| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | N06AX22 |
| UNII | 137R1N49AD |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID3057642 |
Structure
| InChI Key | YJYPHIXNFHFHND-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H17NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 243.31 |
| AlogP | 2.53 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 2.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 4.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 38.33 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 2.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 18.0 |
Pharmacology
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Membrane receptor
Family A G protein-coupled receptor
Small molecule receptor (family A GPCR)
Monoamine receptor
Serotonin receptor
|
- | - | - | 630-708 | - | |
|
Membrane receptor
Family A G protein-coupled receptor
Small molecule receptor (family A GPCR)
Monoamine-derivative receptor (family A GPCR)
Melatonin receptor
|
0.06918-10.1 | 0.0761 | - | 0.06-0.54 | - |
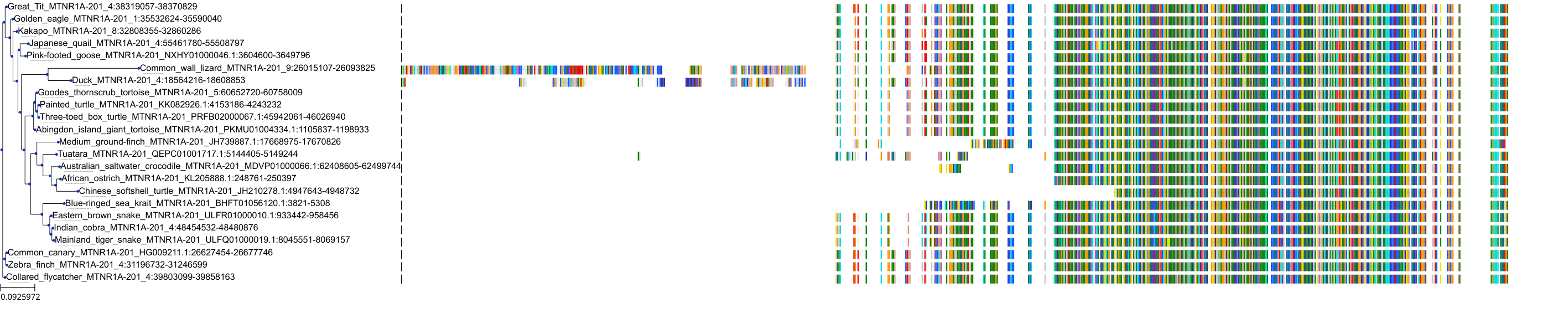
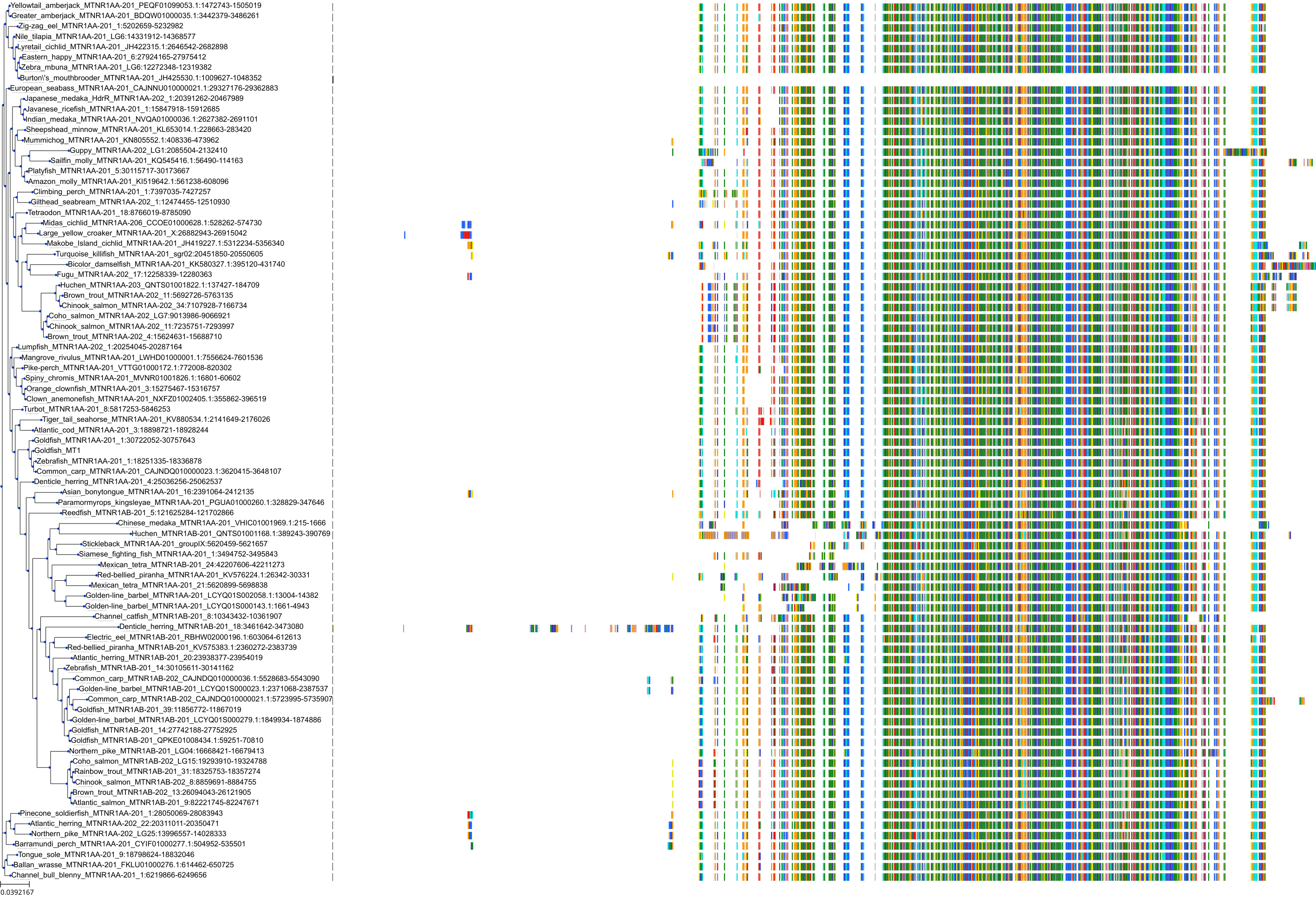
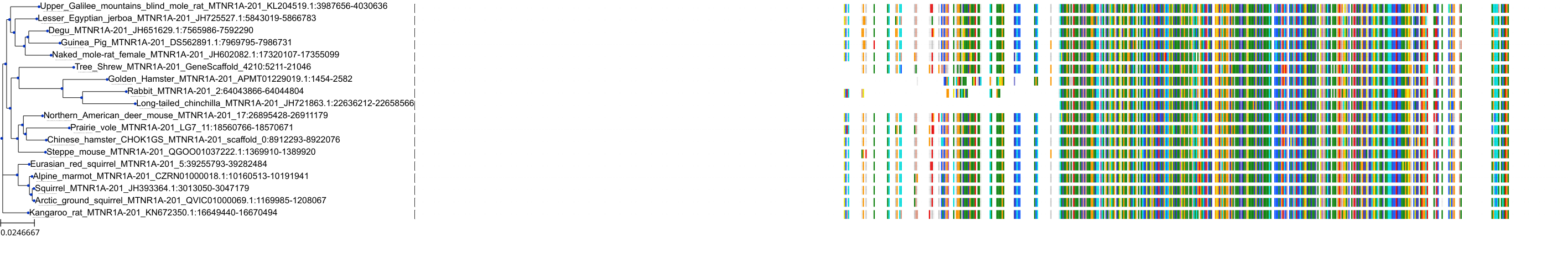
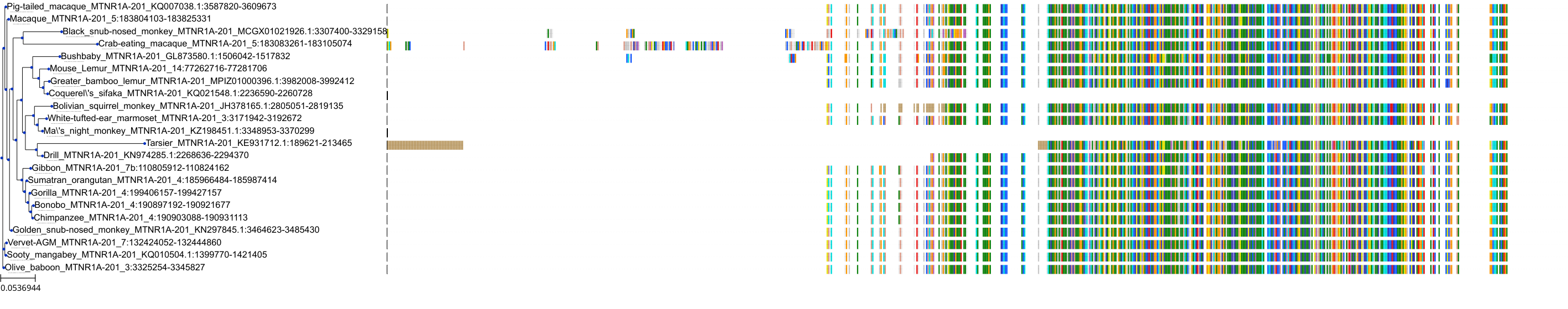
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Serotonin 2c (5-HT2c) receptor Description: 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2C Organism : Homo sapiens P28335 ENSG00000147246 |
||||
|
Protein: Melatonin receptor Description: Melatonin receptor type 1A Organism : Homo sapiens P48039 ENSG00000168412 |
||||
|
Protein: Melatonin receptor Description: Melatonin receptor type 1B Organism : Homo sapiens P49286 ENSG00000134640 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 134990 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL10878 |
| DrugBank | DB06594 |
| DrugCentral | 99 |
| FDA SRS | 137R1N49AD |
| Human Metabolome Database | HMDB0015636 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 198 |
| PDB | AWY |
| PharmGKB | PA165958363 |
| PubChem | 82148 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL114476 |
| ZINC | ZINC000000005608 |
 Gallus gallus
Gallus gallus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus
 Ovis aries
Ovis aries
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus
 Xenopus laevis
Xenopus laevis