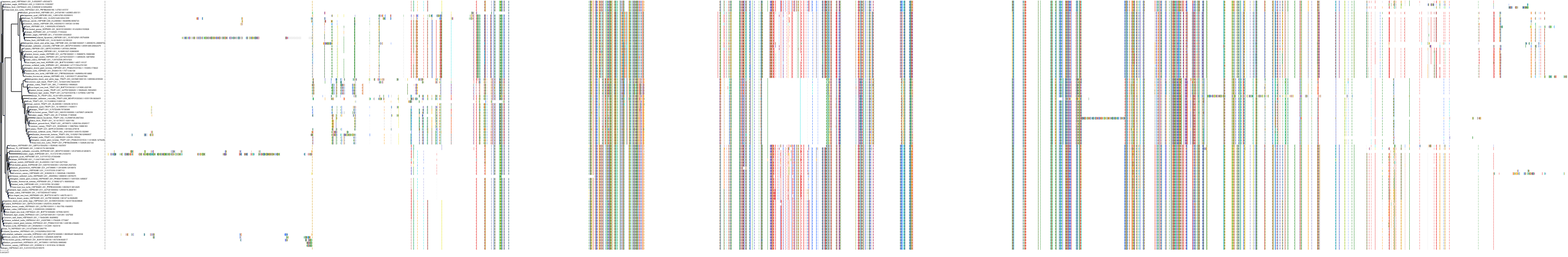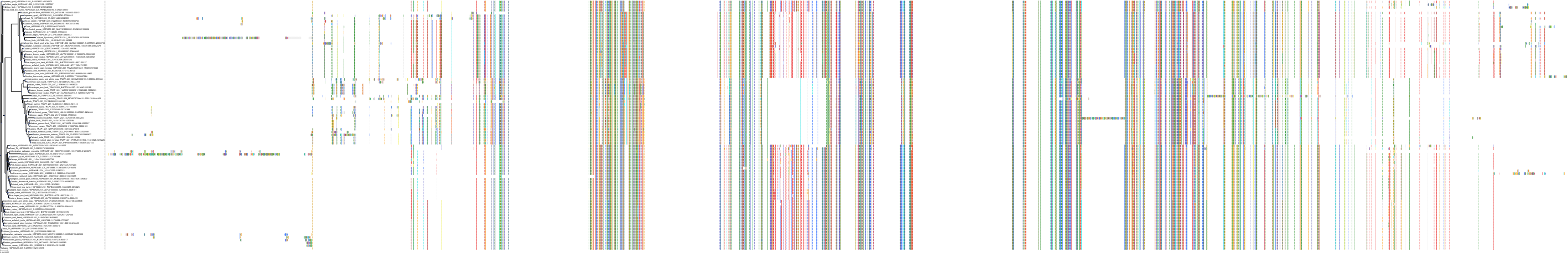| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| UNII | Q7Y33N57ZZ |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID80238485 |
Structure
| InChI Key | IFRGXKKQHBVPCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H31N3O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 409.53 |
| AlogP | 3.12 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 5.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 2.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 4.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 67.25 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 2.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 30.0 |
Pharmacology
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ion channel
Voltage-gated ion channel
Potassium channels
Voltage-gated potassium channel
|
- | - | - | - | 7-42 | |
|
Other cytosolic protein
|
- | 13-350 | - | - | 91.02-100 | |
|
Other membrane protein
|
- | 13-22 | - | - | 100 |
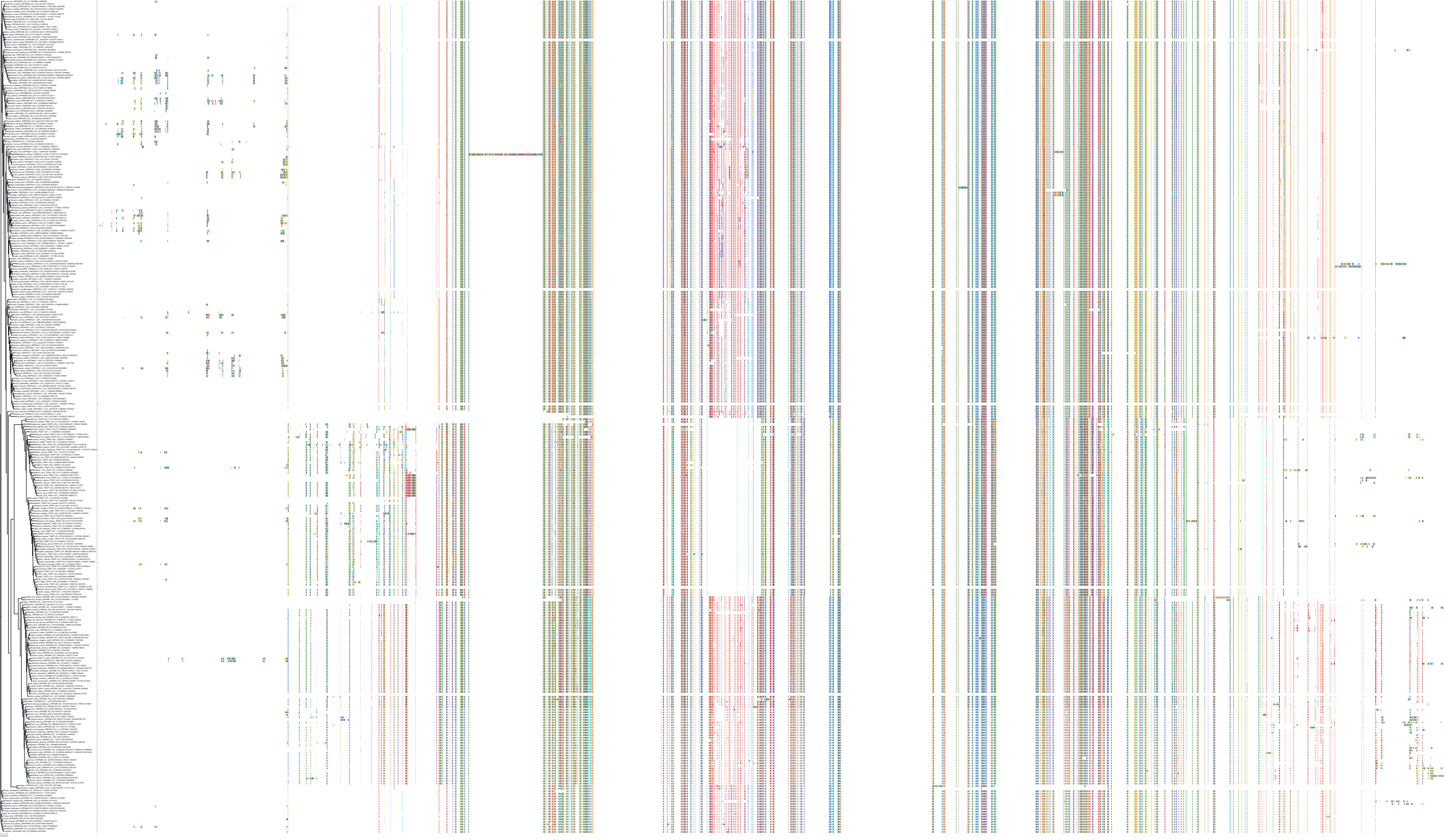
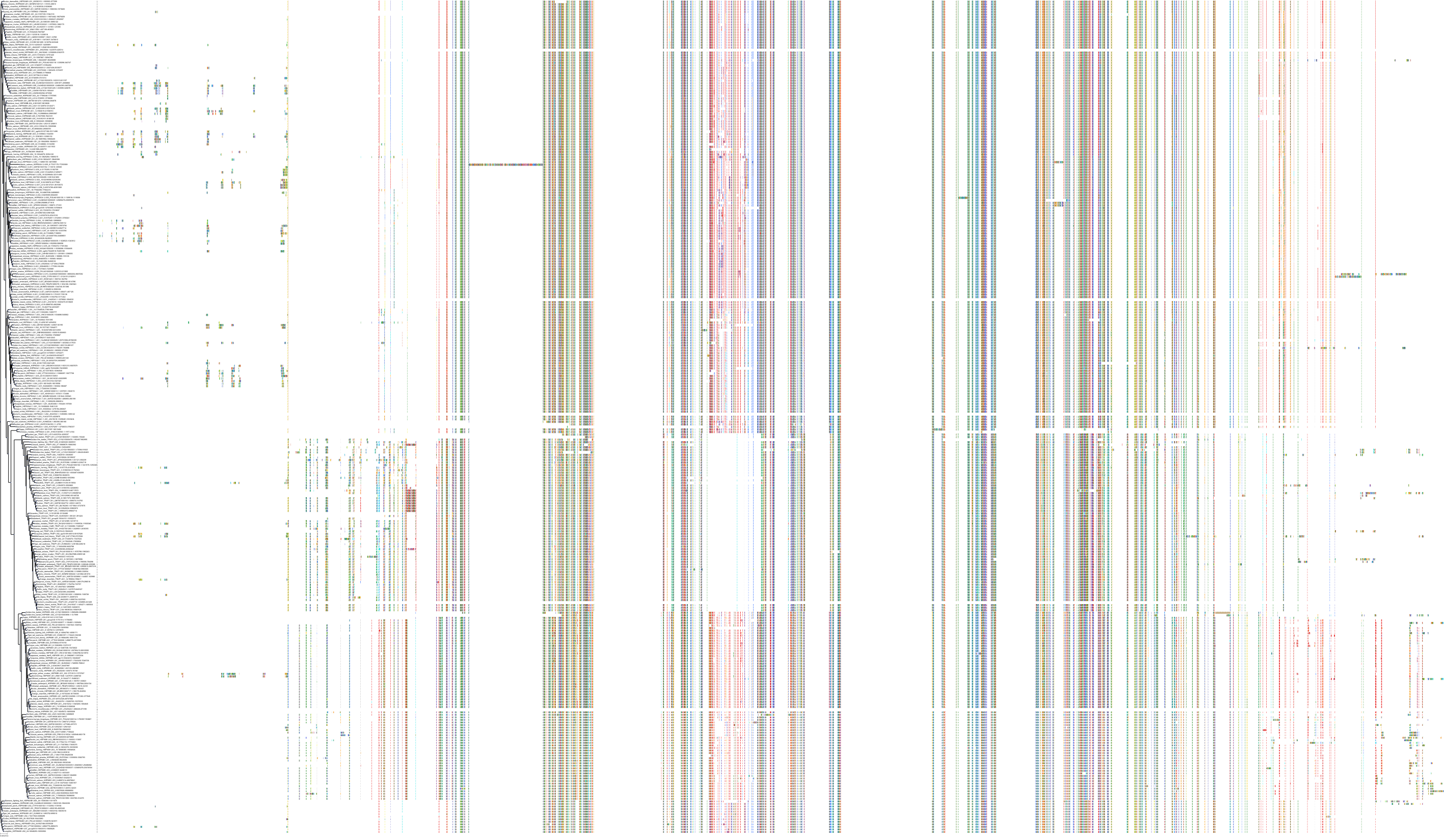
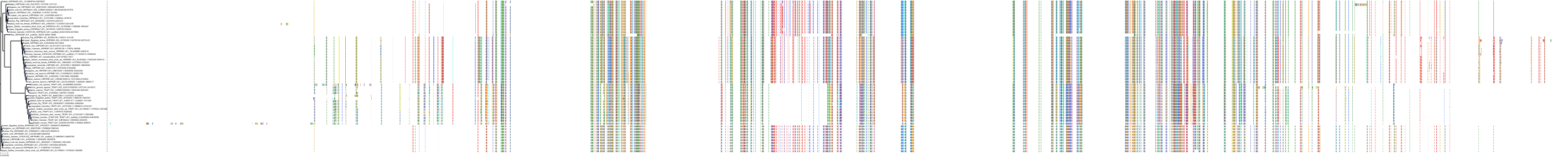
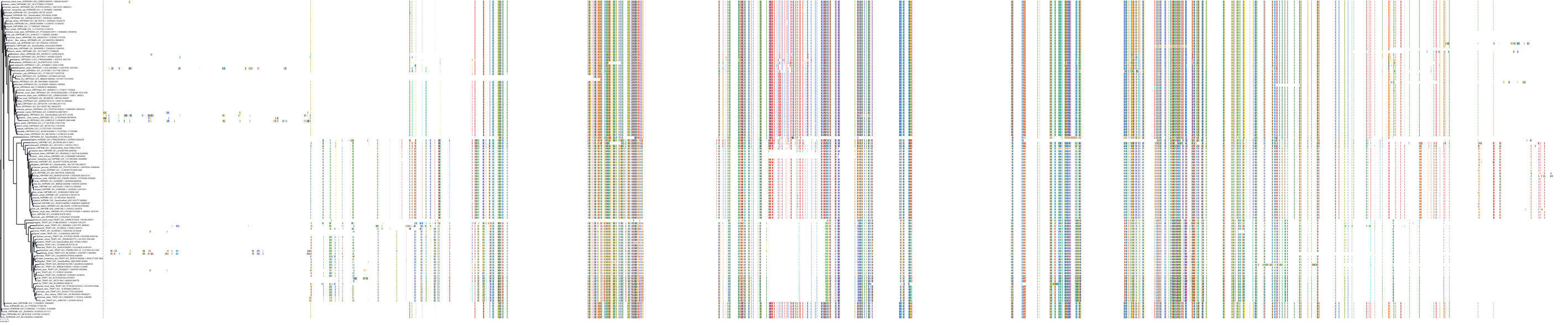
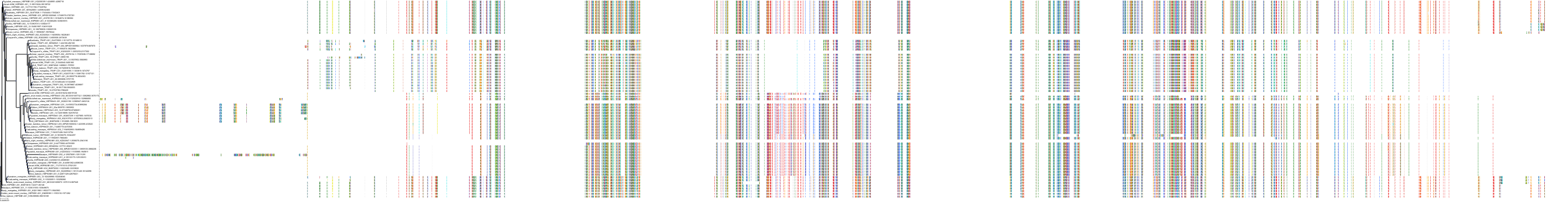
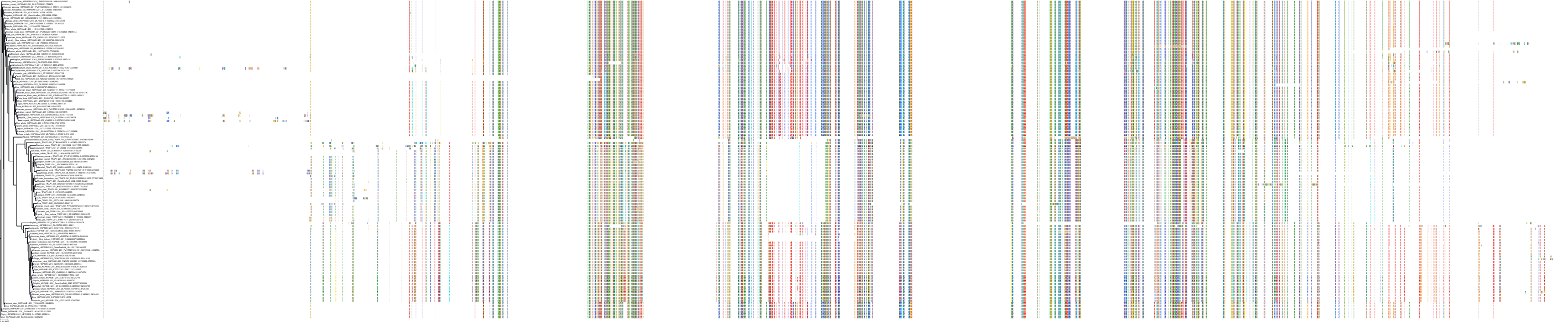
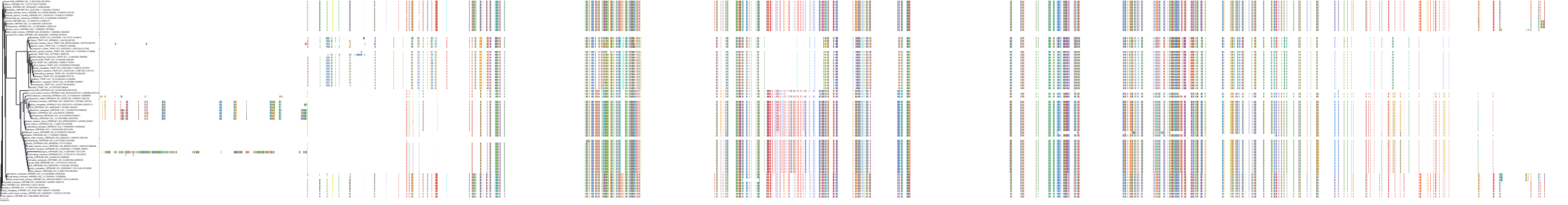
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Heat shock protein HSP90 Description: Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha Organism : Homo sapiens P07900 ENSG00000080824 |
||||
|
Protein: Heat shock protein HSP90 Description: Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta Organism : Homo sapiens P08238 ENSG00000096384 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 140592 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1214827 |
| DrugBank | DB06306 |
| FDA SRS | Q7Y33N57ZZ |
| PDB | XJX |
| PubChem | 11955716 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL382780 |
| ZINC | ZINC000043208226 |
 Canis lupus familiaris
Canis lupus familiaris
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens