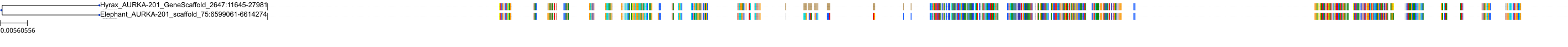| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| UNII | T66ES73M18 |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID30145539 |
Structure
| InChI Key | ZLHFILGSQDJULK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H20ClFN4O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 518.93 |
| AlogP | 5.75 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 7.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 2.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 6.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 105.93 |
| Molecular species | ACID |
| Aromatic Rings | 4.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 37.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Serine/threonine-protein kinase Aurora-A inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
Other protein kinase group
Other protein kinase AUR family
|
- | 0.04-396.5 | - | 0.3 | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase Src family
|
- | 320 | - | - | - | |
|
Ion channel
Ligand-gated ion channel
GABA-A receptor
|
- | 490 | - | - | - | |
|
Other nuclear protein
|
- | 1.1 | - | - | - |
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Serine/threonine-protein kinase Aurora-A Description: Aurora kinase A Organism : Homo sapiens O14965 ENSG00000087586 |
||||
Related Entries
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 125628 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL483158 |
| DrugBank | DB05220 |
| FDA SRS | T66ES73M18 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 7790 |
| PDB | A5B |
| PharmGKB | PA166165015 |
| PubChem | 24771867 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL855823 |
| ZINC | ZINC000040939534 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus