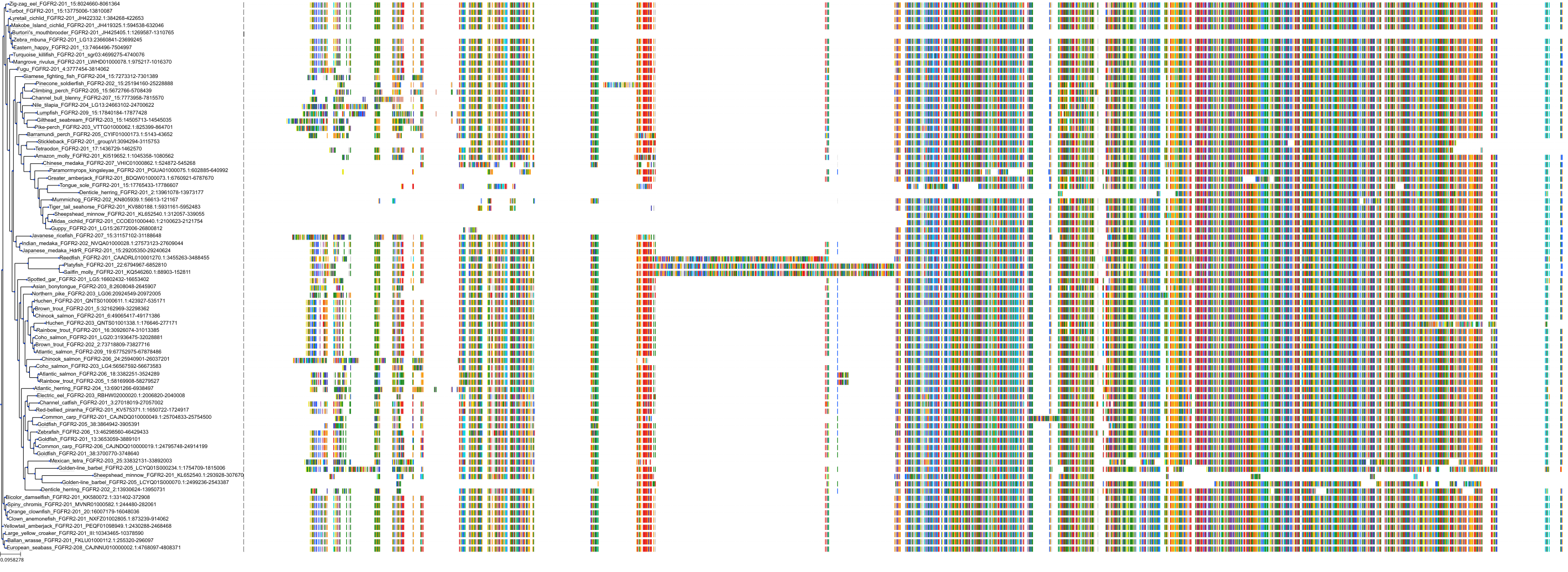
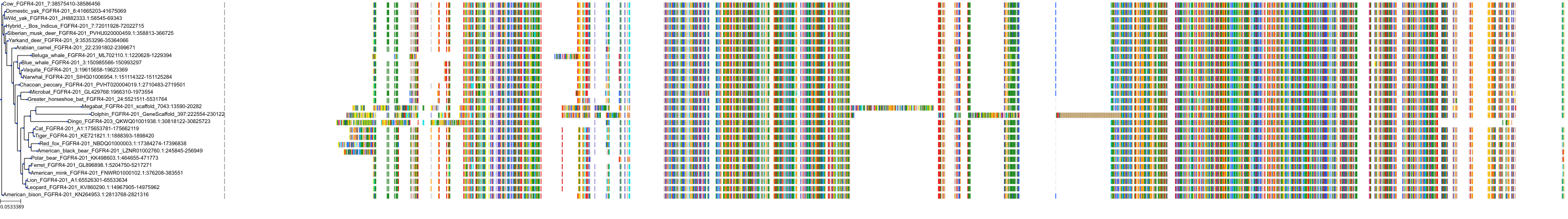
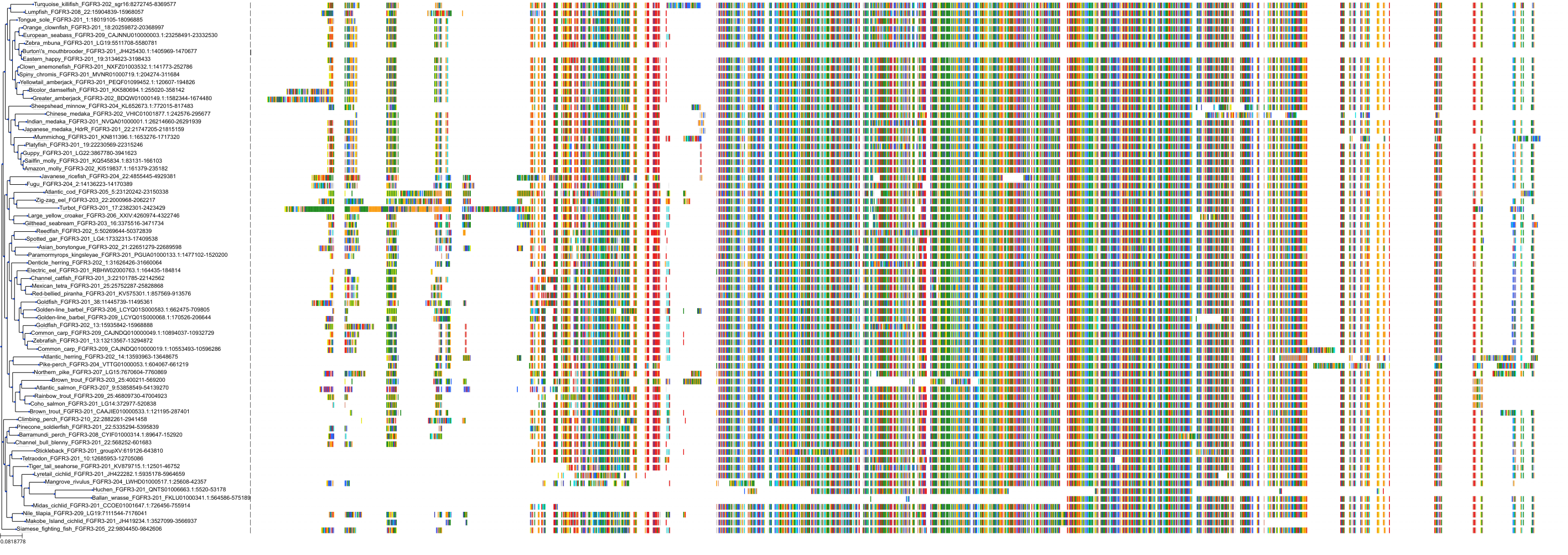
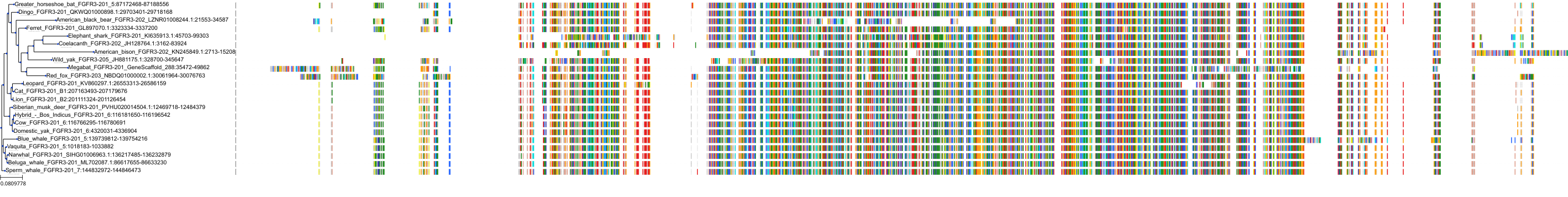
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Fibroblast growth factor receptor Description: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 Organism : Homo sapiens P11362 ENSG00000077782 |
||||
|
Protein: Fibroblast growth factor receptor Description: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 Organism : Homo sapiens P21802 ENSG00000066468 |
||||
|
Protein: Fibroblast growth factor receptor Description: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 Organism : Homo sapiens P22455 ENSG00000160867 |
||||
|
Protein: Fibroblast growth factor receptor Description: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 Organism : Homo sapiens P22607 ENSG00000068078 |
||||
Related Entries
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 63451 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1852688 |
| DrugBank | DB11886 |
| FDA SRS | A4055ME1VK |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 7877 |
| PDB | 07J |
| PubChem | 53235510 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL374435 |
| ZINC | ZINC000072105034 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus