Structure
| InChI Key | WUWDLXZGHZSWQZ-WQLSENKSSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H14N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 238.29 |
| AlogP | 3.12 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 1.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 2.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 1.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 44.89 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 2.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 18.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Stem cell growth factor receptor inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed PubMed |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase FGFR family
|
- | - | - | - | 87 | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase PDGFR family
|
- | 35-680 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase Ret family
|
- | 170 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase VEGFR family
|
- | 8-884 | - | - | 40-40 |
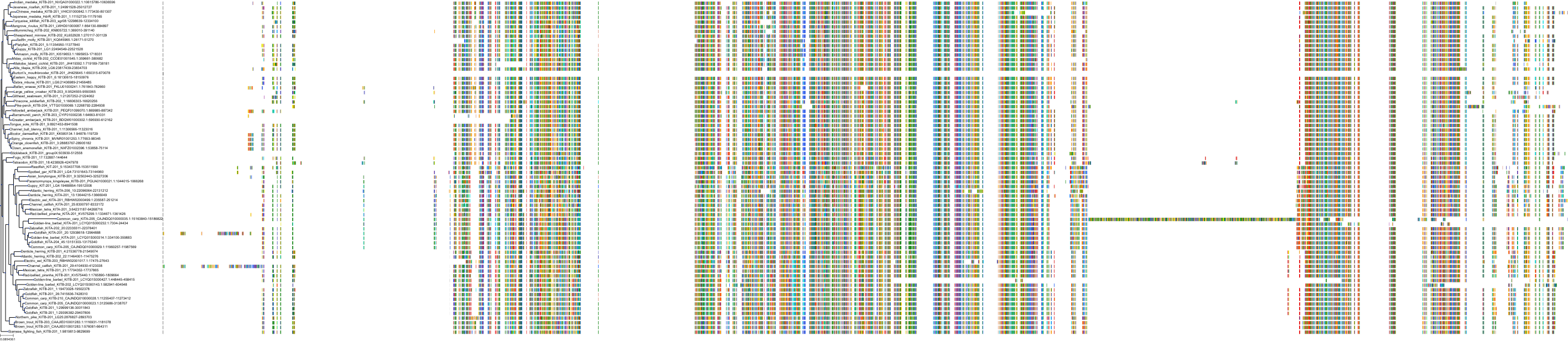
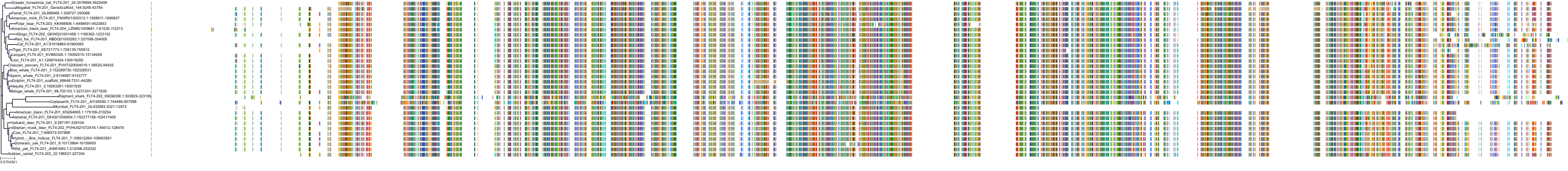
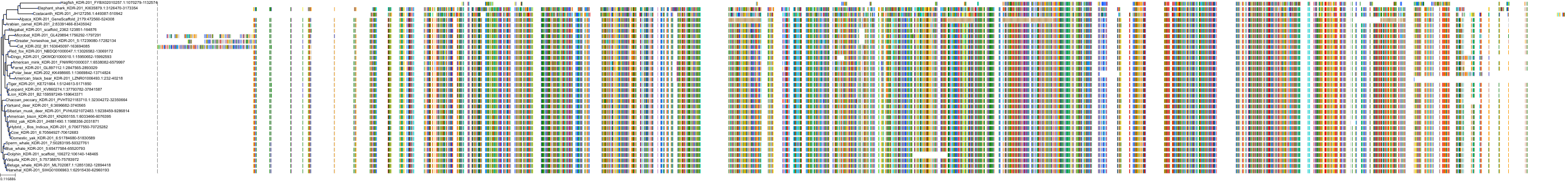
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Stem cell growth factor receptor Description: Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit Organism : Homo sapiens P10721 ENSG00000157404 |
||||
|
Protein: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Description: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 Organism : Homo sapiens P17948 ENSG00000102755 |
||||
|
Protein: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Description: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 Organism : Homo sapiens P35916 ENSG00000037280 |
||||
|
Protein: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Description: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 Organism : Homo sapiens P35968 ENSG00000128052 |
||||
Related Entries
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 91083 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL276711 |
| DrugBank | DB06436 |
| FDA SRS | 71IA9S35AJ |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 5056 |
| PDB | X2M |
| PubChem | 5329098 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL19571 |
| ZINC | ZINC000012410091 |
 Gallus gallus
Gallus gallus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus