| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| UNII | D5EQV23TDS |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID20165524 |
Structure
| InChI Key | OCSMOTCMPXTDND-OUAUKWLOSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H29N3O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 331.41 |
| AlogP | -0.21 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 5.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 5.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 7.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 127.76 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 0.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 23.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Matrix metalloproteinase 12 inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed PubMed PubMed |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Protease
Metallo protease
Metallo protease MAM clan
Metallo protease M10A subfamily
|
- | 0.41-200 | - | 0.6-84 | - | |
|
Enzyme
Protease
Metallo protease
Metallo protease MAM clan
Metallo protease M12B subfamily
|
- | 3.8-3.8 | - | 0.4-6.3 | 30 |
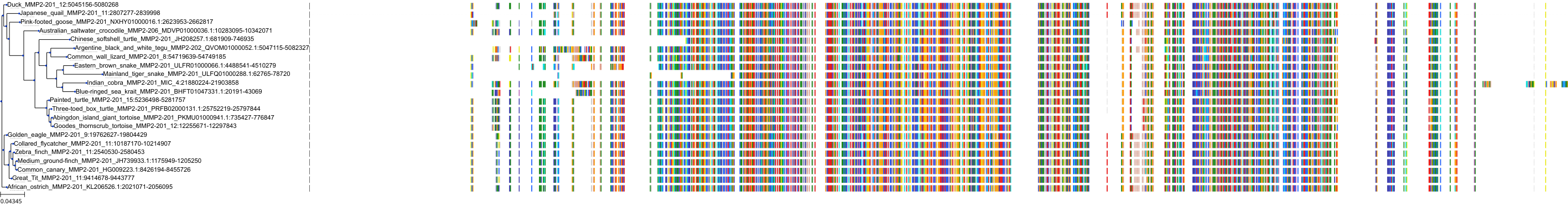
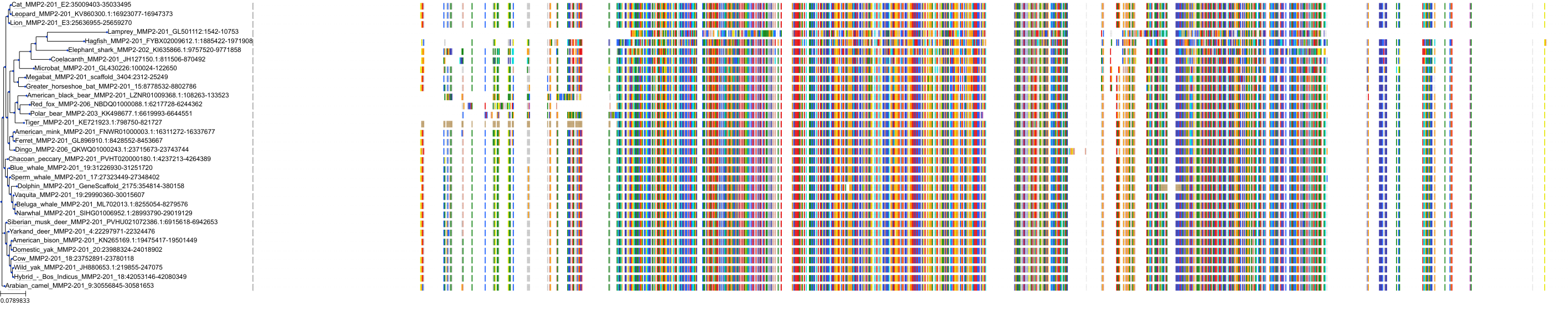
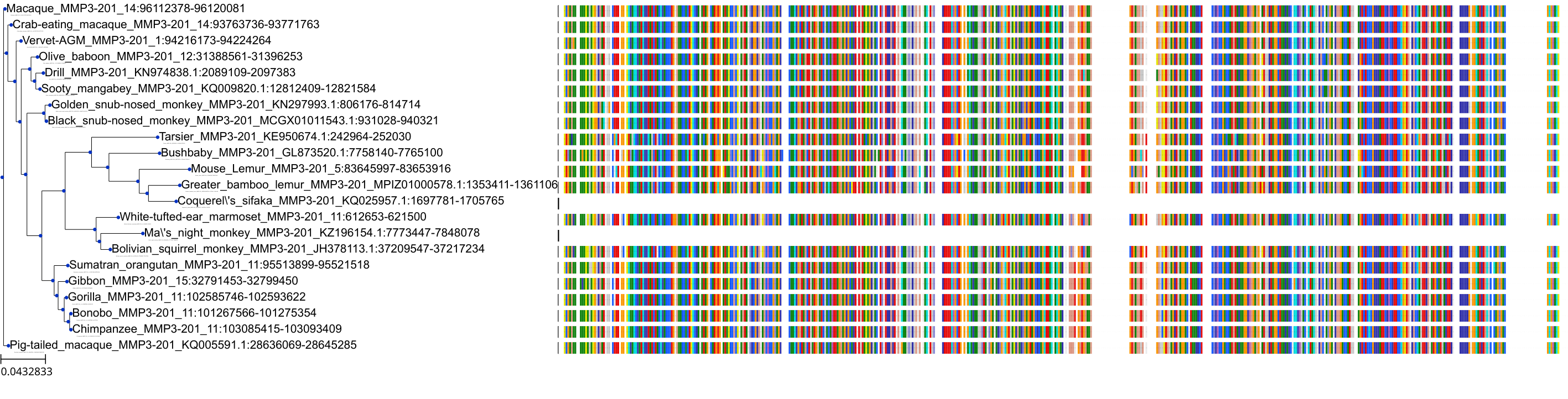
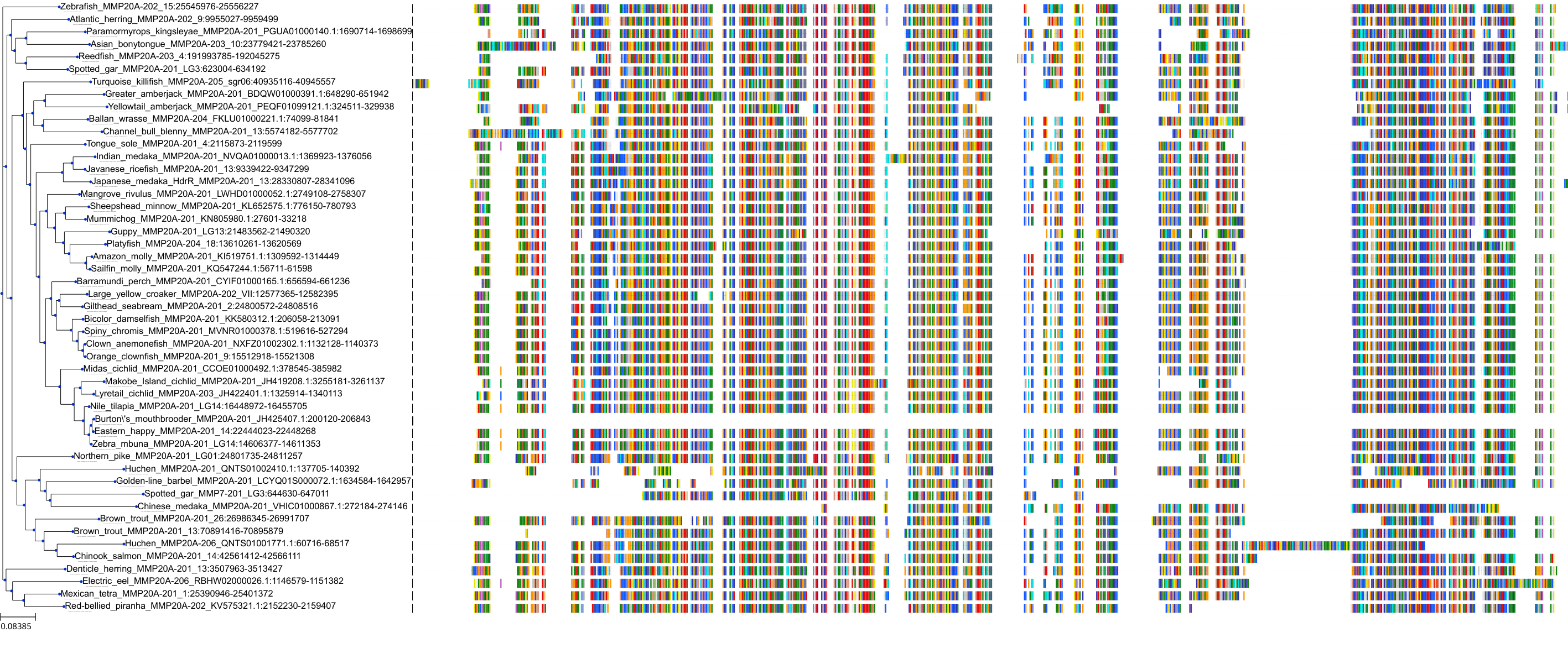
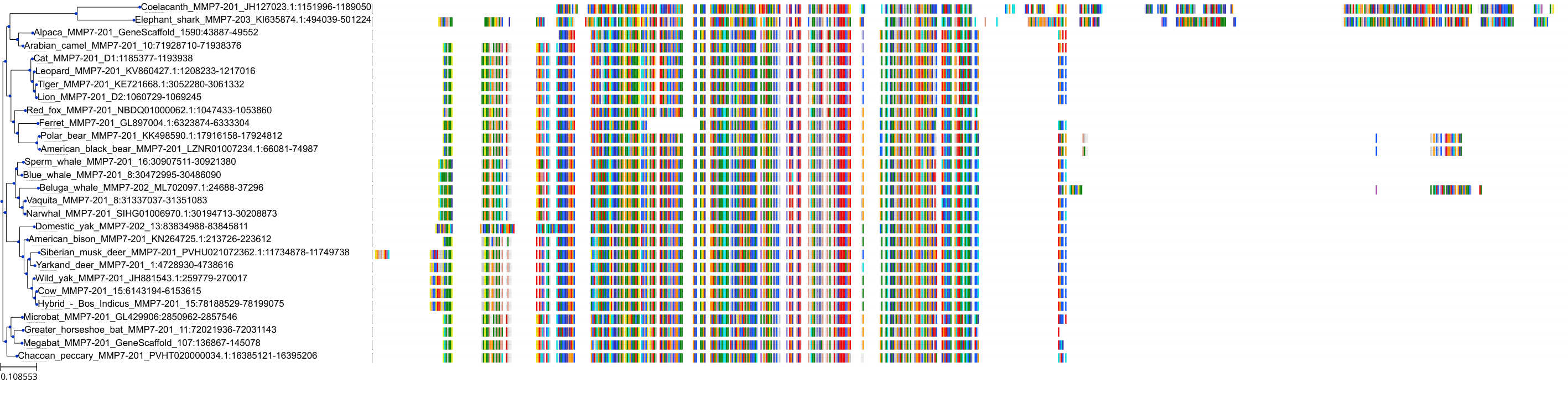
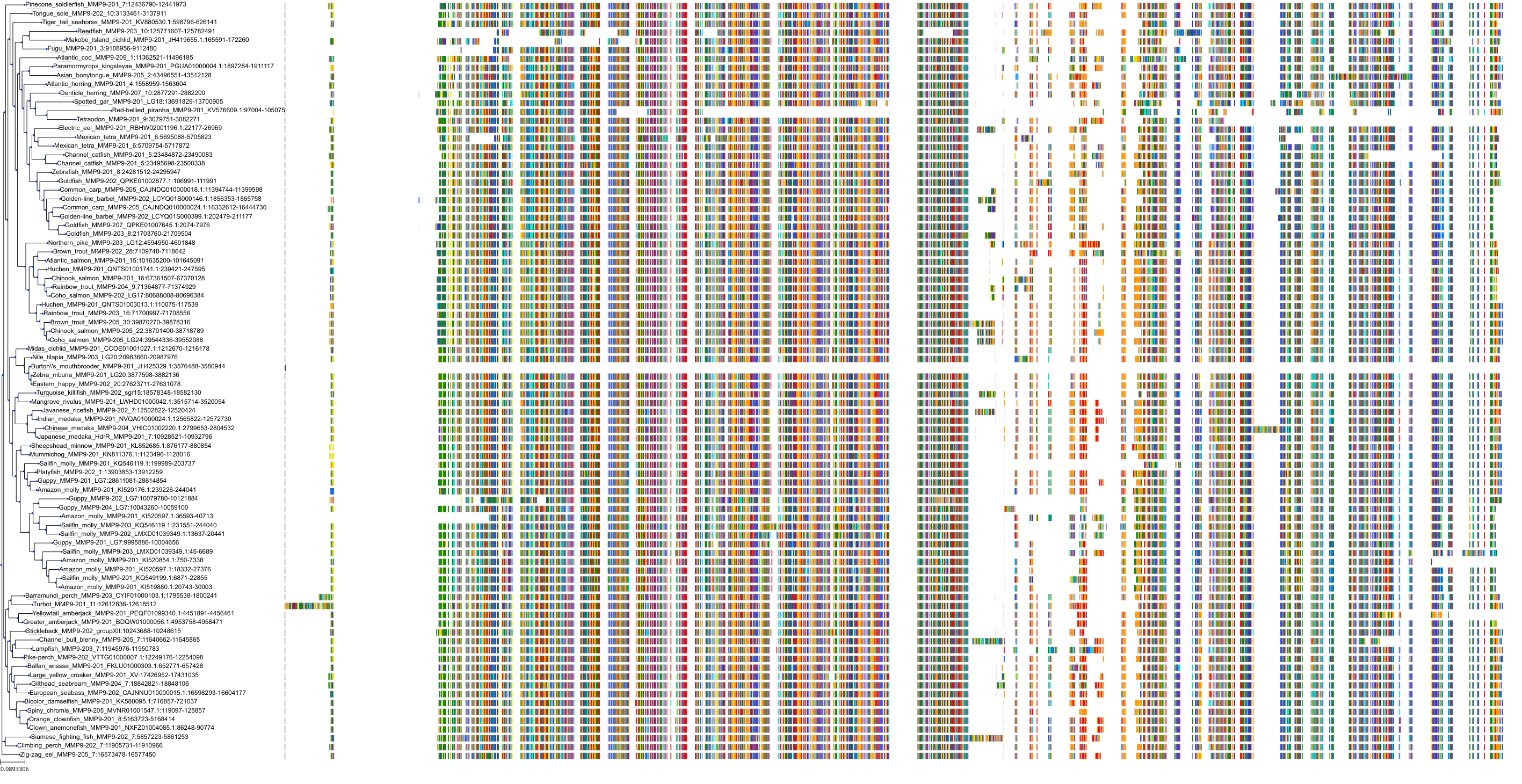
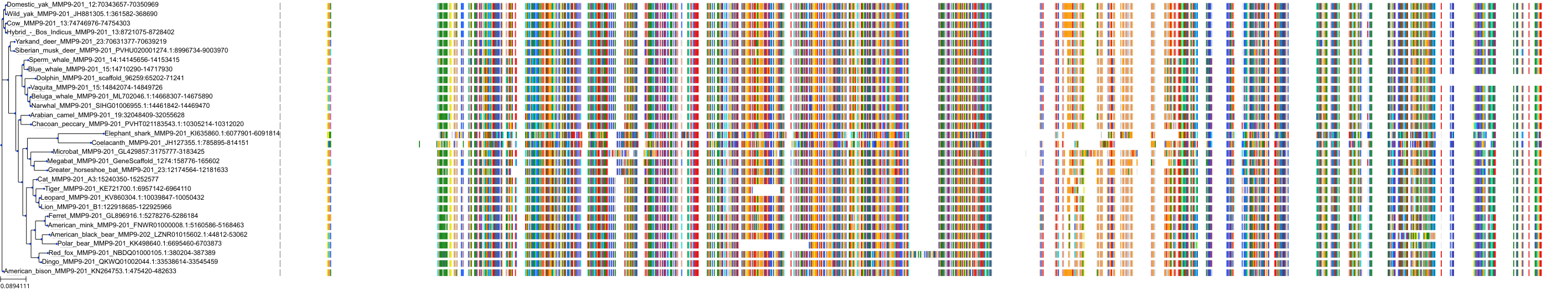
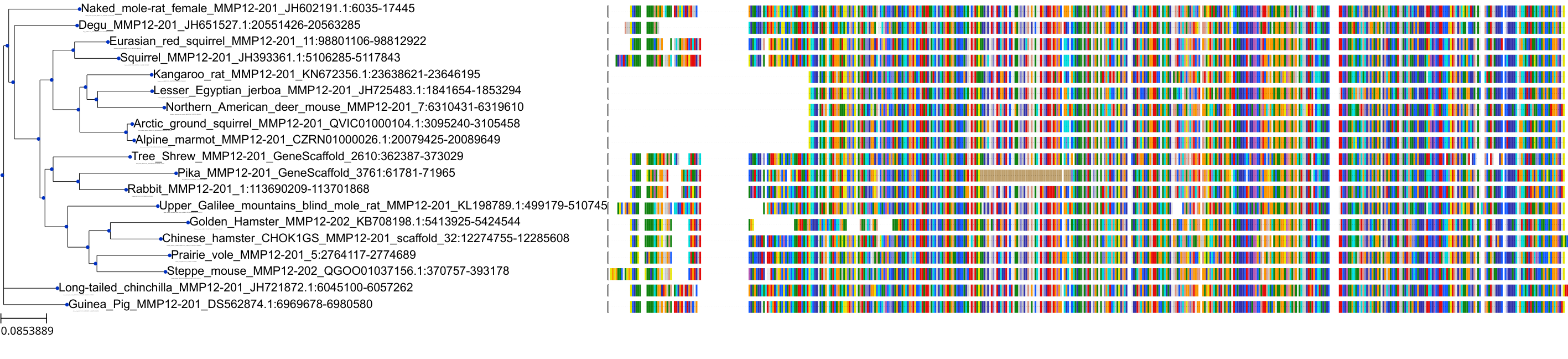
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Matrix metalloproteinase-1 Description: Interstitial collagenase Organism : Homo sapiens P03956 ENSG00000196611 |
||||
|
Protein: Matrix metalloproteinase-2 Description: 72 kDa type IV collagenase Organism : Homo sapiens P08253 ENSG00000087245 |
||||
|
Protein: Matrix metalloproteinase 3 Description: Stromelysin-1 Organism : Homo sapiens P08254 ENSG00000149968 |
||||
|
Protein: Matrix metalloproteinase 7 Description: Matrilysin Organism : Homo sapiens P09237 ENSG00000137673 |
||||
|
Protein: Matrix metalloproteinase 9 Description: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 Organism : Homo sapiens P14780 ENSG00000100985 |
||||
|
Protein: Matrix metalloproteinase 12 Description: Macrophage metalloelastase Organism : Homo sapiens P39900 ENSG00000262406 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 50662 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL279785 |
| DrugBank | DB00786 |
| FDA SRS | D5EQV23TDS |
| Human Metabolome Database | HMDB0014924 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 5220 |
| PDB | 097 |
| PharmGKB | PA164748329 |
| PubChem | 119031 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL34033 |
| ZINC | ZINC000001544157 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus