| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| UNII | UMF554N5FG |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID60150095 |
Structure
| InChI Key | VAZAPHZUAVEOMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H15N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 269.3 |
| AlogP | 2.48 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 3.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 3.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 3.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 84.22 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 2.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 20.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Histone deacetylase inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Epigenetic regulator
Eraser
Histone deacetylase
HDAC class I
|
- | 41-900 | - | 50-550 | 42-81 | |
|
Epigenetic regulator
Eraser
Histone deacetylase
HDAC class IIa
|
- | - | - | - | 42-81 | |
|
Epigenetic regulator
Eraser
Histone deacetylase
HDAC class IIb
|
- | - | - | - | 18-81 | |
|
Epigenetic regulator
Eraser
Histone deacetylase
HDAC class IV
|
- | - | - | - | 42-81 | |
|
Unclassified protein
|
- | 190 | - | - | - |
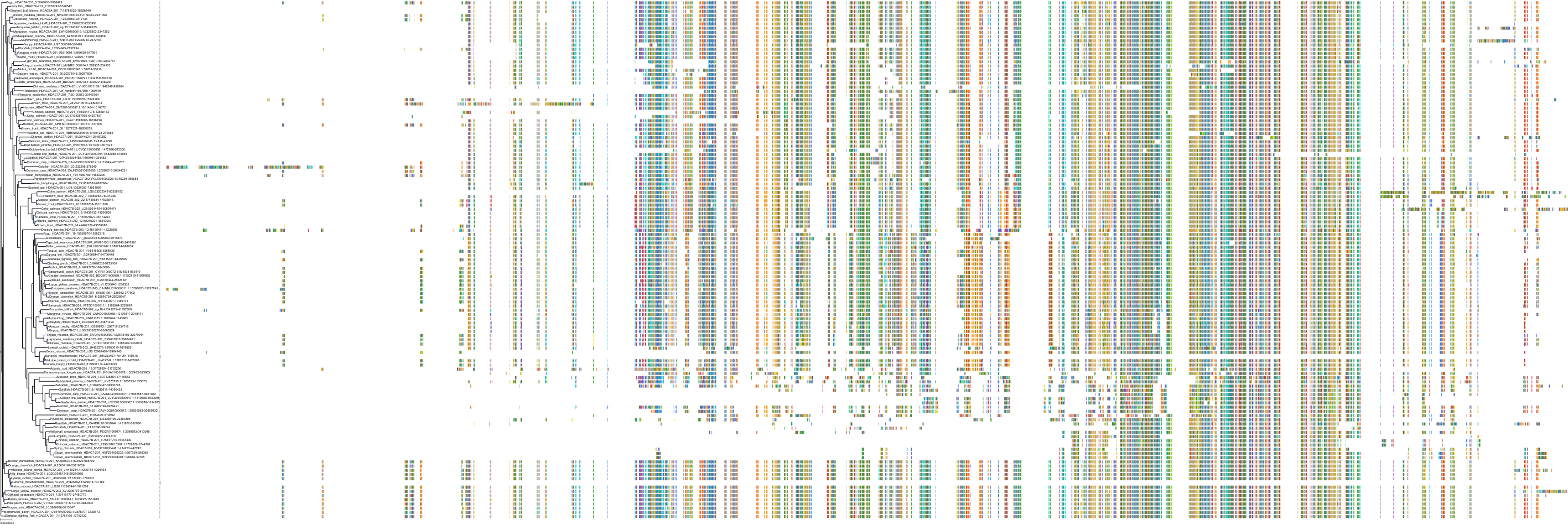
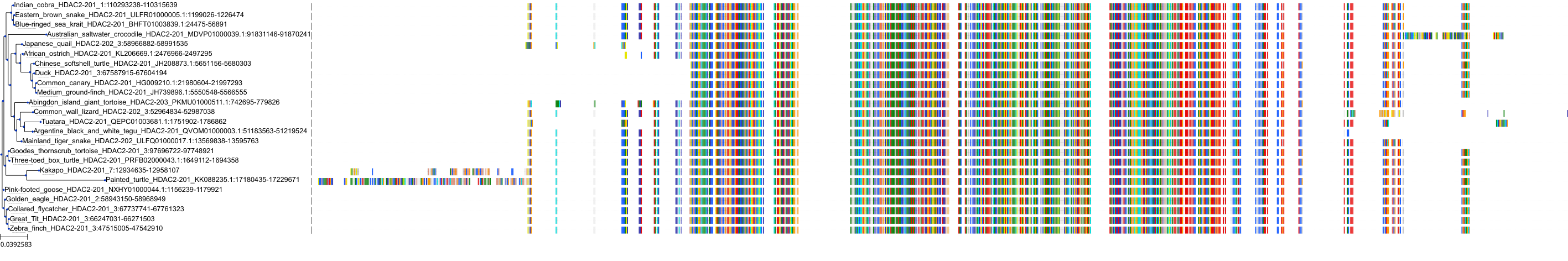
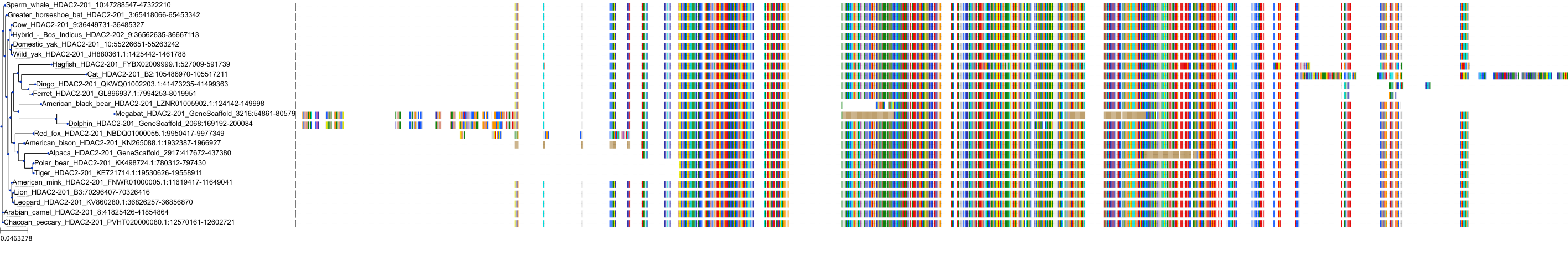
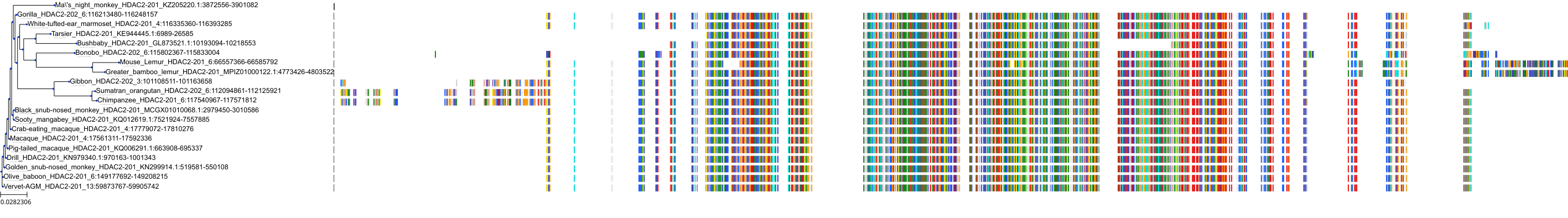
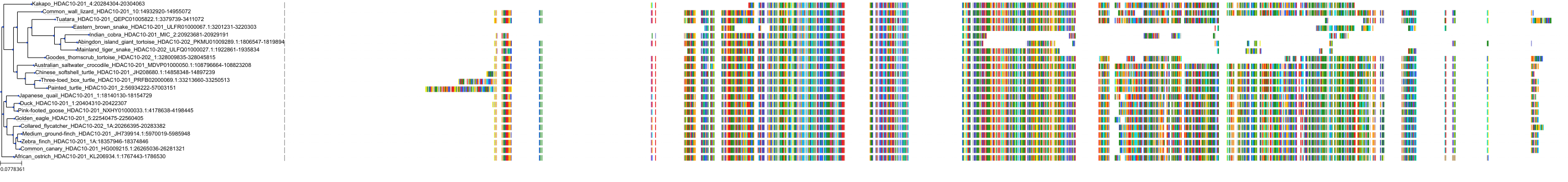
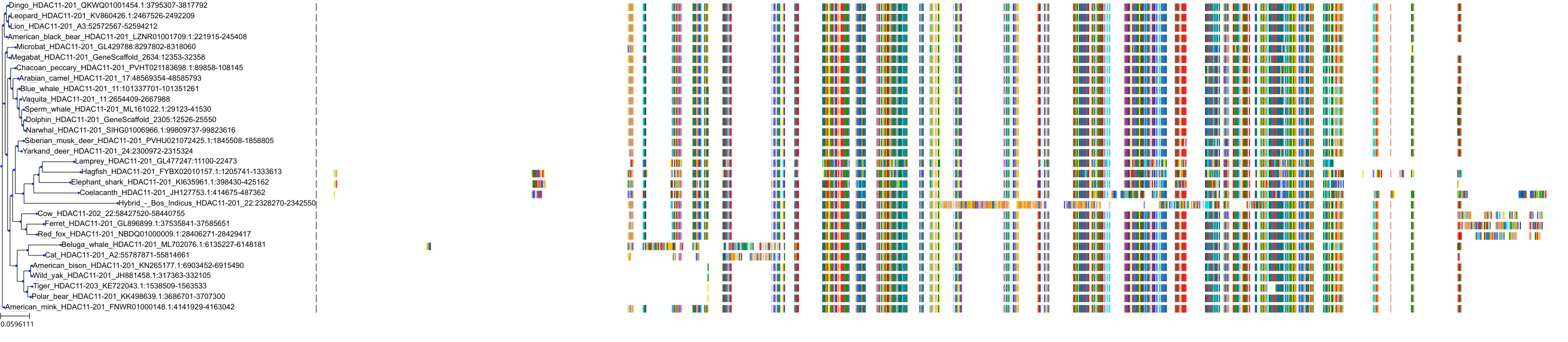
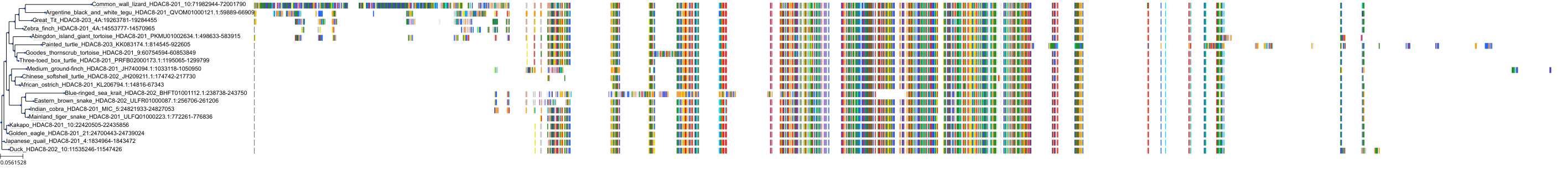
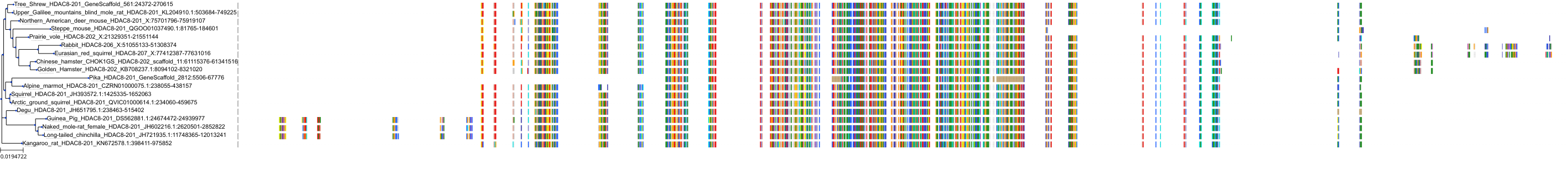
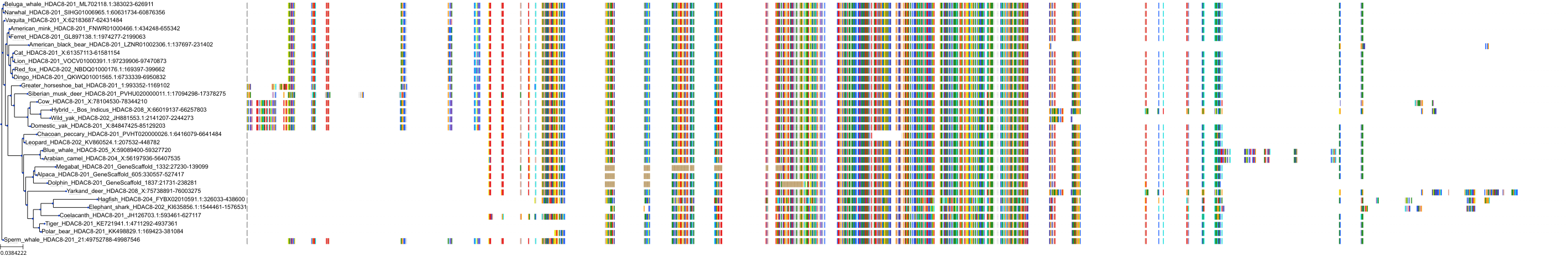
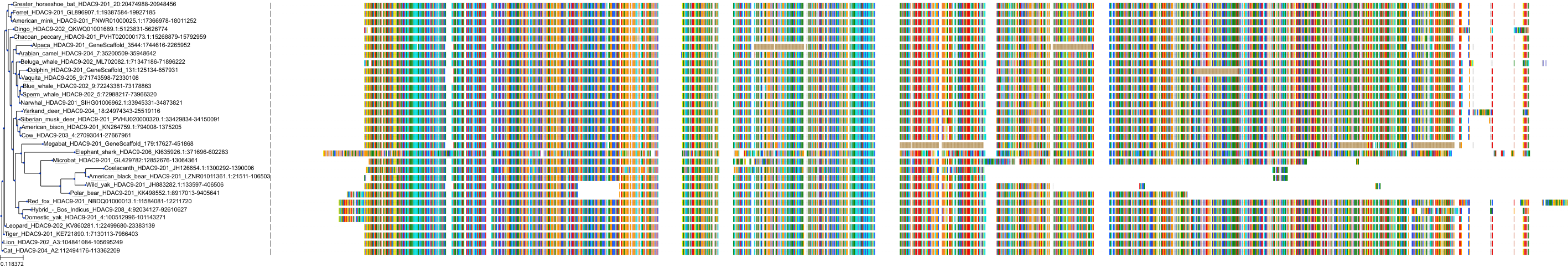
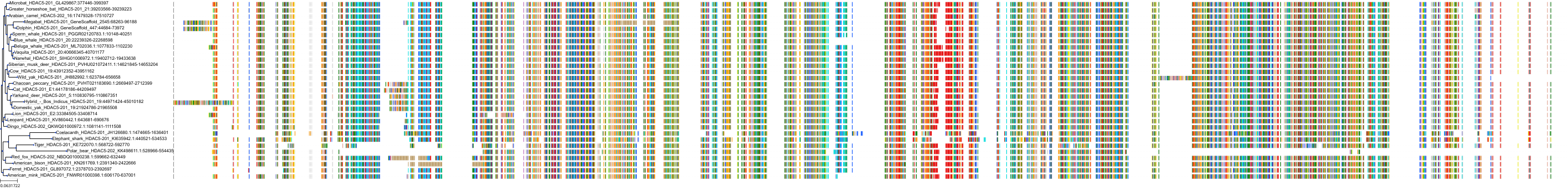
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Histone deacetylase Description: Histone deacetylase 3 Organism : Homo sapiens O15379 ENSG00000171720 |
||||
|
Protein: Histone deacetylase Description: Histone deacetylase 1 Organism : Homo sapiens Q13547 ENSG00000116478 |
||||
|
Protein: Histone deacetylase Description: Histone deacetylase 7 Organism : Homo sapiens Q8WUI4 ENSG00000061273 |
||||
|
Protein: Histone deacetylase Description: Histone deacetylase 2 Organism : Homo sapiens Q92769 ENSG00000196591 |
||||
|
Protein: Histone deacetylase Description: Polyamine deacetylase HDAC10 Organism : Homo sapiens Q969S8 ENSG00000100429 |
||||
|
Protein: Histone deacetylase Description: Histone deacetylase 11 Organism : Homo sapiens Q96DB2 ENSG00000163517 |
||||
|
Protein: Histone deacetylase Description: Histone deacetylase 8 Organism : Homo sapiens Q9BY41 ENSG00000147099 |
||||
|
Protein: Histone deacetylase Description: Histone deacetylase 6 Organism : Homo sapiens Q9UBN7 ENSG00000094631 |
||||
|
Protein: Histone deacetylase Description: Histone deacetylase 9 Organism : Homo sapiens Q9UKV0 ENSG00000048052 |
||||
|
Protein: Histone deacetylase Description: Histone deacetylase 5 Organism : Homo sapiens Q9UQL6 ENSG00000108840 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 90195 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL235191 |
| DrugBank | DB12291 |
| FDA SRS | UMF554N5FG |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 8367 |
| PubChem | 2746 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL144794 |
| ZINC | ZINC000000003803 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus