Structure
| InChI Key | DYNHJHQFHQTFTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H29N5O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 443.55 |
| AlogP | 3.92 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 7.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 5.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 78.43 |
| Molecular species | BASE |
| Aromatic Rings | 4.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 33.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Platelet-derived growth factor receptor inhibitor | INHIBITOR | Other PubMed |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase PDGFR family
|
- | 0.06-35 | 0.15-22 | - | 95-100 |
Target Conservation
|
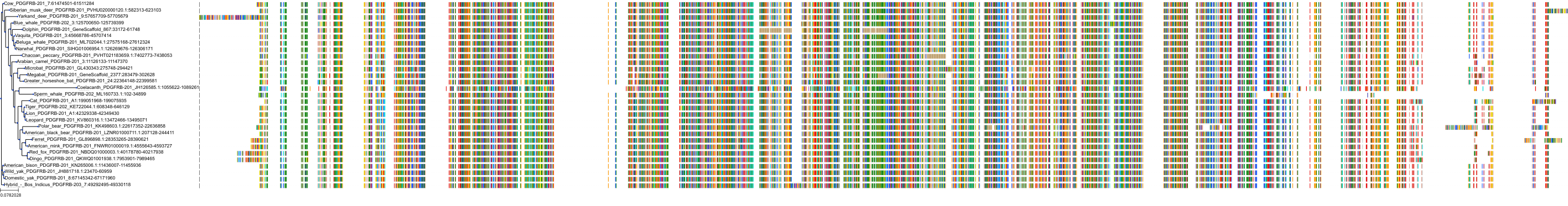
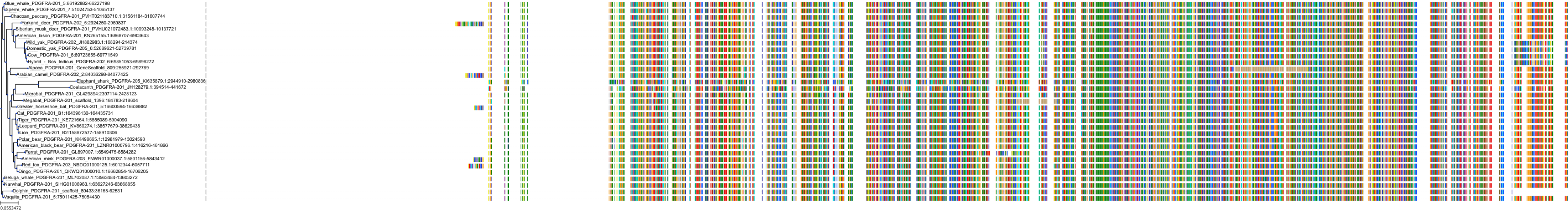
Protein: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor Description: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta Organism : Homo sapiens P09619 ENSG00000113721 |
||||
|
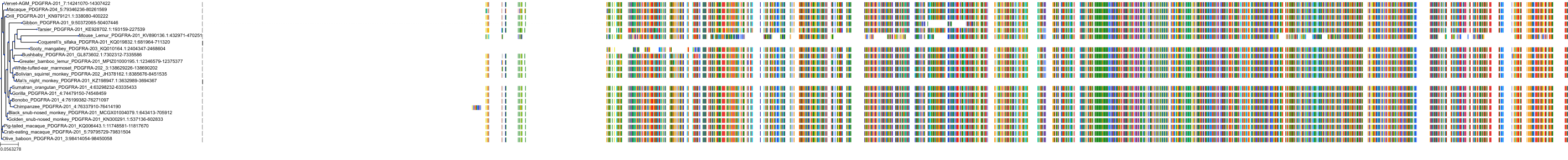
Protein: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor Description: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha Organism : Homo sapiens P16234 ENSG00000134853 |
||||
|
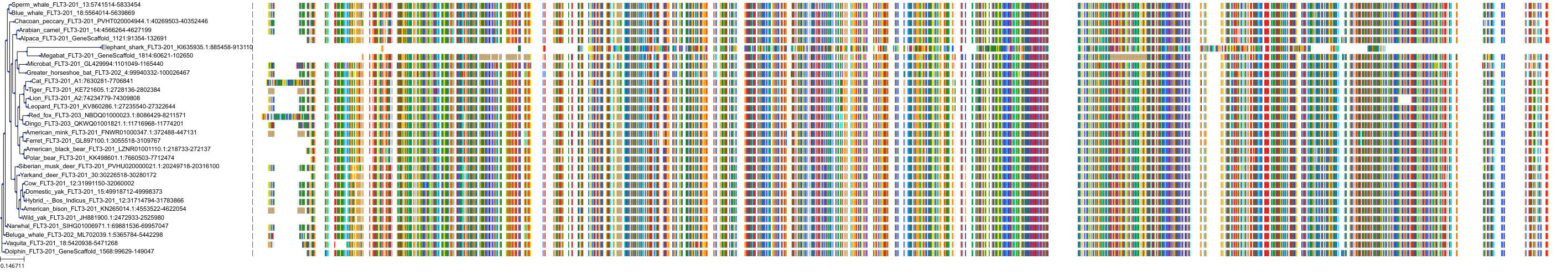
Protein: Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor FLT3 Description: Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 Organism : Homo sapiens P36888 ENSG00000122025 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 145365 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2105728 |
| DrugBank | DB11832 |
| FDA SRS | LQF7I567TQ |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 7882 |
| PDB | 6T2 |
| PubChem | 10366136 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL2730601 |
| ZINC | ZINC000003820043 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens