| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | L01XX58 |
| UNII | 71596A9R13 |
Structure
| InChI Key | FBKMWOJEPMPVTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H13BrFN7O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 438.24 |
| AlogP | 0.42 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 8.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 5.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 7.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 167.76 |
| Molecular species | ACID |
| Aromatic Rings | 2.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 25.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Oxidoreductase
|
8-13 | 3.4-710 | - | - | 32-101.2 |
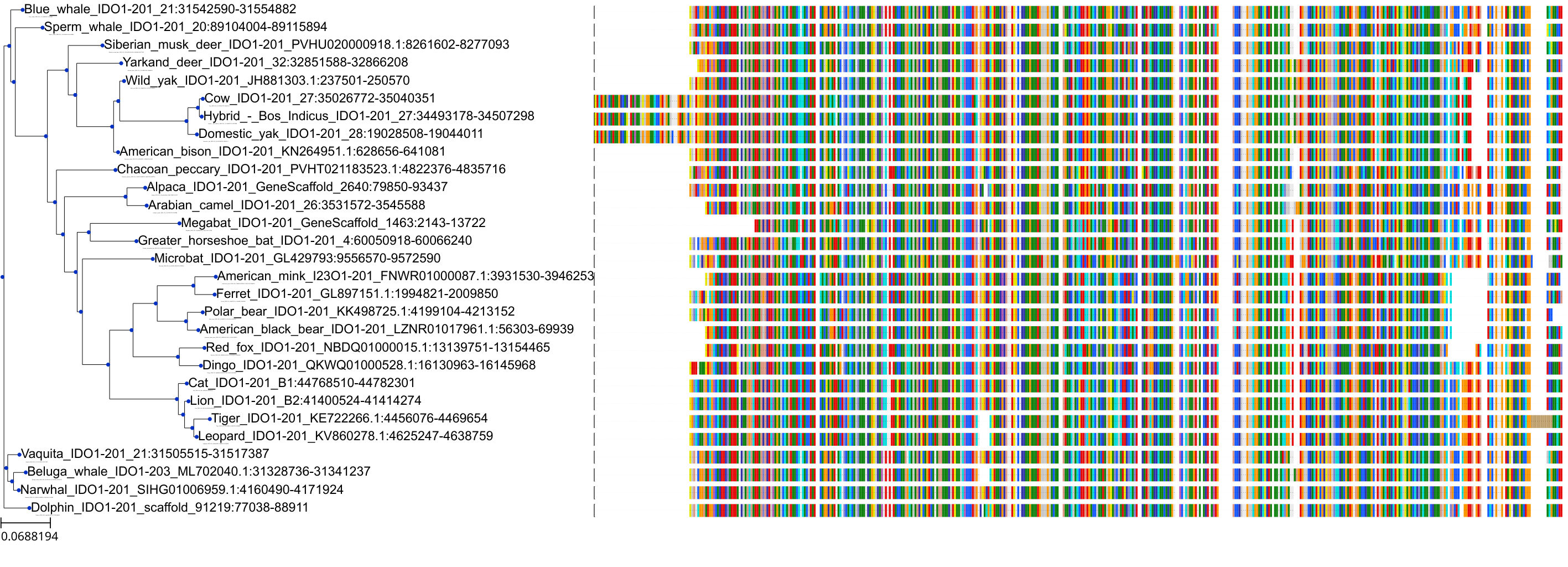
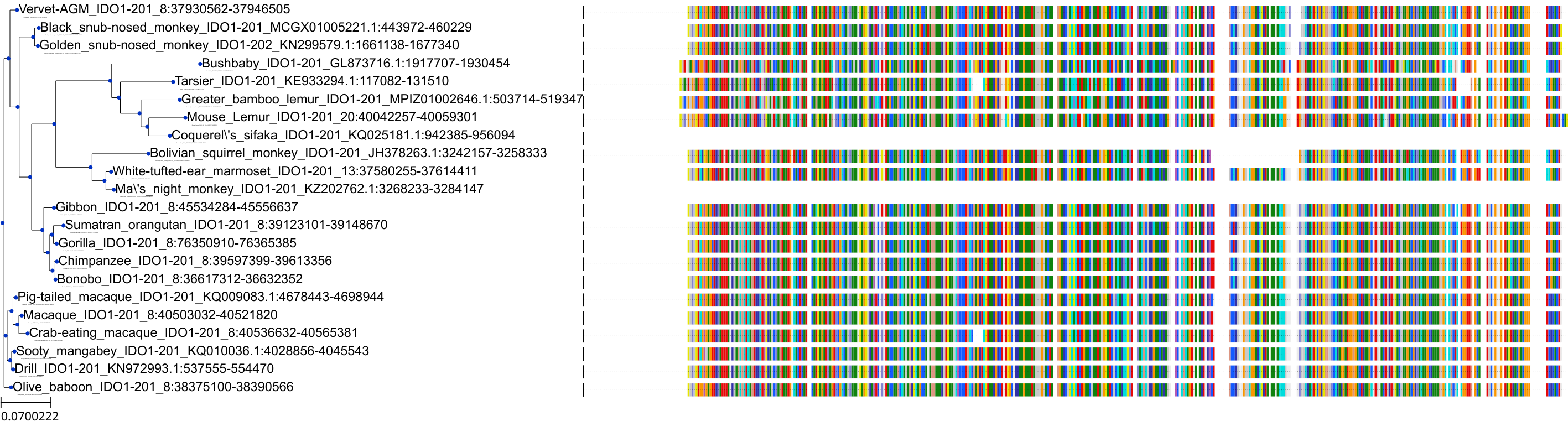
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase Description: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 Organism : Homo sapiens P14902 ENSG00000131203 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL3545369 |
| DrugBank | DB11717 |
| FDA SRS | 71596A9R13 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 8221 |
| PDB | BBJ |
| PubChem | 135564890 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL18823200 |
| ZINC | ZINC000113208009 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus