| Trade Names | |
| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | C09CA07 |
| UNII | U5SYW473RQ |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID8023636 |
Structure
| InChI Key | RMMXLENWKUUMAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C33H30N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 514.63 |
| AlogP | 7.26 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 5.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 7.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 72.94 |
| Molecular species | ACID |
| Aromatic Rings | 6.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 39.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Type-1 angiotensin II receptor antagonist | ANTAGONIST | PubMed PubMed DailyMed Wikipedia |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Protease
Metallo protease
Metallo protease MAE clan
Metallo protease M2 family
|
- | - | - | - | 97 | |
|
Enzyme
|
- | 420-540 | - | 100-190 | 97 | |
|
Membrane receptor
Family A G protein-coupled receptor
Peptide receptor (family A GPCR)
Short peptide receptor (family A GPCR)
Angiotensin receptor
|
- | 0.33-150 | - | 0.23-0.23 | - | |
|
Transcription factor
Nuclear receptor
Nuclear hormone receptor subfamily 1
Nuclear hormone receptor subfamily 1 group C
Nuclear hormone receptor subfamily 1 group C member 3
|
700 | - | - | - | 61.3-91 | |
|
Transporter
Electrochemical transporter
SLC superfamily of solute carriers
SLC21/SLCO family of organic anion transporting polypeptides
|
- | - | - | 960 | 41.88-109.4 | |
|
Transporter
Electrochemical transporter
SLC superfamily of solute carriers
SLC47 family of multidrug and toxin extrusion transporters
|
- | - | - | - | 38 |
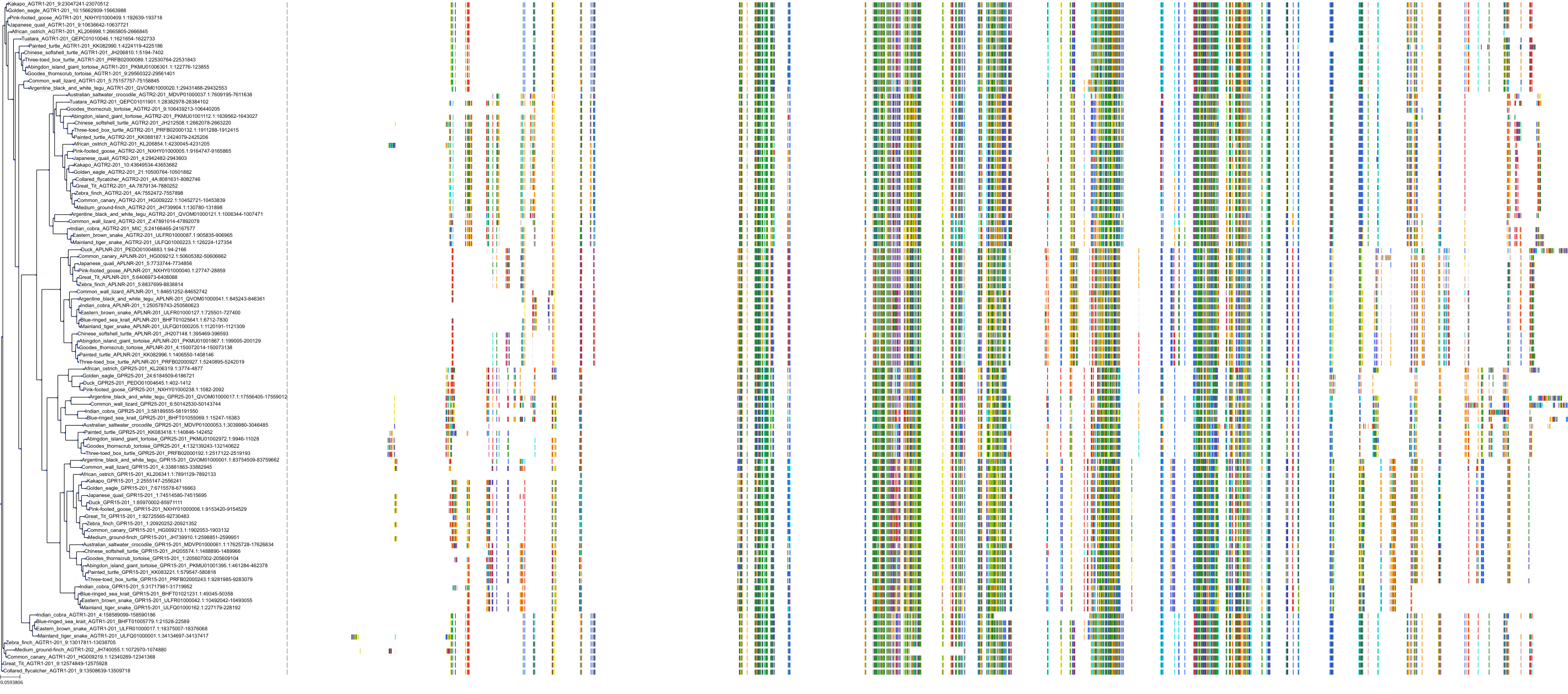
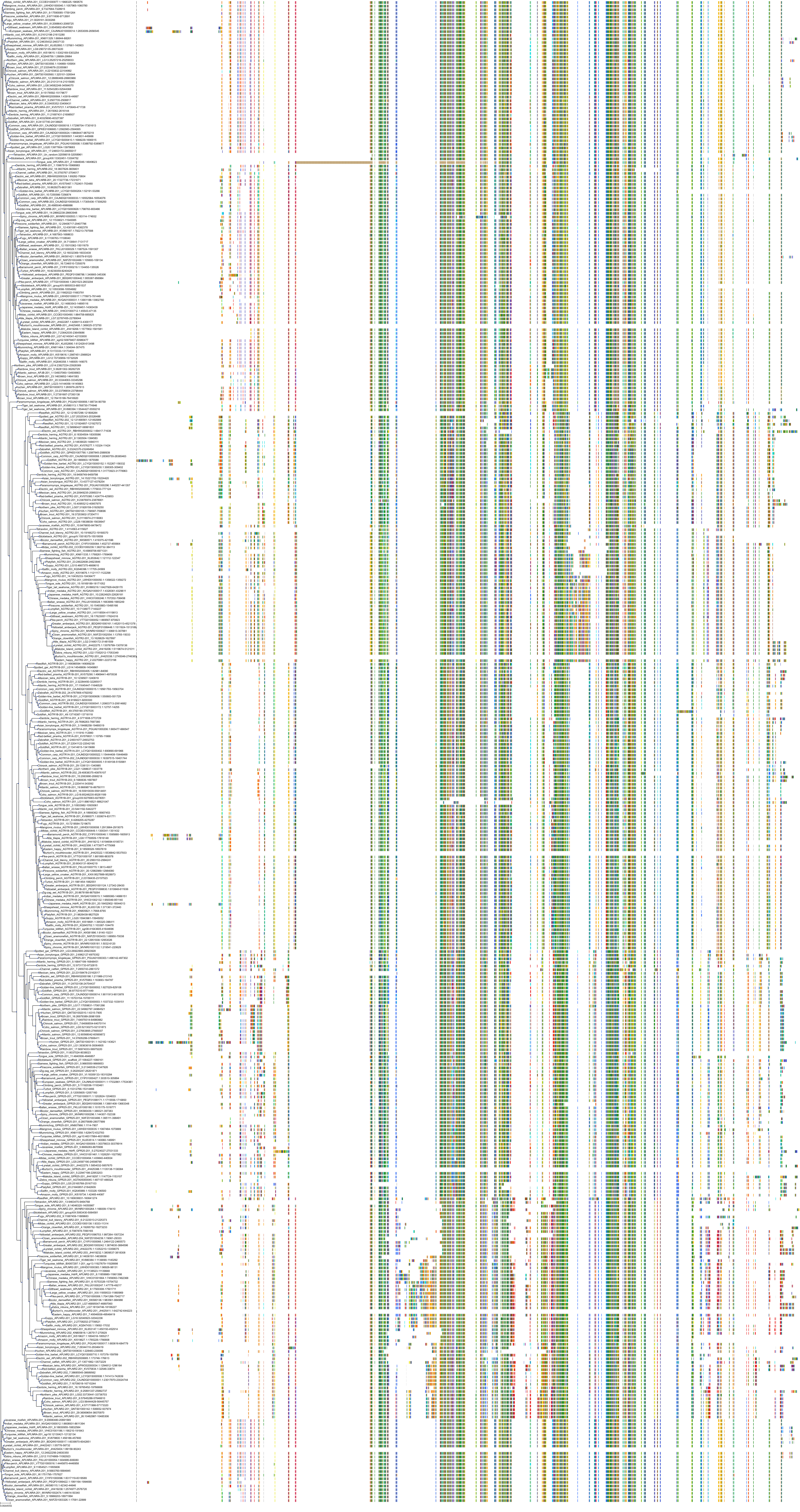
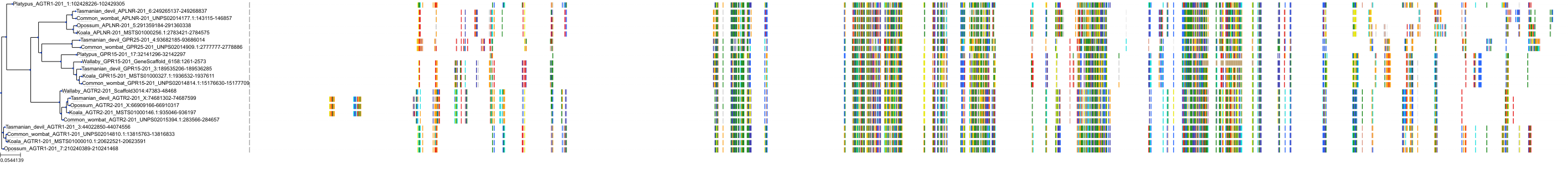
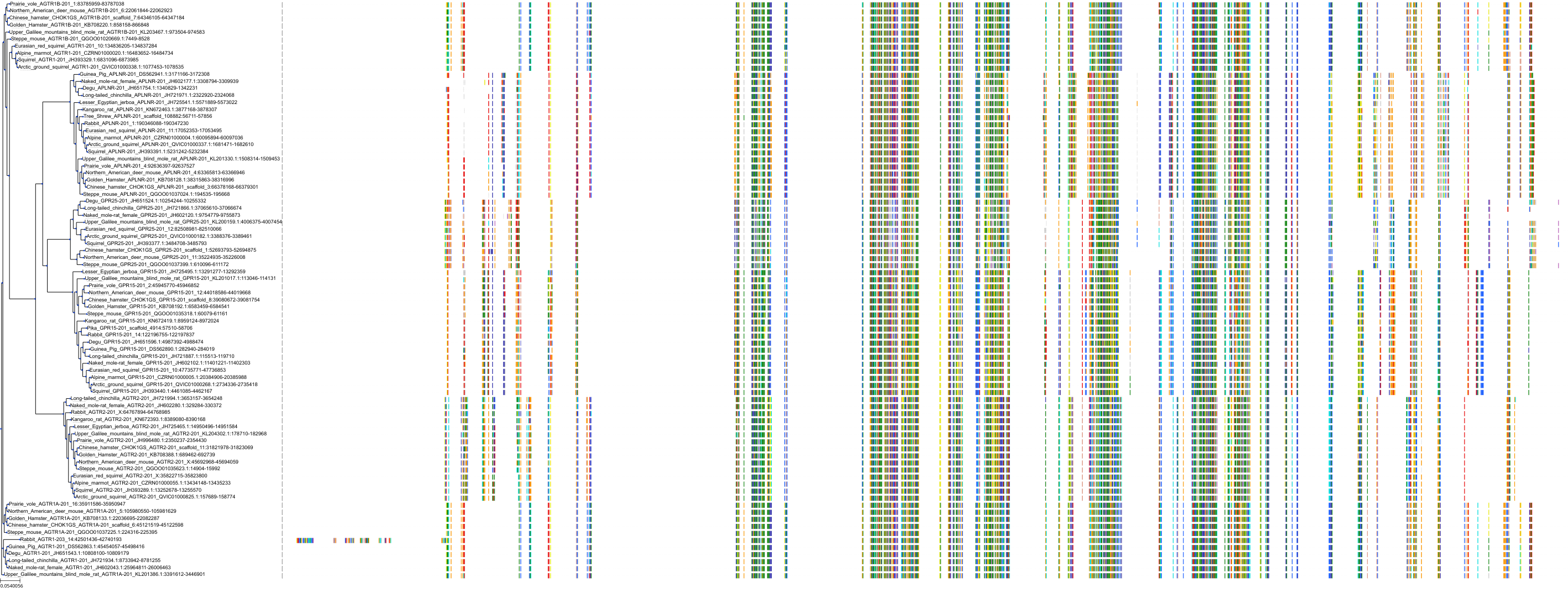
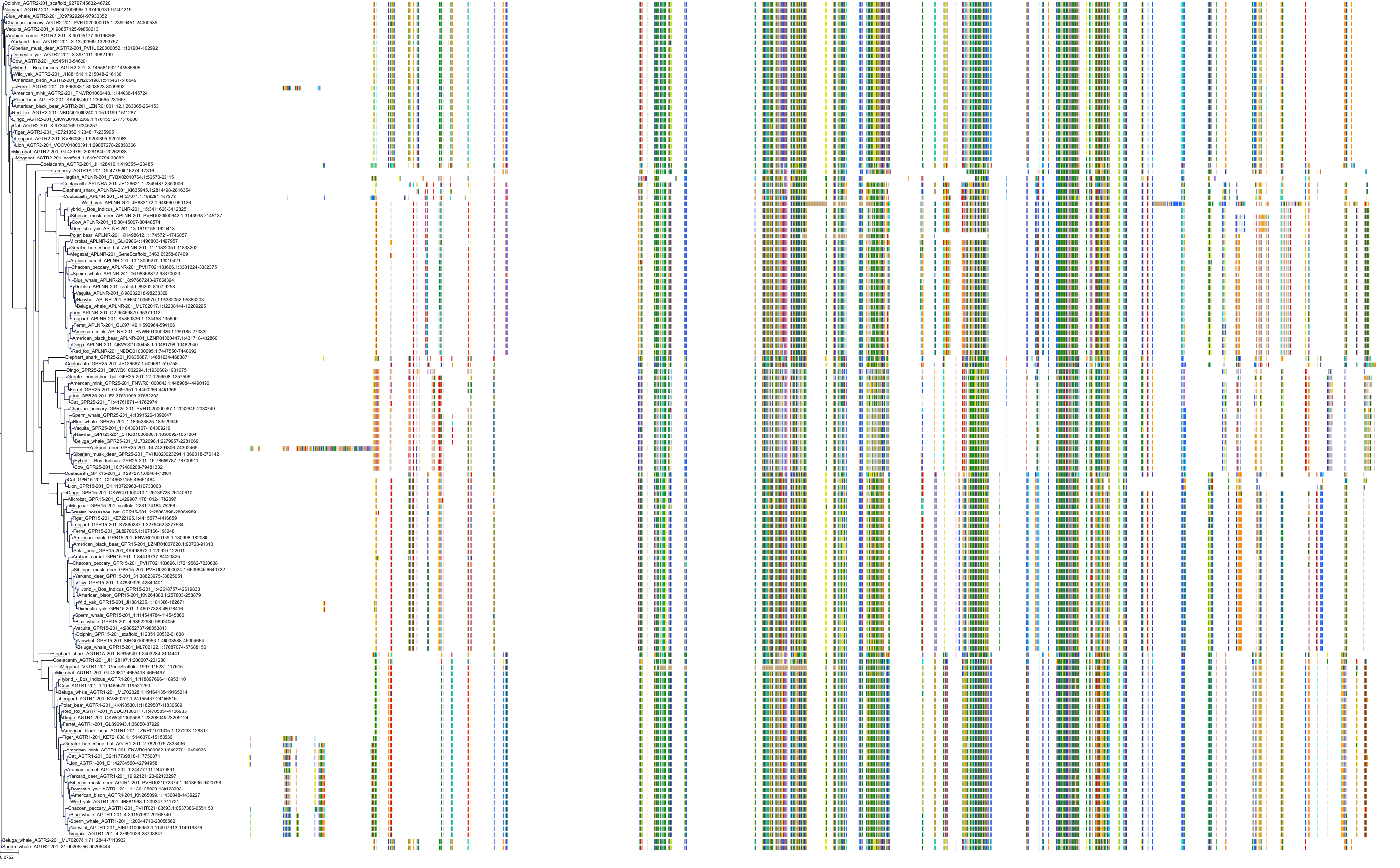
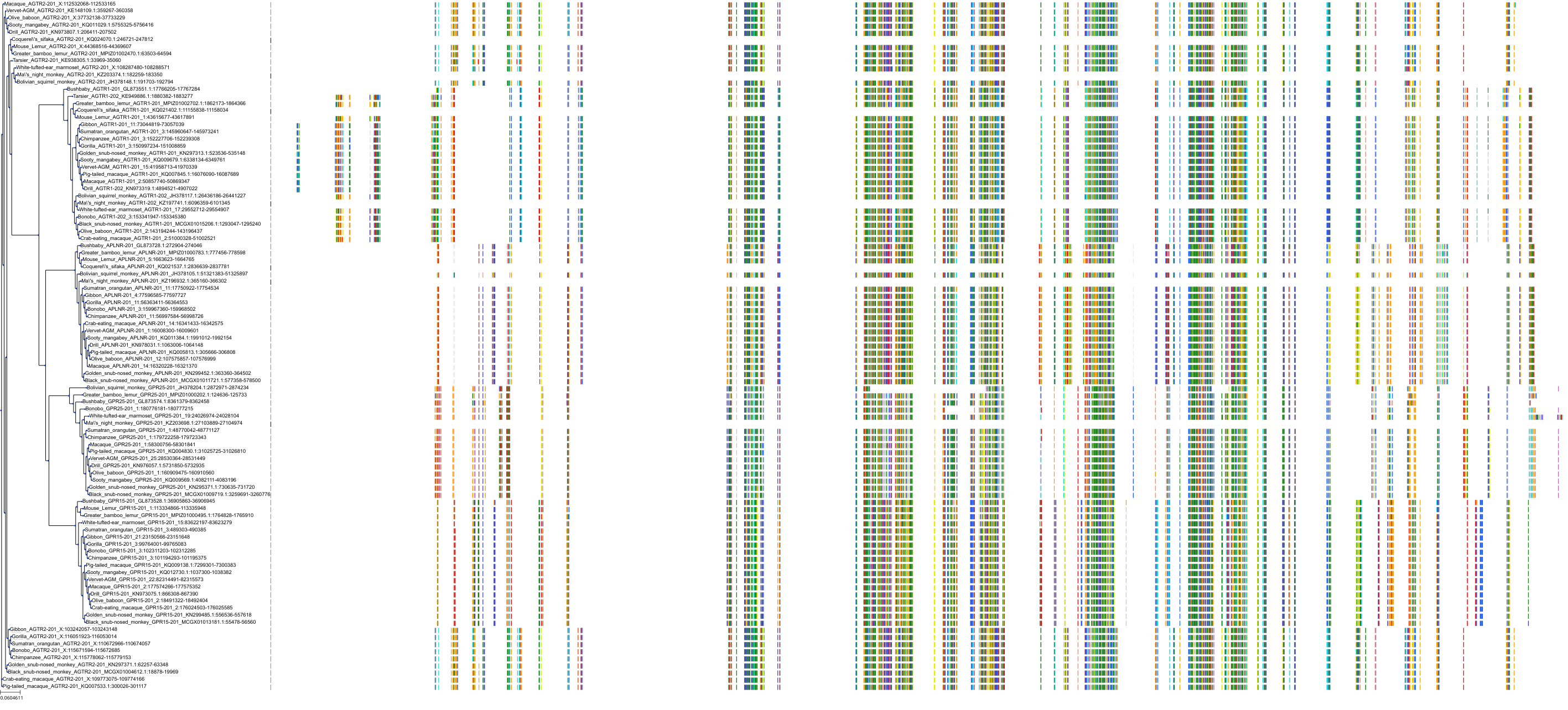
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Type-1 angiotensin II receptor Description: Type-1 angiotensin II receptor Organism : Homo sapiens P30556 ENSG00000144891 |
||||
Environmental Exposure
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 9434 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1017 |
| DrugBank | DB00966 |
| DrugCentral | 2583 |
| FDA SRS | U5SYW473RQ |
| Human Metabolome Database | HMDB0015101 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 592 |
| KEGG | C07710 |
| PDB | TLS |
| PharmGKB | PA451605 |
| PubChem | 65999 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL4464 |
| ZINC | ZINC000001530886 |
 Cricetulus griseus
Cricetulus griseus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus