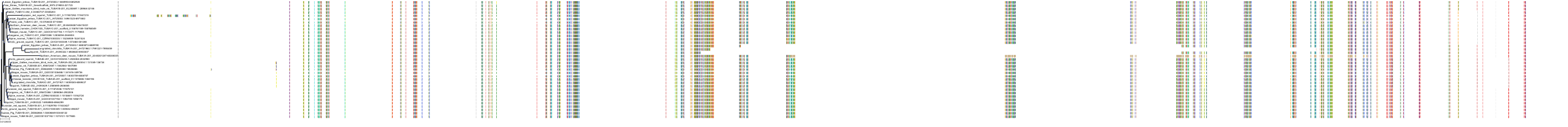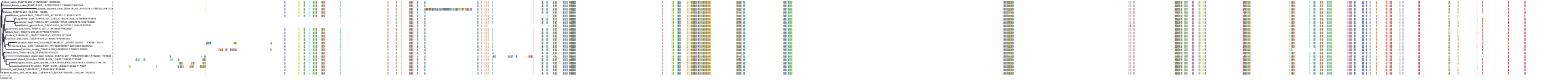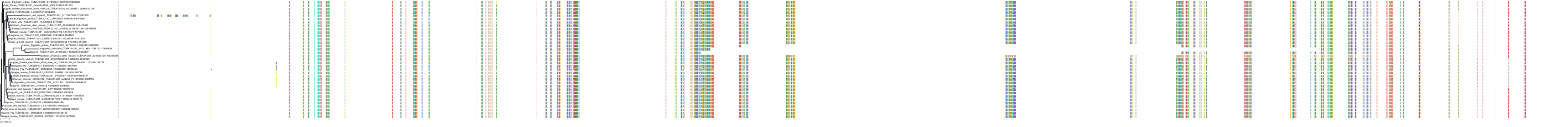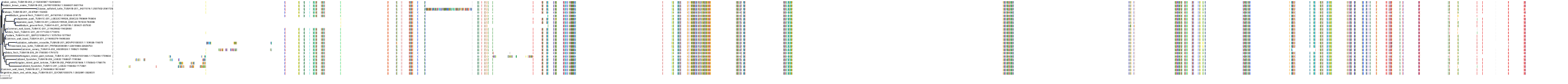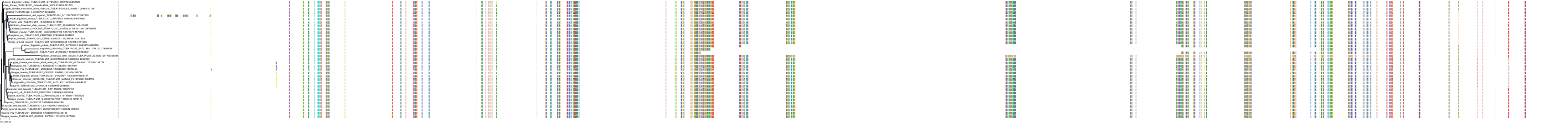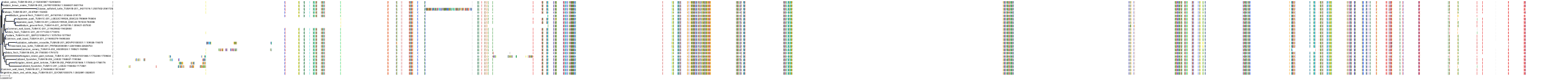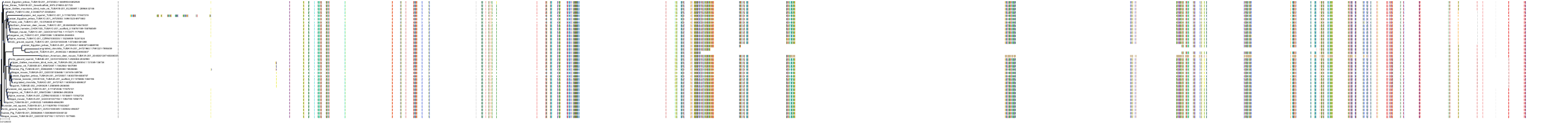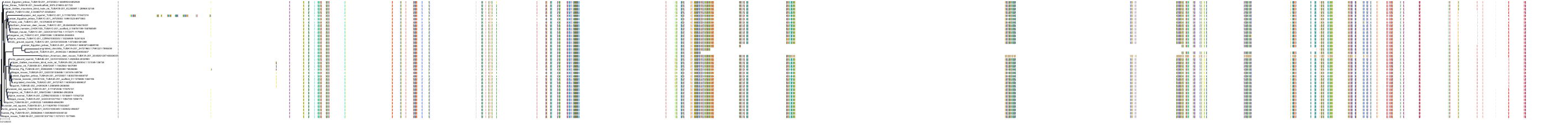Structure
| InChI Key | UNRCMCRRFYFGFX-TYPNBTCFSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H20N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 336.4 |
| AlogP | 0.74 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 3.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 3.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 2.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 94.4 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 3.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 25.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Tubulin inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Cytochrome P450
Cytochrome P450 family 2
Cytochrome P450 family 2C
Cytochrome P450 2C9
|
- | 530 | - | - | - | |
|
Structural protein
|
- | - | - | - | 18.34-27.85 |
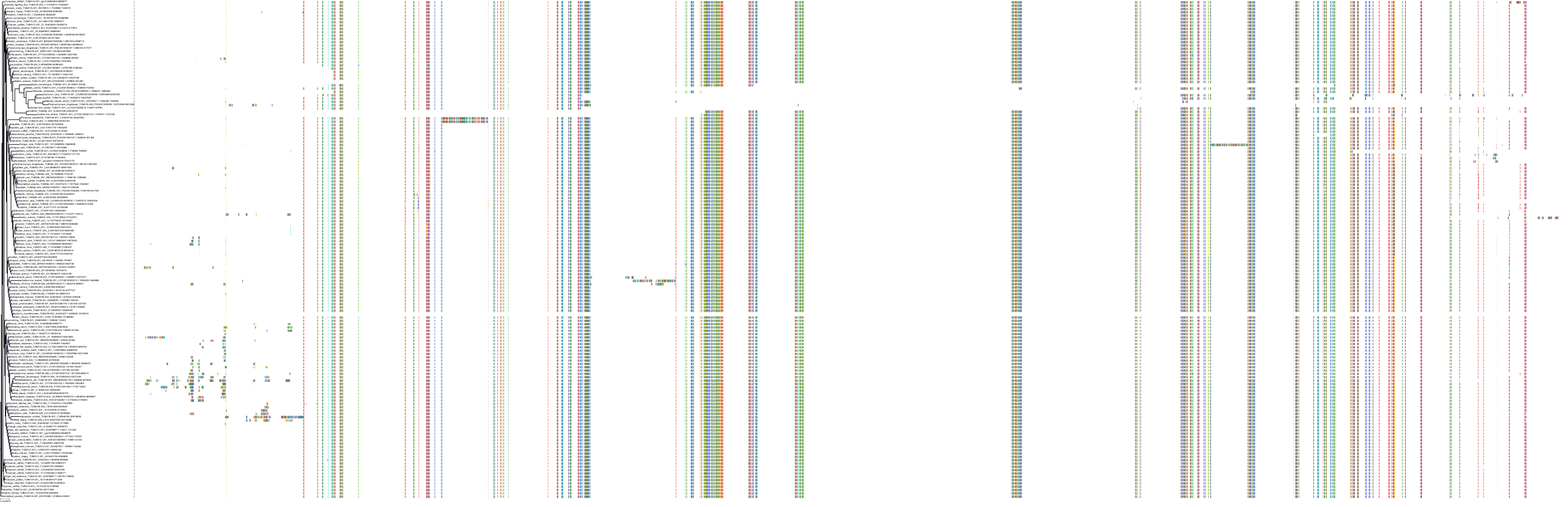
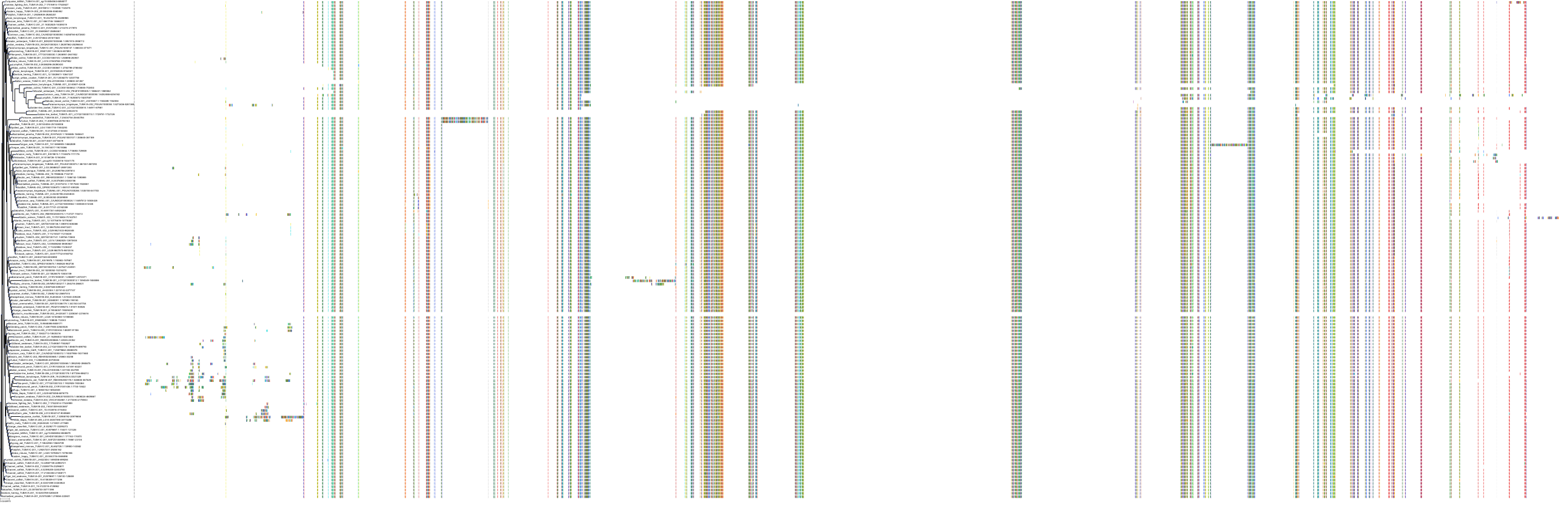
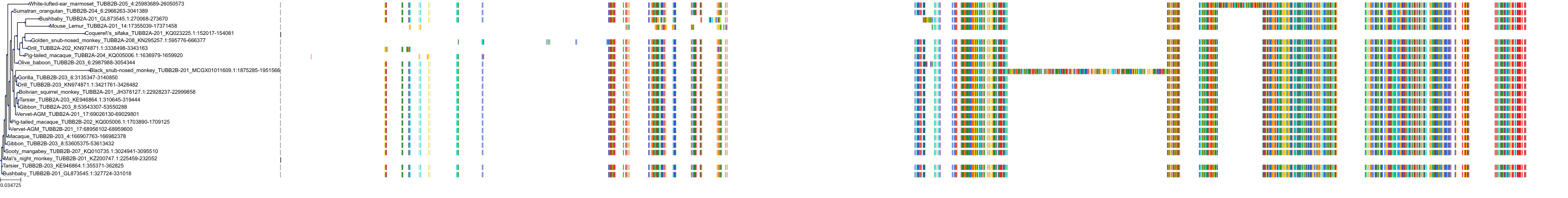
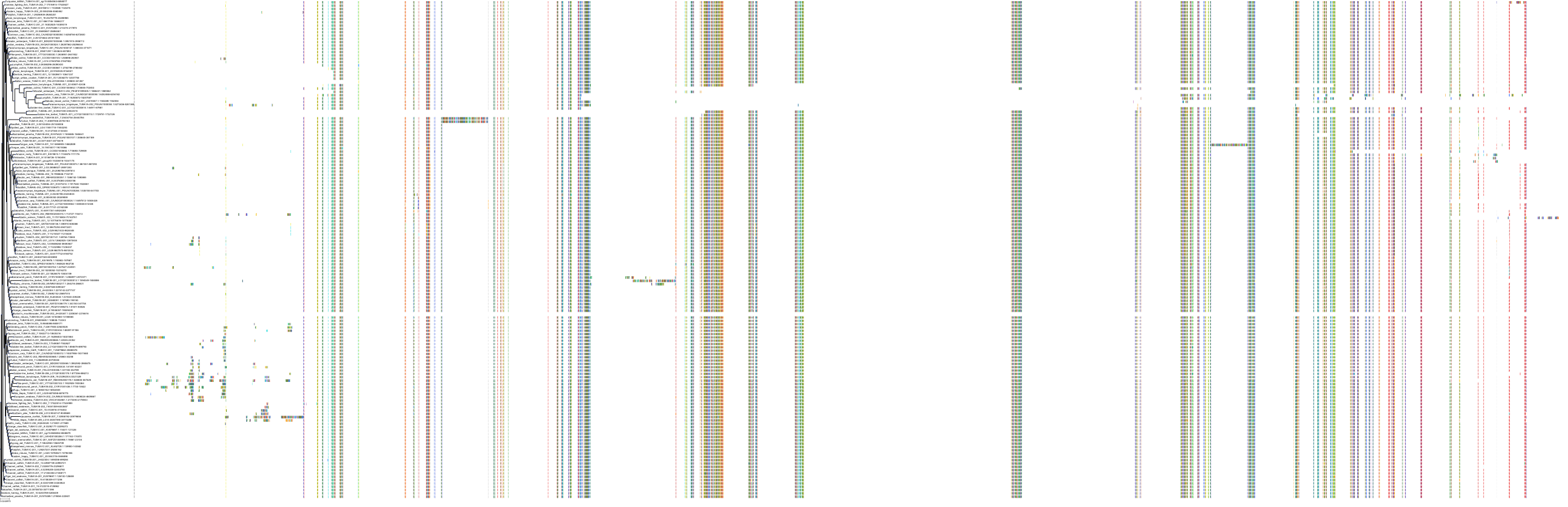
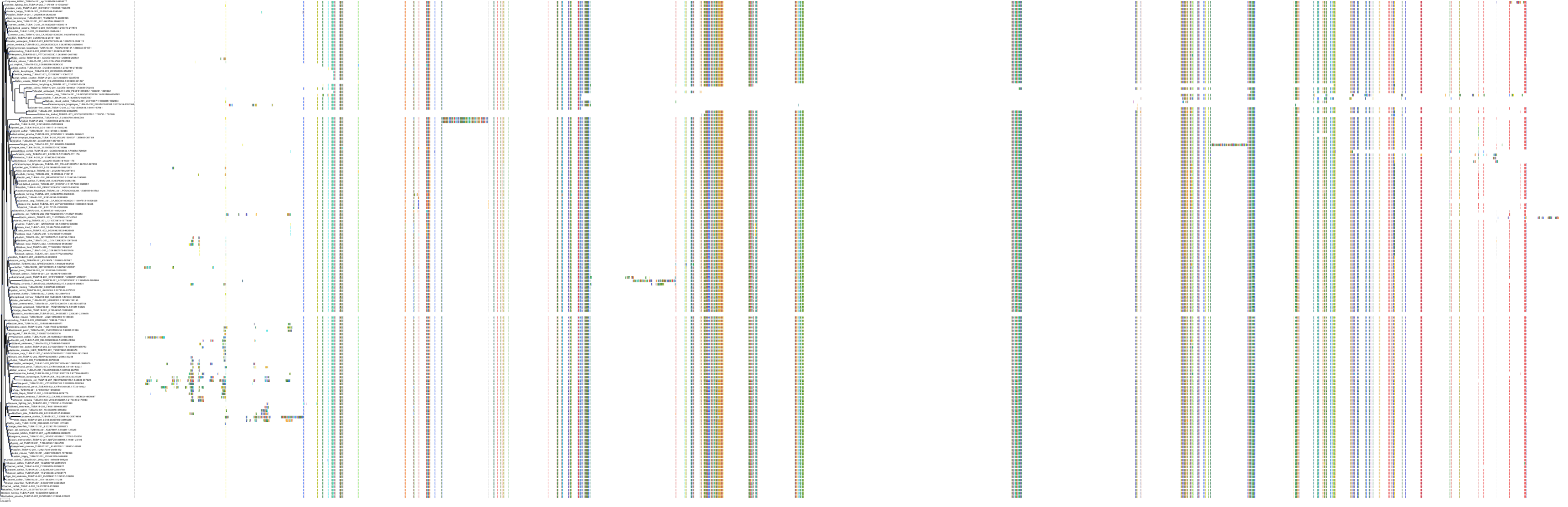
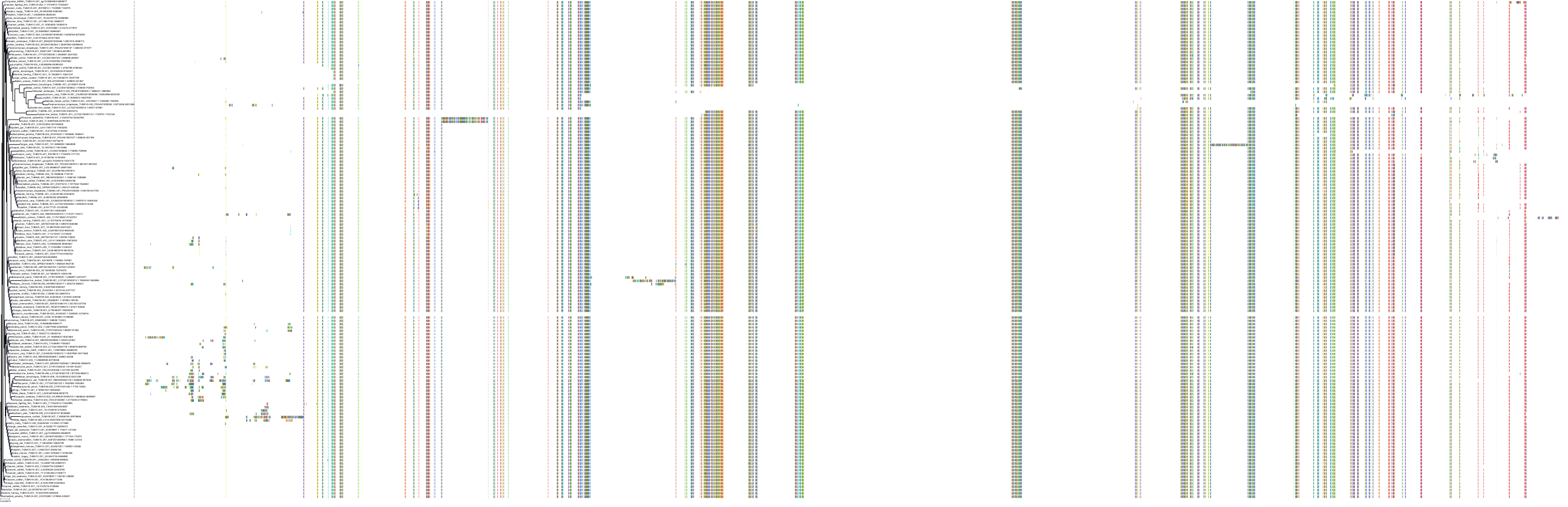
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Tubulin Description: Tubulin beta-4A chain Organism : Homo sapiens P04350 ENSG00000104833 |
||||
|
Protein: Tubulin Description: Tubulin beta chain Organism : Homo sapiens P07437 ENSG00000196230 |
||||
|
Protein: Tubulin Description: Tubulin alpha-3C chain Organism : Homo sapiens P0DPH7 ENSG00000198033 |
||||
|
Protein: Tubulin Description: Tubulin alpha-1B chain Organism : Homo sapiens P68363 ENSG00000123416 |
||||
|
Protein: Tubulin Description: Tubulin alpha-4A chain Organism : Homo sapiens P68366 ENSG00000127824 |
||||
|
Protein: Tubulin Description: Tubulin beta-4B chain Organism : Homo sapiens P68371 ENSG00000188229 |
||||
|
Protein: Tubulin Description: Tubulin beta-3 chain Organism : Homo sapiens Q13509 ENSG00000258947 |
||||
|
Protein: Tubulin Description: Tubulin beta-2A chain Organism : Homo sapiens Q13885 ENSG00000137267 |
||||
|
Protein: Tubulin Description: Tubulin beta-8 chain Organism : Homo sapiens Q3ZCM7 ENSG00000261456 |
||||
|
Protein: Tubulin Description: Tubulin alpha-3E chain Organism : Homo sapiens Q6PEY2 ENSG00000152086 |
||||
|
Protein: Tubulin Description: Tubulin alpha-1A chain Organism : Homo sapiens Q71U36 ENSG00000167552 |
||||
|
Protein: Tubulin Description: Tubulin alpha-1C chain Organism : Homo sapiens Q9BQE3 ENSG00000167553 |
||||
|
Protein: Tubulin Description: Tubulin beta-6 chain Organism : Homo sapiens Q9BUF5 ENSG00000176014 |
||||
|
Protein: Tubulin Description: Tubulin beta-2B chain Organism : Homo sapiens Q9BVA1 ENSG00000137285 |
||||
|
Protein: Tubulin Description: Tubulin beta-1 chain Organism : Homo sapiens Q9H4B7 ENSG00000101162 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1096380 |
| DrugBank | DB05992 |
| FDA SRS | 986FY7F8XR |
| PDB | PN6 |
| PubChem | 9949641 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL79095 |
| ZINC | ZINC000003819466 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Sus scrofa
Sus scrofa