| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| UNII | 6L5D03D975 |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID10153718 |
Structure
| InChI Key | WPHKIQPVPYJNAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H21FN6O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 488.55 |
| AlogP | 5.18 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 7.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 4.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 6.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 118.09 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 5.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 35.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Platelet-derived growth factor receptor inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed |
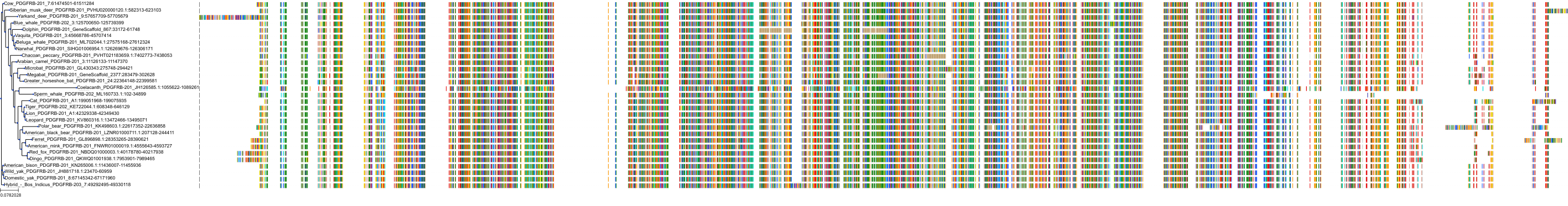
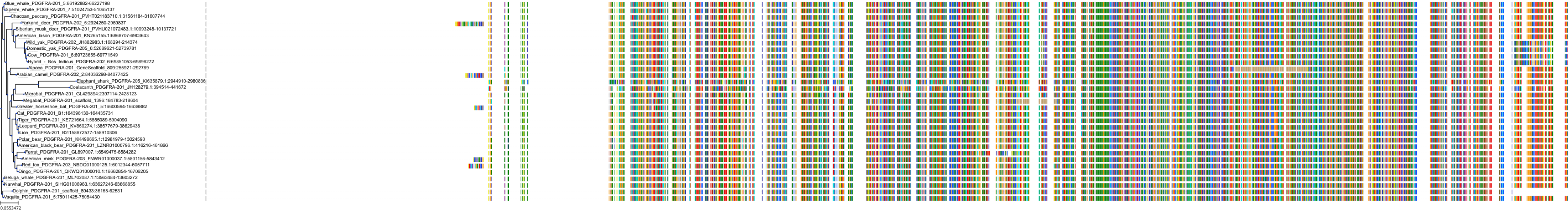
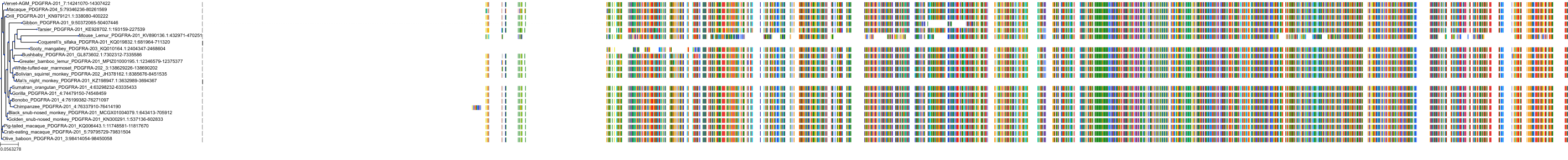
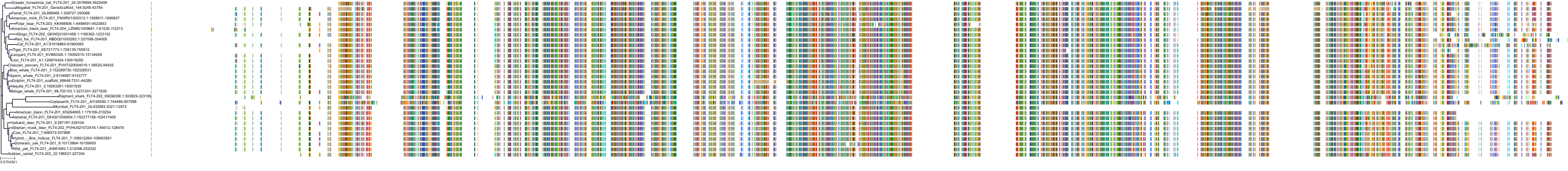
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor Description: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta Organism : Homo sapiens P09619 ENSG00000113721 |
||||
|
Protein: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor Description: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha Organism : Homo sapiens P16234 ENSG00000134853 |
||||
|
Protein: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Description: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 Organism : Homo sapiens P17948 ENSG00000102755 |
||||
|
Protein: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Description: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 Organism : Homo sapiens P35916 ENSG00000037280 |
||||
|
Protein: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Description: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 Organism : Homo sapiens P35968 ENSG00000128052 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1980297 |
| DrugBank | DB11694 |
| FDA SRS | 6L5D03D975 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 9914 |
| PubChem | 46207586 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL3381224 |
| ZINC | ZINC000063298074 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens