Structure
| InChI Key | SPMVMDHWKHCIDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H19ClN4O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 454.87 |
| AlogP | 5.64 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 7.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 2.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 6.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 107.74 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 4.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 32.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed PubMed |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase Eph family
|
- | 17.5 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase PDGFR family
|
- | 2.26 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase VEGFR family
|
- | 0.16-340 | - | - | - |
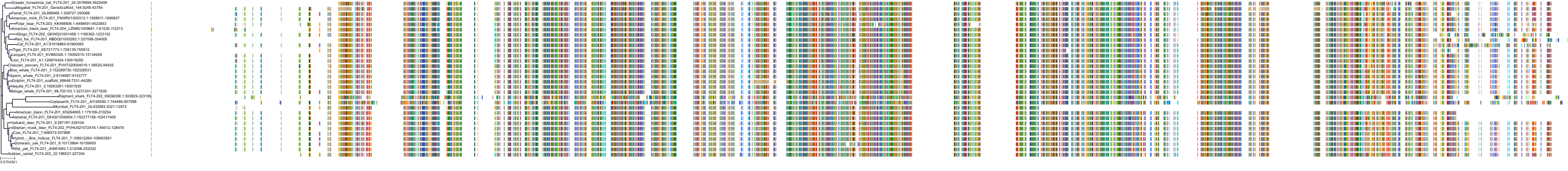
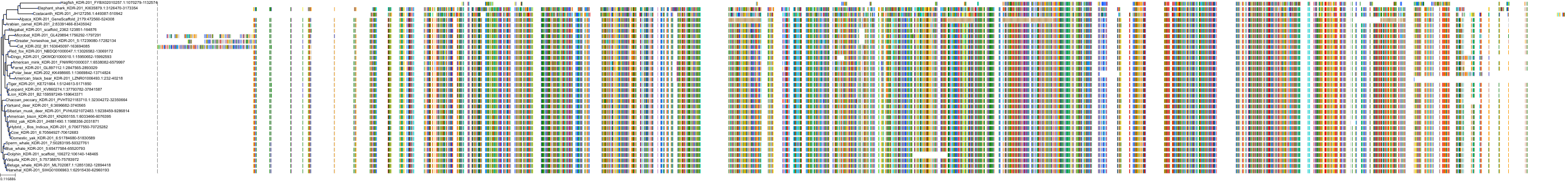
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Description: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 Organism : Homo sapiens P17948 ENSG00000102755 |
||||
|
Protein: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Description: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 Organism : Homo sapiens P35916 ENSG00000037280 |
||||
|
Protein: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Description: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 Organism : Homo sapiens P35968 ENSG00000128052 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 91327 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1289494 |
| DrugBank | DB11800 |
| DrugCentral | 5258 |
| FDA SRS | 172030934T |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 6058 |
| PDB | AV9 |
| PubChem | 9911830 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL172883 |
| ZINC | ZINC000001489430 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens