| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| UNII | 9KD24QGH76 |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID90191355 |
Structure
| InChI Key | OUKYUETWWIPKQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H32ClN5O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 542.04 |
| AlogP | 3.94 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 10.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 8.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 90.44 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 3.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 38.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
Other protein kinase group
Other protein kinase WEE family
|
- | 418 | - | 39.8 | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase Abl family
|
- | 30-30 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase Csk family
|
- | 840-840 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase EGFR family
|
- | 66 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase PDGFR family
|
- | 200-200 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase Src family
|
- | 0.7-76 | - | - | - |
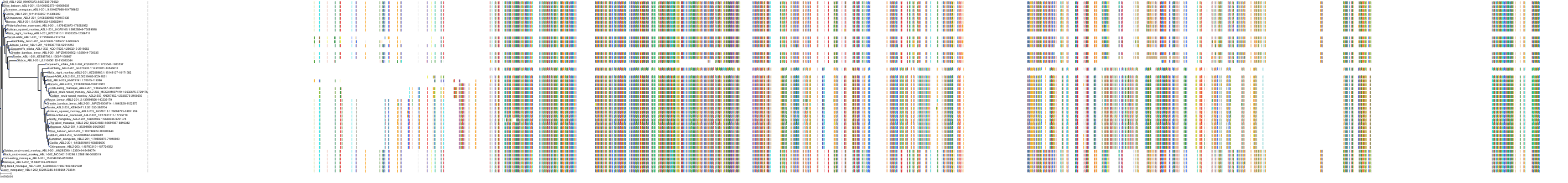
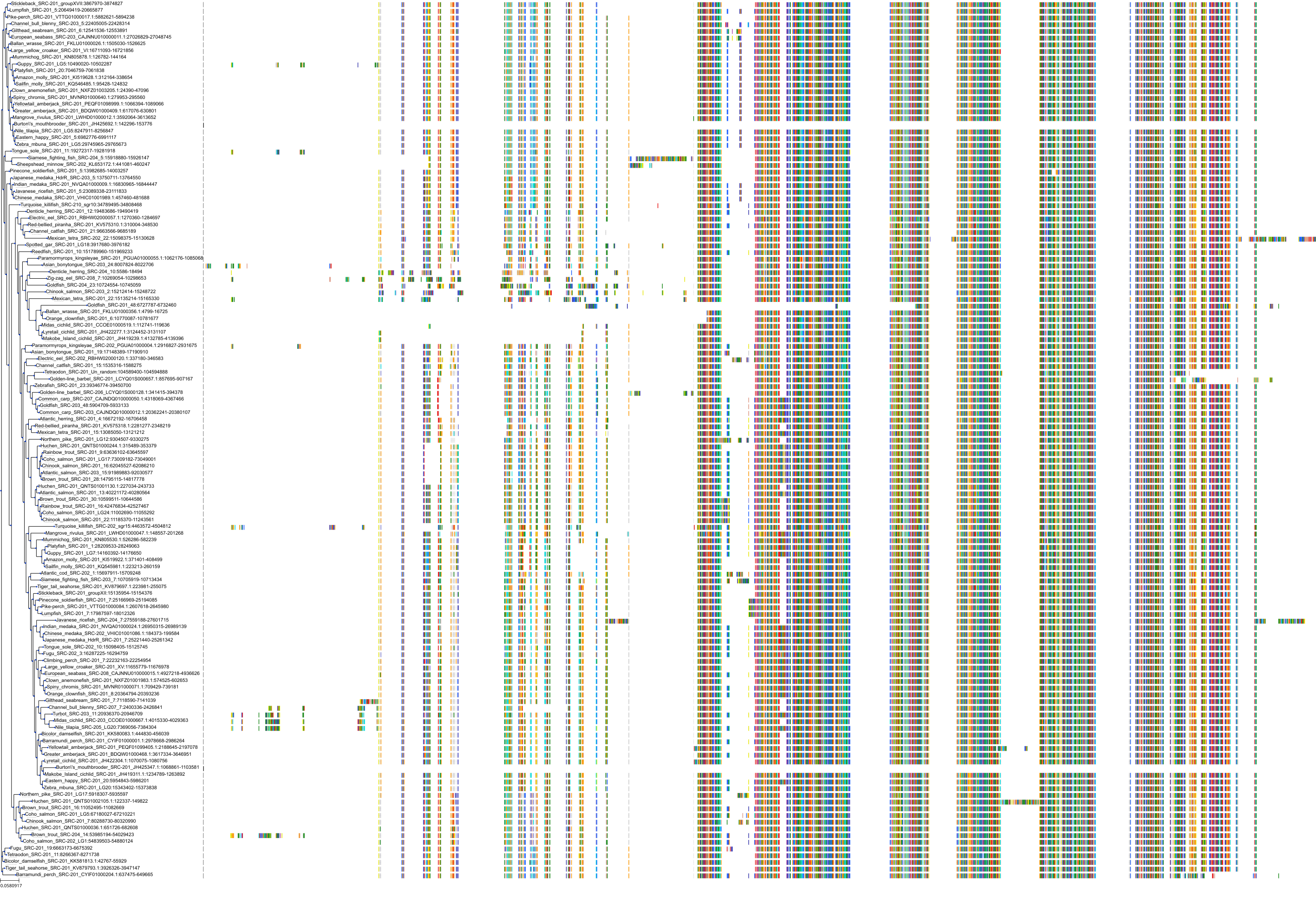
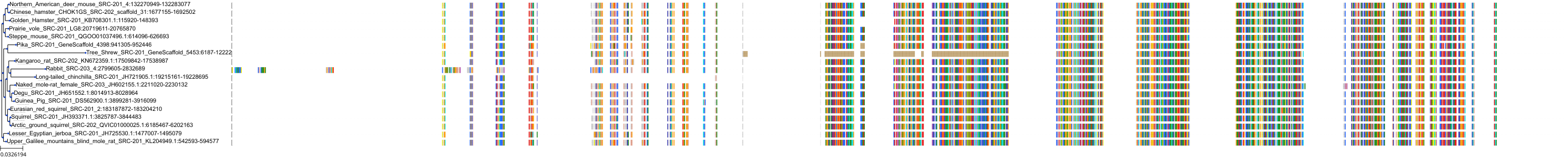
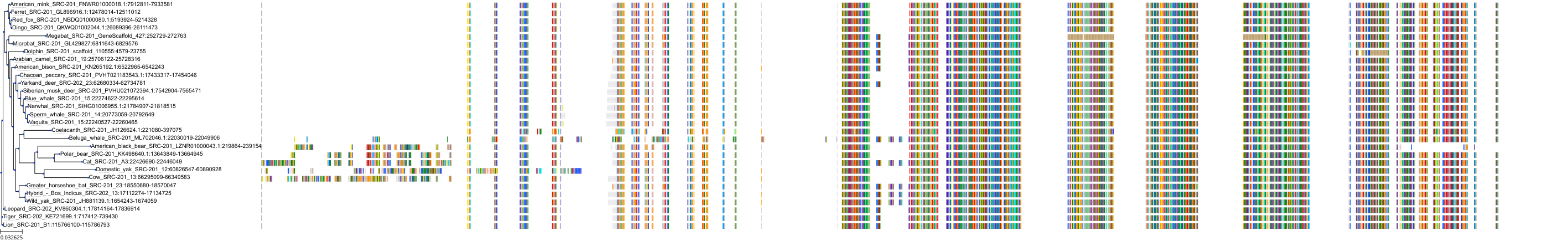
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL Description: Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 Organism : Homo sapiens P00519 ENSG00000097007 |
||||
|
Protein: Tyrosine-protein kinase SRC Description: Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src Organism : Homo sapiens P12931 ENSG00000197122 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL217092 |
| DrugBank | DB11805 |
| FDA SRS | 9KD24QGH76 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 7731 |
| PDB | H8H |
| PubChem | 10302451 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL41547 |
| ZINC | ZINC000024811973 |
 Agrobacterium sp.
Agrobacterium sp.
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens