| Trade Names | |
| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | N07BA03 |
| UNII | W6HS99O8ZO |
Structure
| InChI Key | JQSHBVHOMNKWFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C13H13N3 |
| Molecular Weight | 211.27 |
| AlogP | 1.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 3.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 37.81 |
| Molecular species | BASE |
| Aromatic Rings | 2.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 16.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Neuronal acetylcholine receptor; alpha4/beta2 partial agonist | PARTIAL AGONIST | FDA |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ion channel
Ligand-gated ion channel
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit
|
0.06-950 | 38.9-200 | - | 0.05-617 | 32-38 | |
|
Ion channel
Ligand-gated ion channel
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor beta subunit
|
0.06-950 | 38.9-200 | - | 0.05-617 | 32-38 | |
|
Transporter
Electrochemical transporter
SLC superfamily of solute carriers
SLC21/SLCO family of organic anion transporting polypeptides
|
- | - | - | - | 0.8-27.3 |
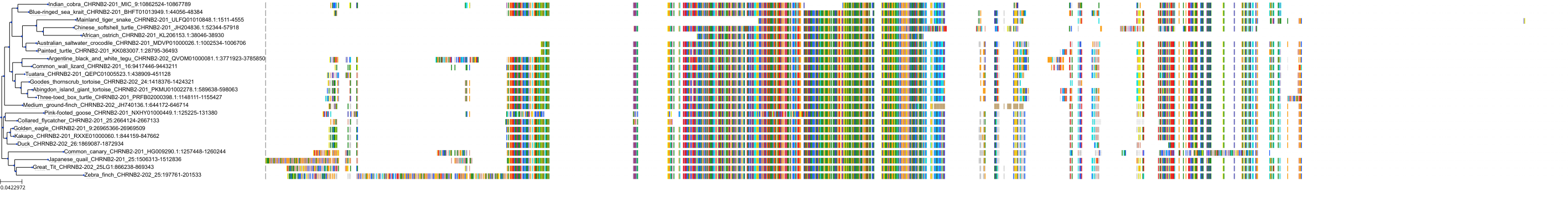
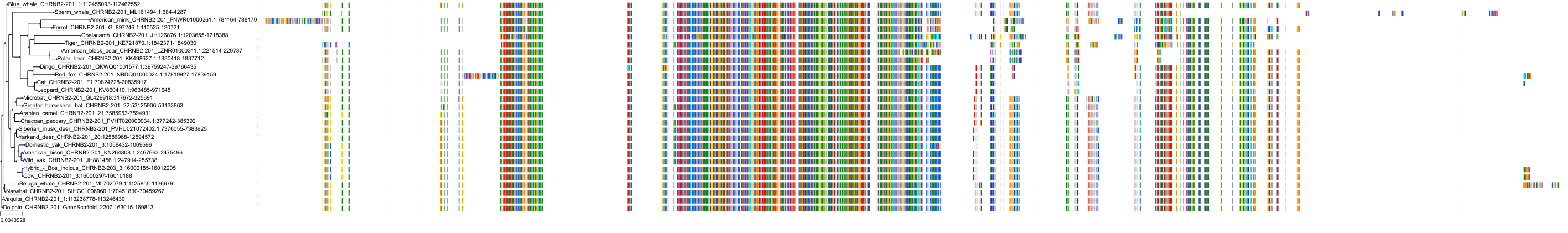
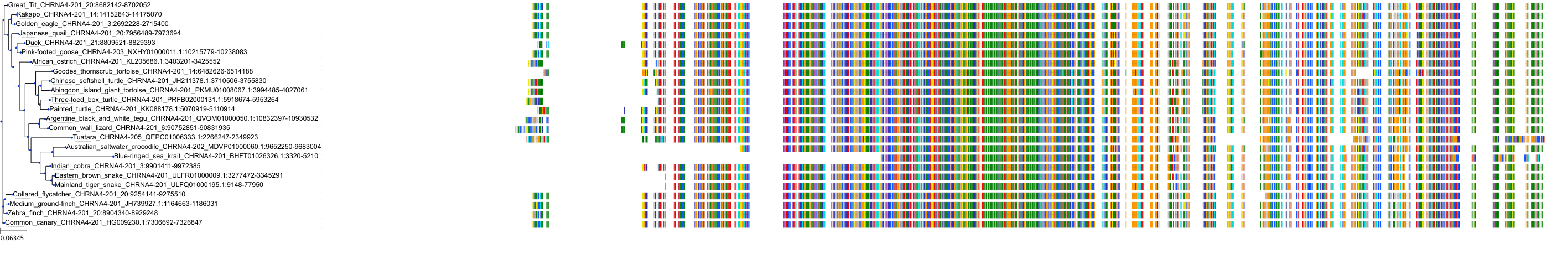
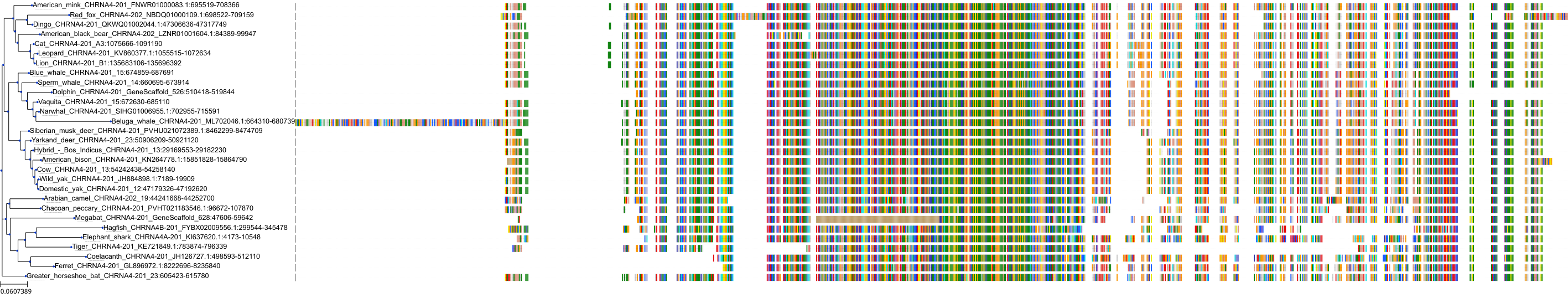
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Neuronal acetylcholine receptor; alpha4/beta2 Description: Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit beta-2 Organism : Homo sapiens P17787 ENSG00000160716 |
||||
|
Protein: Neuronal acetylcholine receptor; alpha4/beta2 Description: Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-4 Organism : Homo sapiens P43681 ENSG00000101204 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1396 |
| DrugBank | DB01273 |
| FDA SRS | W6HS99O8ZO |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 5459 |
| PubChem | 5310966 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL225687 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus