| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| UNII | 8ATB1C1R6X |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID6046686 |
Structure
| InChI Key | CFBUZOUXXHZCFB-OYOVHJISSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H25NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 343.42 |
| AlogP | 4.05 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 4.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 5.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 79.55 |
| Molecular species | ACID |
| Aromatic Rings | 1.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 25.0 |
Pharmacology
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Phosphodiesterase
Phosphodiesterase 4
Phosphodiesterase 4A
|
- | 10-700 | - | 38-38 | 45.28 | |
|
Enzyme
Phosphodiesterase
Phosphodiesterase 4
Phosphodiesterase 4B
|
- | 10-700 | - | 38-38 | 45.28-91.3 | |
|
Enzyme
Phosphodiesterase
Phosphodiesterase 4
Phosphodiesterase 4C
|
- | 10-840 | - | 38-38 | 45.28-98.5 | |
|
Enzyme
Phosphodiesterase
Phosphodiesterase 4
Phosphodiesterase 4D
|
- | 10-700 | - | 38-38 | 45.28-98.8 |
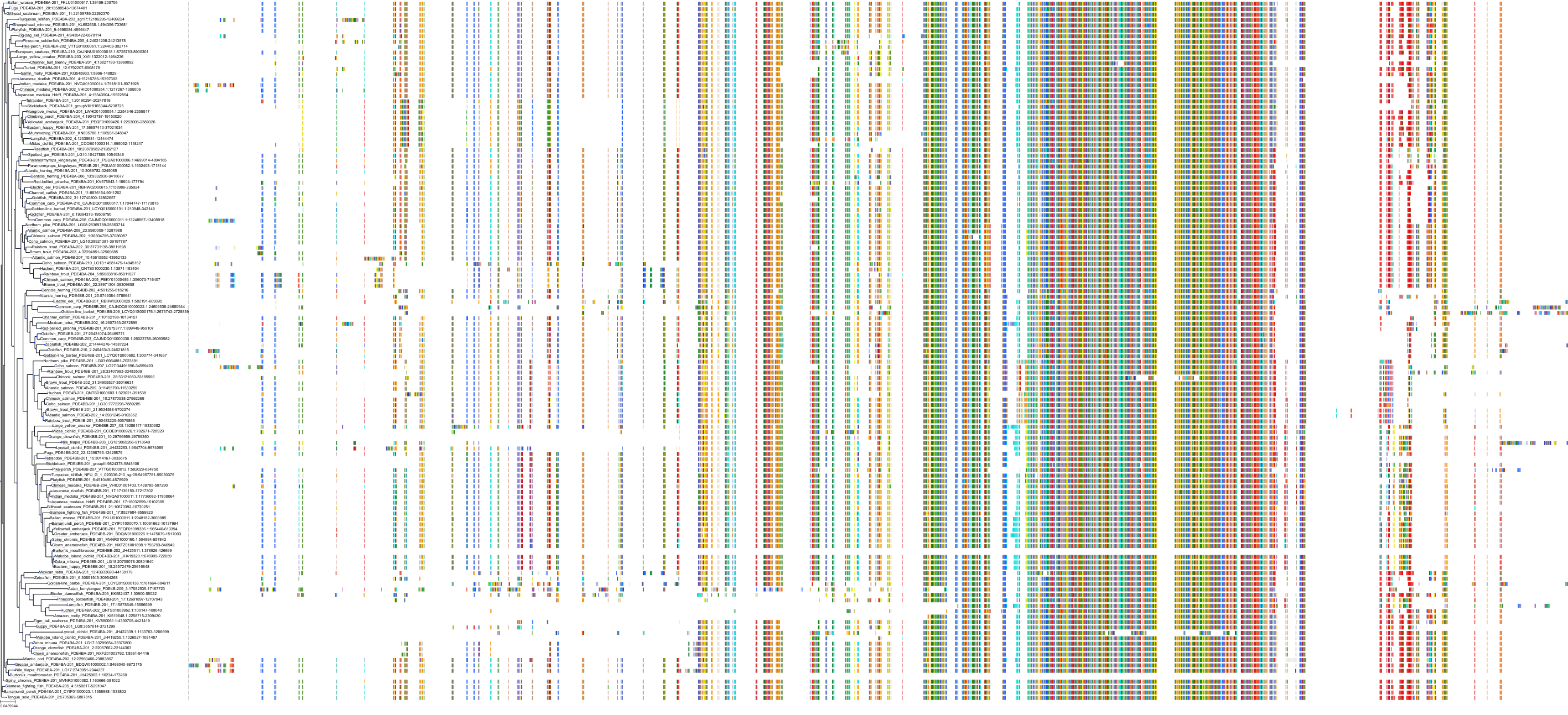
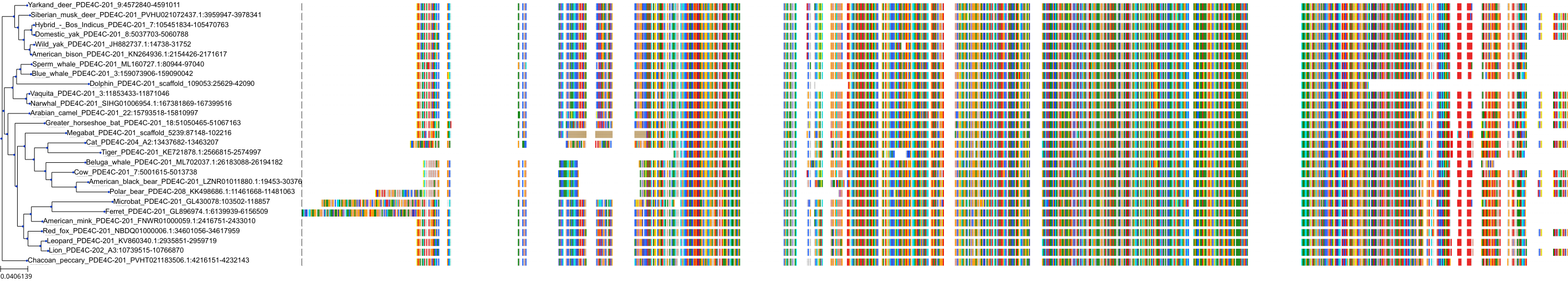
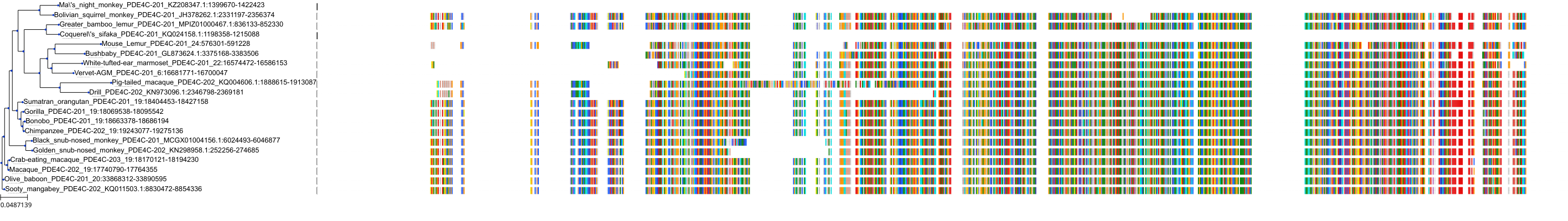
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Phosphodiesterase 4 Description: cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4A Organism : Homo sapiens P27815 ENSG00000065989 |
||||
|
Protein: Phosphodiesterase 4 Description: cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4B Organism : Homo sapiens Q07343 ENSG00000184588 |
||||
|
Protein: Phosphodiesterase 4 Description: cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4C Organism : Homo sapiens Q08493 ENSG00000105650 |
||||
|
Protein: Phosphodiesterase 4 Description: cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4D Organism : Homo sapiens Q08499 ENSG00000113448 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL511115 |
| DrugBank | DB03849 |
| FDA SRS | 8ATB1C1R6X |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 7407 |
| PDB | CIO |
| PubChem | 151170 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL27515 |
| ZINC | ZINC000100042108 |
 Cavia porcellus
Cavia porcellus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus
 Mustela putorius furo
Mustela putorius furo
 Oryctolagus cuniculus
Oryctolagus cuniculus
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus