| Trade Names | |
| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | R03DA04 |
| UNII | 0I55128JYK |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID5021336 |
Structure
| InChI Key | ZFXYFBGIUFBOJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C7H8N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 180.17 |
| AlogP | -1.04 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 5.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 72.68 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 2.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 13.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Adenosine receptor antagonist | ANTAGONIST | PubMed PubMed PubMed PubMed Wikipedia |
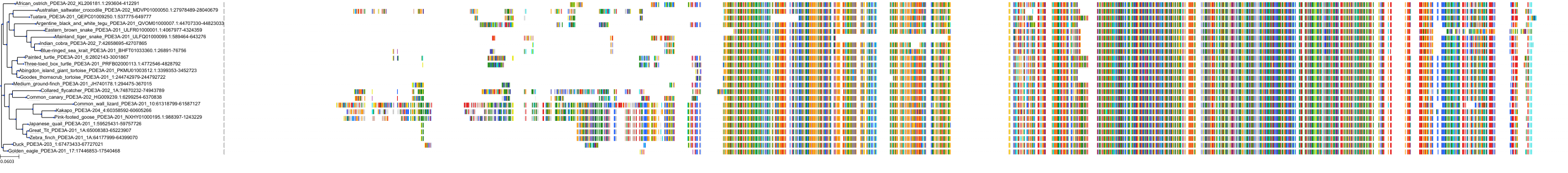
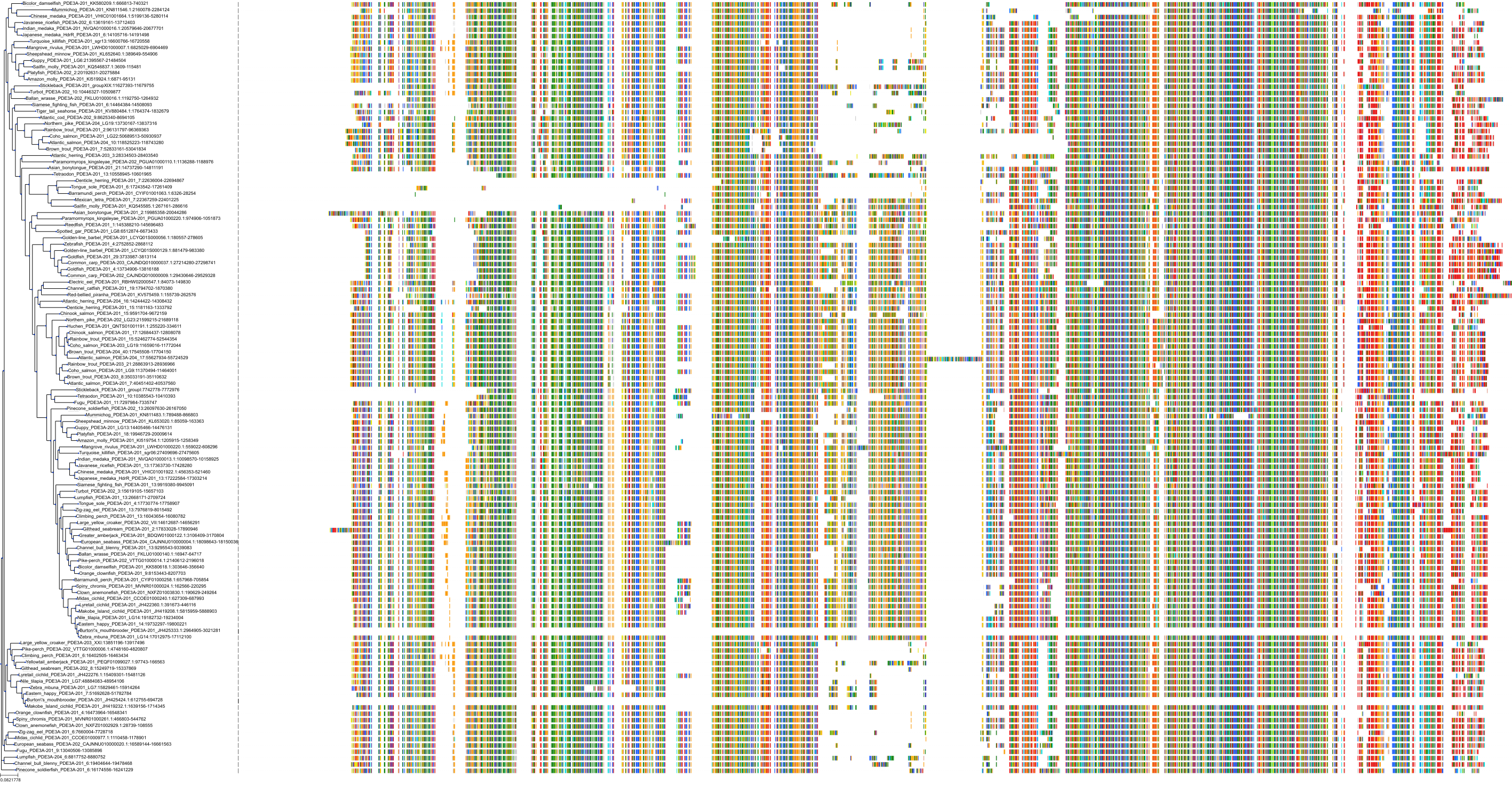
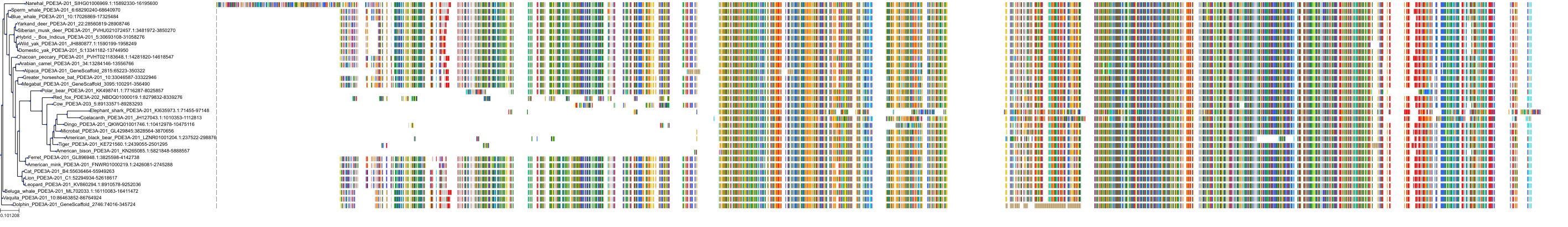
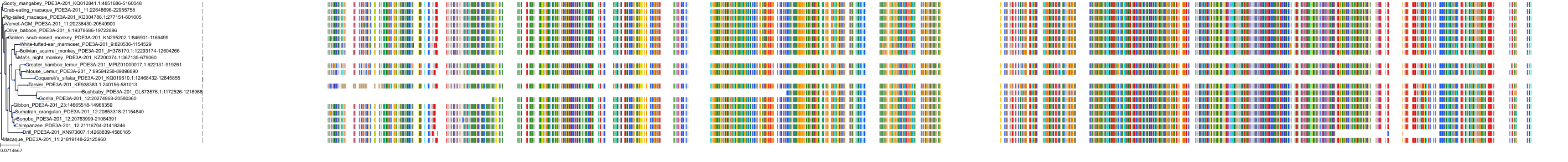
Target Conservation
|
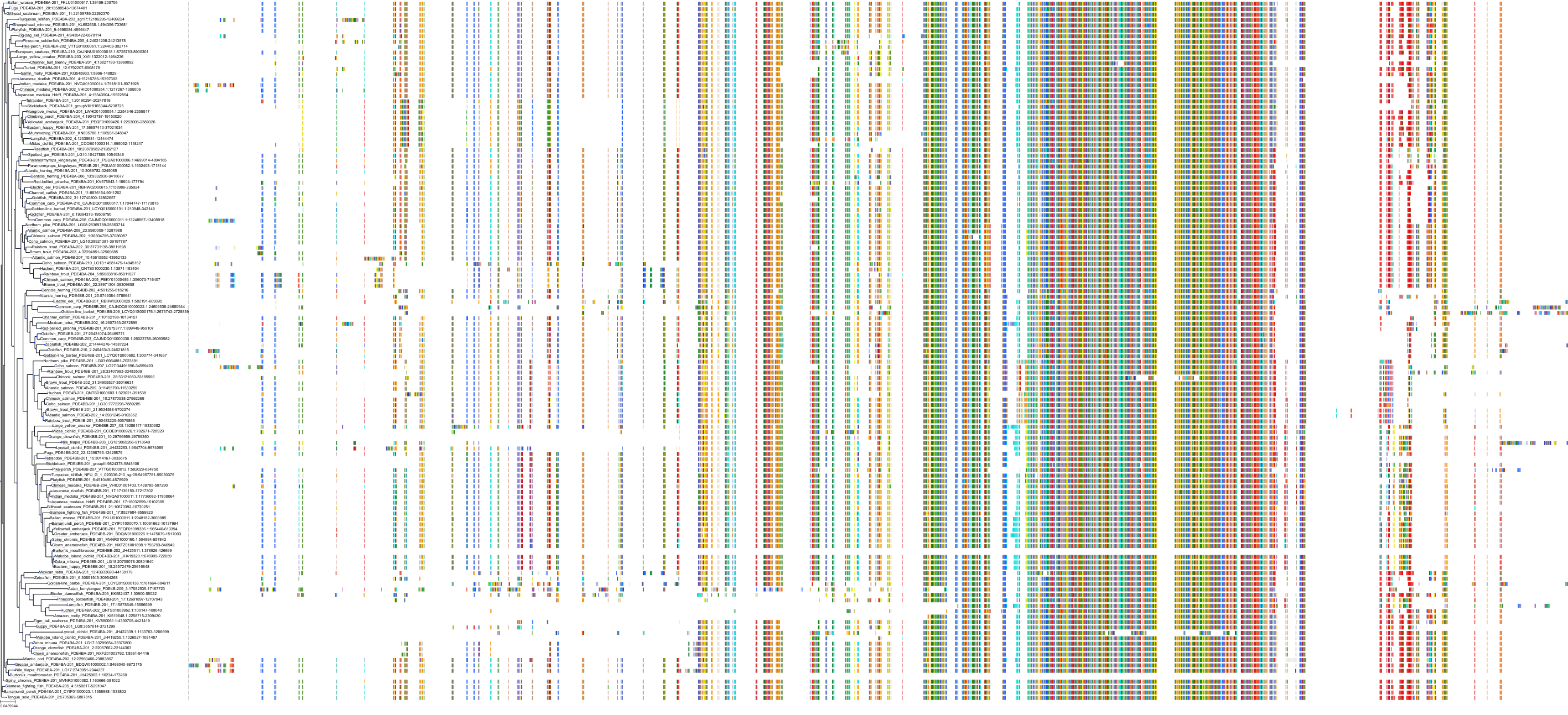
Protein: Phosphodiesterase 4 Description: cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4A Organism : Homo sapiens P27815 ENSG00000065989 |
||||
|
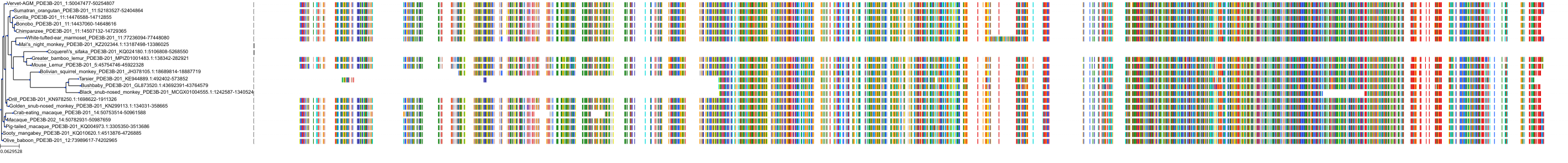
Protein: Phosphodiesterase 4 Description: cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4B Organism : Homo sapiens Q07343 ENSG00000184588 |
||||
|
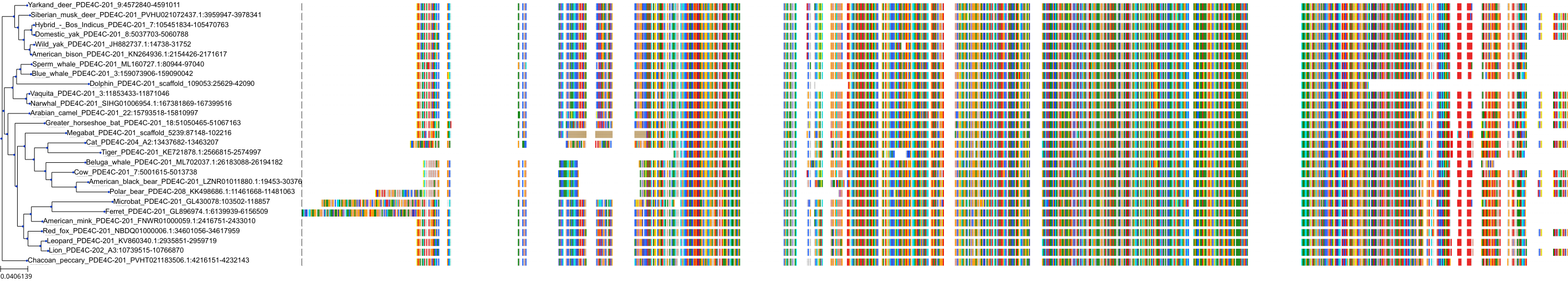
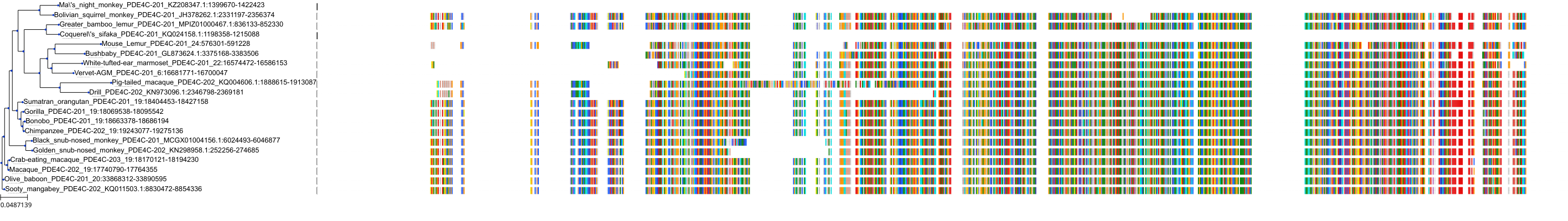
Protein: Phosphodiesterase 4 Description: cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4C Organism : Homo sapiens Q08493 ENSG00000105650 |
||||
|
Protein: Phosphodiesterase 4 Description: cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4D Organism : Homo sapiens Q08499 ENSG00000113448 |
||||
|
Protein: Phosphodiesterase 3 Description: cGMP-inhibited 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 3B Organism : Homo sapiens Q13370 ENSG00000152270 |
||||
|
Protein: Phosphodiesterase 3 Description: cGMP-inhibited 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 3A Organism : Homo sapiens Q14432 ENSG00000172572 |
||||
Related Entries
Environmental Exposure
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 28177 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL190 |
| DrugBank | DB00277 |
| DrugCentral | 2620 |
| FDA SRS | 0I55128JYK |
| Human Metabolome Database | HMDB0001889 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 413 |
| KEGG | C07130 |
| PDB | TEP |
| PharmGKB | PA451647 |
| PubChem | 91268 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL4915 |
| ZINC | ZINC000018043251 |
 Bos taurus
Bos taurus
 Canis lupus familiaris
Canis lupus familiaris
 Cavia porcellus
Cavia porcellus
 Cricetulus griseus
Cricetulus griseus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus
 Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus pyogenes
 Sus scrofa
Sus scrofa