Structure
| InChI Key | CHNUOJQWGUIOLD-NFZZJPOKSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H13NO3S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 319.41 |
| AlogP | 2.92 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 4.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 4.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 57.61 |
| Molecular species | ACID |
| Aromatic Rings | 1.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 21.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Aldose reductase inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Oxidoreductase
|
- | 10-860 | - | - | 25-94.55 |
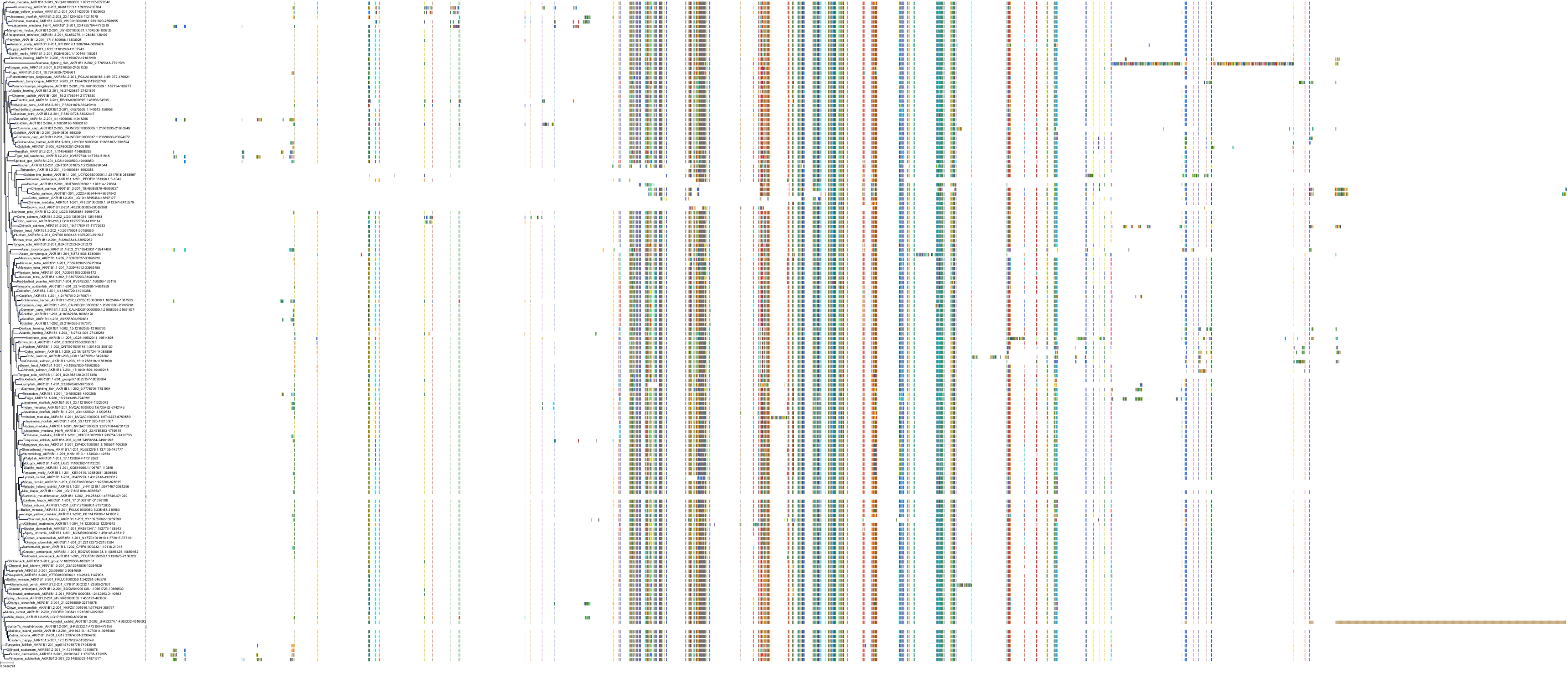
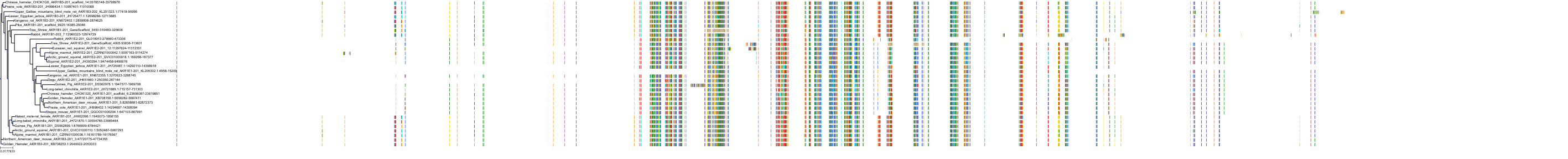
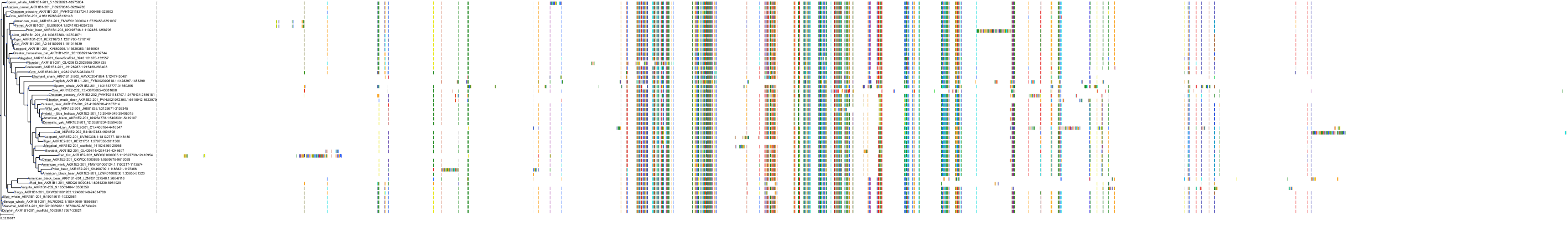
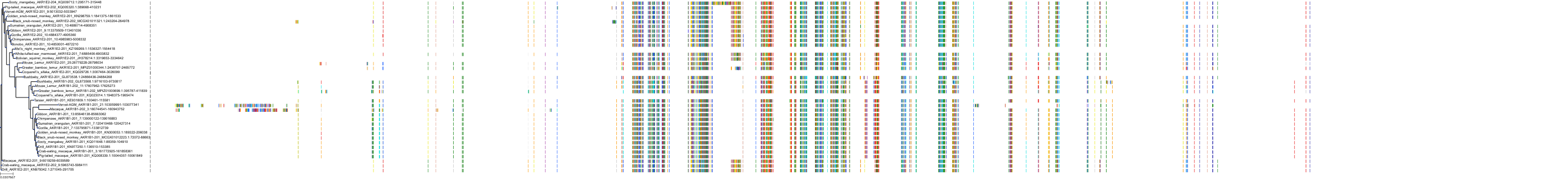
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Aldose reductase Description: Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B1 Organism : Homo sapiens P15121 ENSG00000085662 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 31539 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL56337 |
| DrugBank | DB15293 |
| DrugCentral | 1021 |
| FDA SRS | 424DV0807X |
| PubChem | 1549120 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL49049 |
| ZINC | ZINC000001533688 |
 Bos taurus
Bos taurus
 Capra hircus
Capra hircus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus