| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| UNII | 72AUA0603W |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID10647329 |
Structure
| InChI Key | MHXGEROHKGDZGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H22F3N5O |
| Molecular Weight | 405.42 |
| AlogP | 4.05 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 6.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 5.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 54.69 |
| Molecular species | BASE |
| Aromatic Rings | 3.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 29.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Serine/threonine-protein kinase PIM inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed PubMed |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
CAMK protein kinase group
CAMK protein kinase PIM family
|
200 | 7-618 | - | 12-610 | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
Other protein kinase group
Other protein kinase Haspin family
|
- | 34 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase PDGFR family
|
- | 21-44 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase Src family
|
- | 240 | - | - | - | |
|
Ion channel
Voltage-gated ion channel
Potassium channels
Voltage-gated potassium channel
|
- | 511-980 | - | - | - |
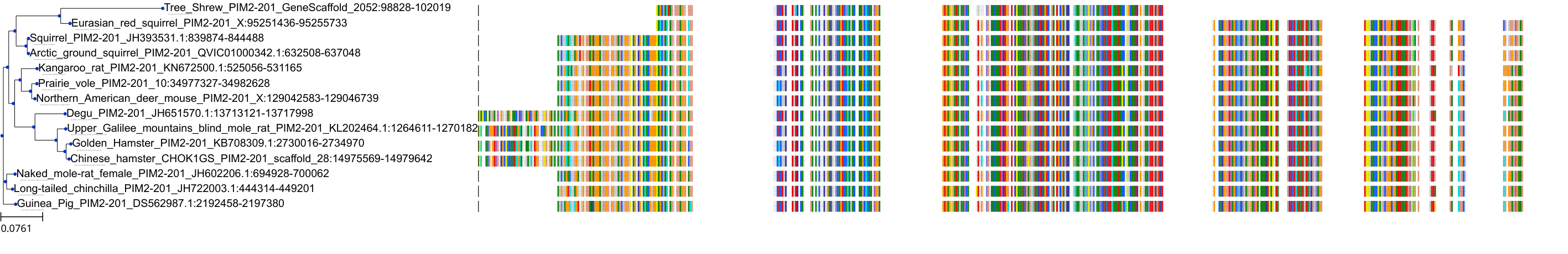
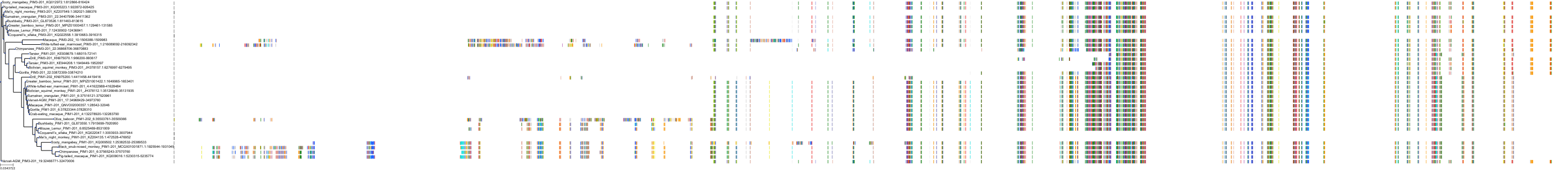
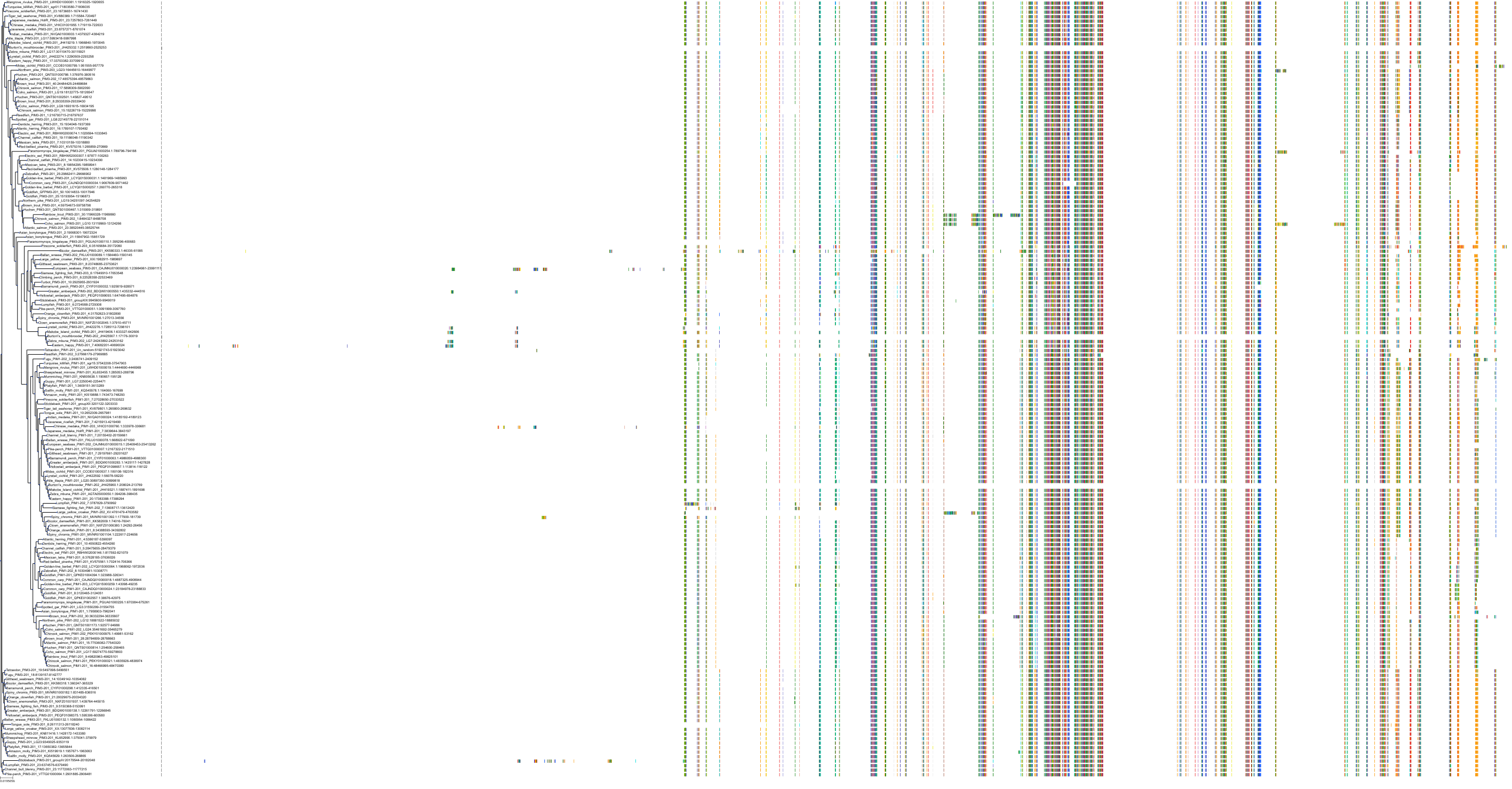
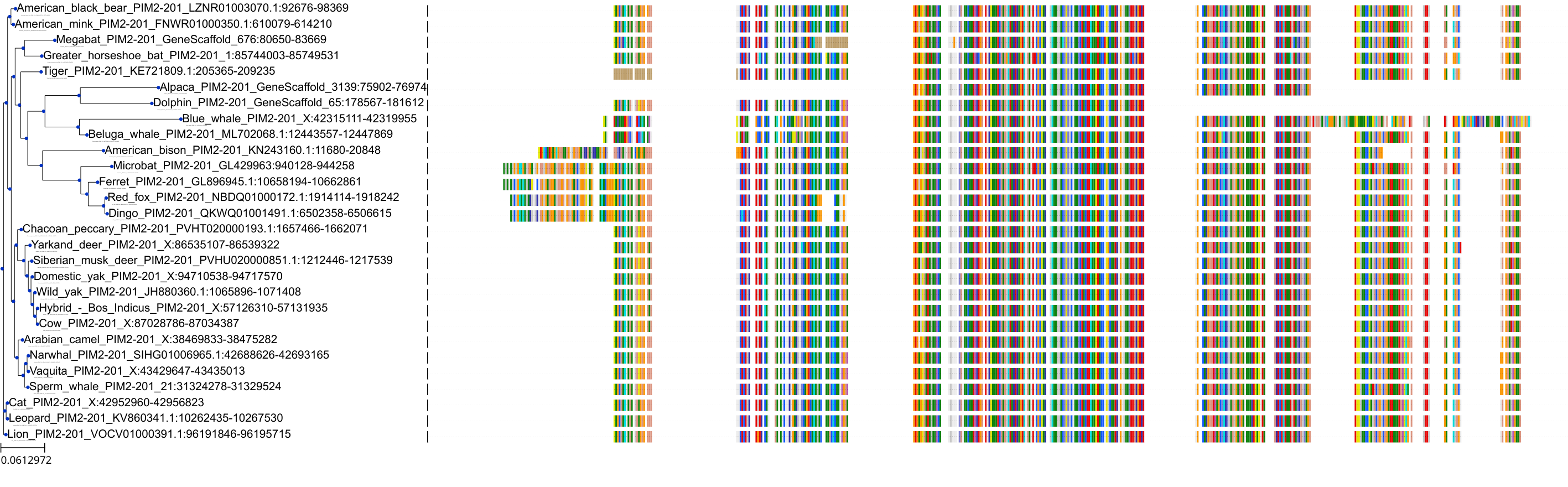
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Serine/threonine-protein kinase PIM Description: Serine/threonine-protein kinase pim-1 Organism : Homo sapiens P11309 ENSG00000137193 |
||||
|
Protein: Serine/threonine-protein kinase PIM Description: Serine/threonine-protein kinase pim-3 Organism : Homo sapiens Q86V86 ENSG00000198355 |
||||
|
Protein: Serine/threonine-protein kinase PIM Description: Serine/threonine-protein kinase pim-2 Organism : Homo sapiens Q9P1W9 ENSG00000102096 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 95061 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1952329 |
| DrugBank | DB12494 |
| FDA SRS | 72AUA0603W |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 8784 |
| PubChem | 24795070 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL102498 |
| ZINC | ZINC000068205235 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens