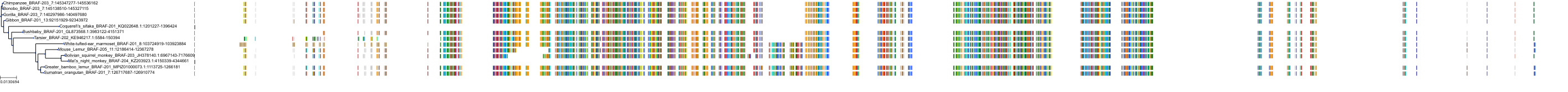| Trade Names | |
| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | L01EX05 |
| UNII | 24T2A1DOYB |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID60226441 |
Structure
| InChI Key | FNHKPVJBJVTLMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H15ClF4N4O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 482.82 |
| AlogP | 5.69 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 4.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 3.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 5.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 92.35 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 3.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 33.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Discoidin domain-containing receptor 2 inhibitor | INHIBITOR | Expert |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase FGFR family
|
- | 1.5 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase PDGFR family
|
- | 1.5-239.1 | - | - | 0-88 | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase Tie family
|
- | 1.5 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase VEGFR family
|
- | 1.5-13 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TKL protein kinase group
TKL protein kinase RAF family
|
- | 1.5-40 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Protease
Serine protease
Serine protease SC clan
Serine protease S33 family
|
- | 0.5 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Transferase
|
- | - | - | - | 89-96 |
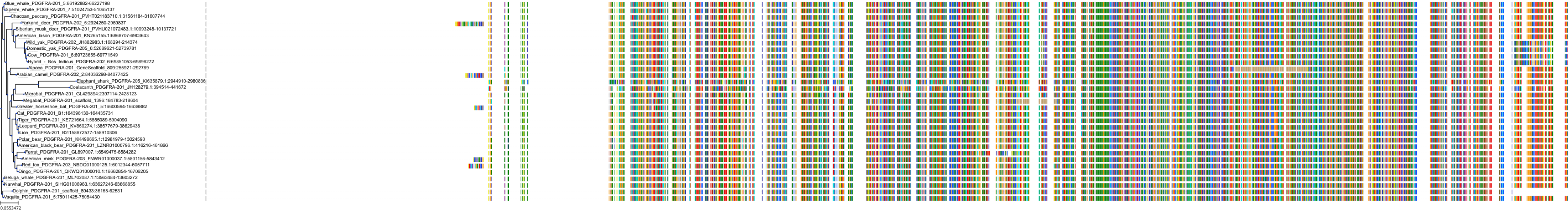
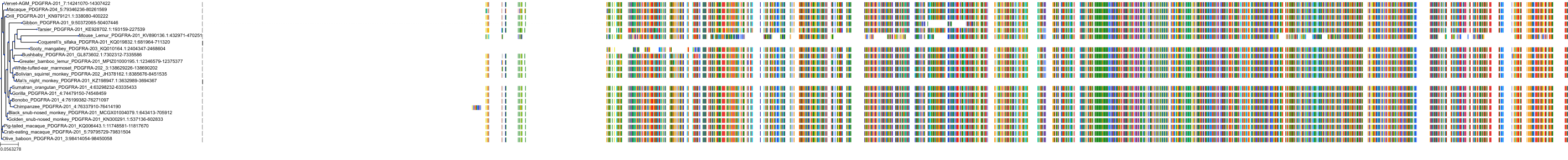
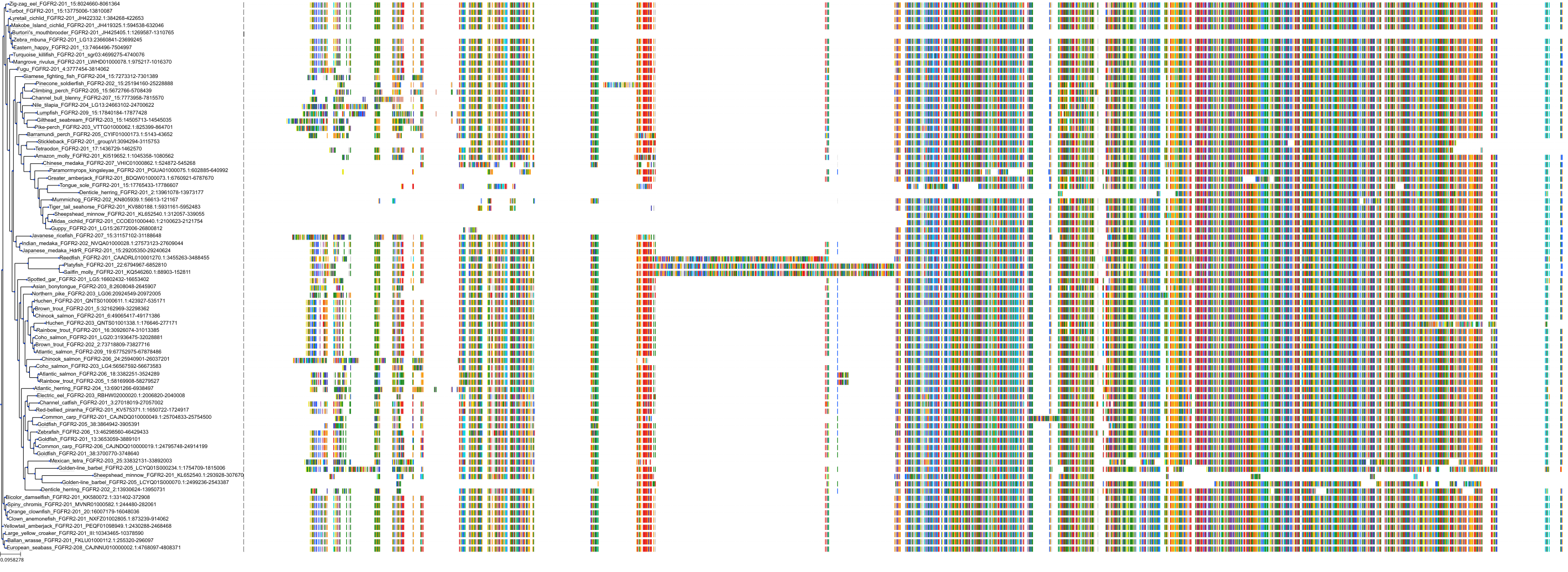
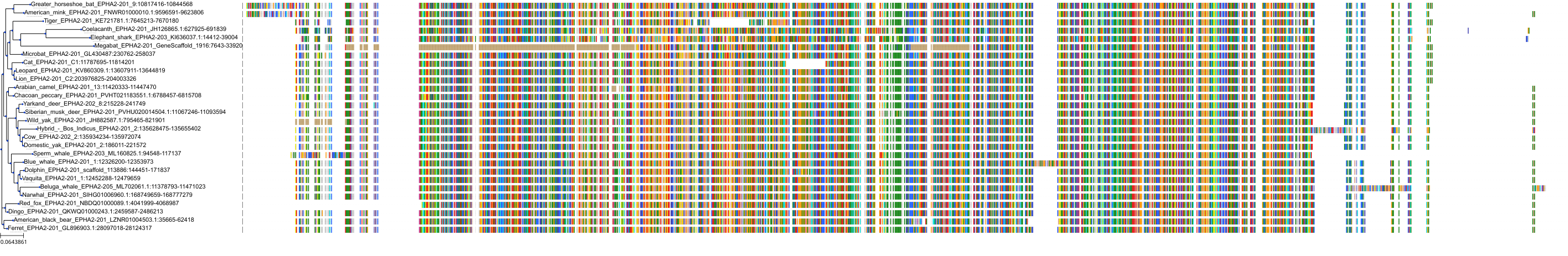
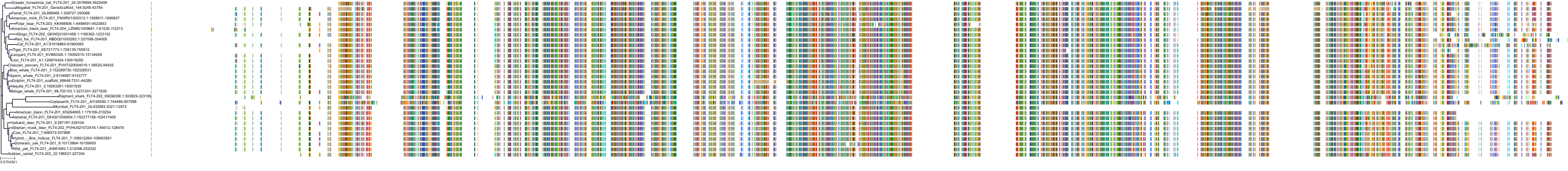
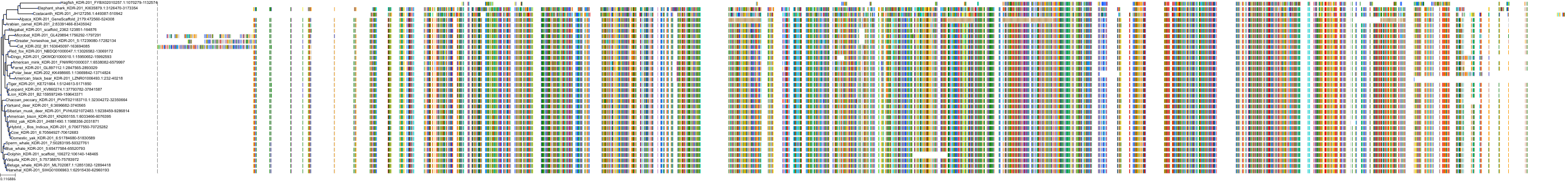
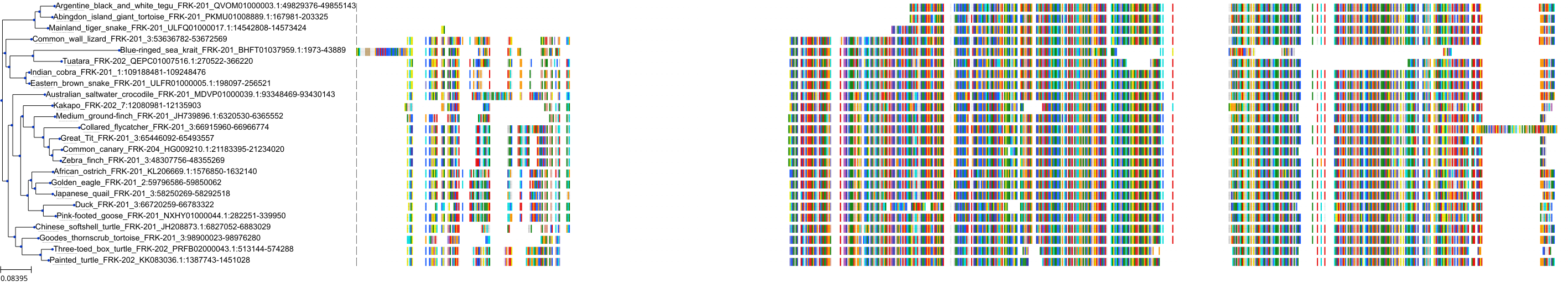
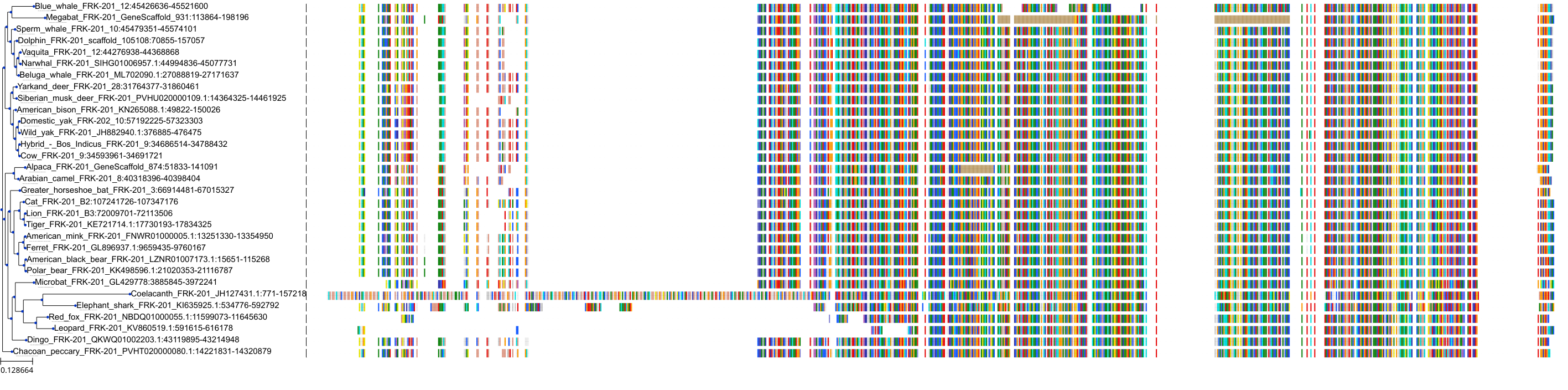
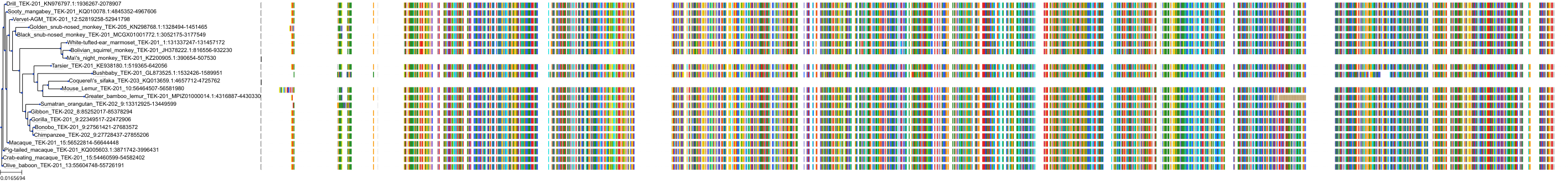
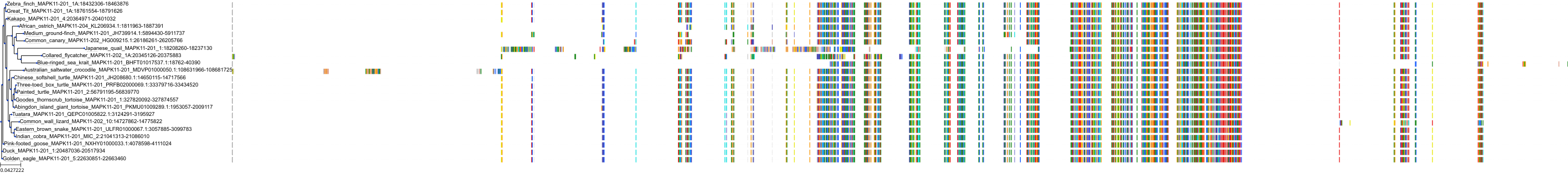
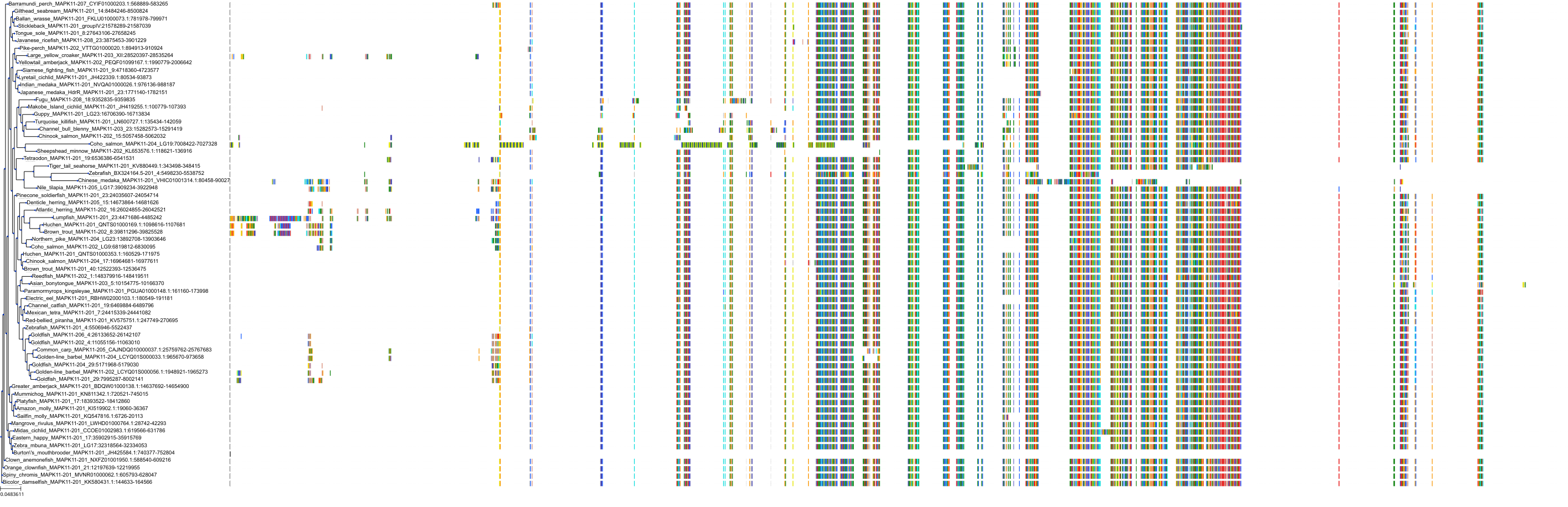
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL Description: Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 Organism : Homo sapiens P00519 ENSG00000097007 |
||||
|
Protein: Serine/threonine-protein kinase RAF Description: RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase Organism : Homo sapiens P04049 ENSG00000132155 |
||||
|
Protein: Nerve growth factor receptor Trk-A Description: High affinity nerve growth factor receptor Organism : Homo sapiens P04629 ENSG00000198400 |
||||
|
Protein: Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor RET Description: Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret Organism : Homo sapiens P07949 ENSG00000165731 |
||||
|
Protein: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor Description: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta Organism : Homo sapiens P09619 ENSG00000113721 |
||||
|
Protein: Stem cell growth factor receptor Description: Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit Organism : Homo sapiens P10721 ENSG00000157404 |
||||
|
Protein: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 Description: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 Organism : Homo sapiens P11362 ENSG00000077782 |
||||
|
Protein: Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf Description: Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf Organism : Homo sapiens P15056 ENSG00000157764 |
||||
|
Protein: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor Description: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha Organism : Homo sapiens P16234 ENSG00000134853 |
||||
|
Protein: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Description: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 Organism : Homo sapiens P17948 ENSG00000102755 |
||||
|
Protein: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 Description: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 Organism : Homo sapiens P21802 ENSG00000066468 |
||||
|
Protein: Ephrin type-A receptor 2 Description: Ephrin type-A receptor 2 Organism : Homo sapiens P29317 ENSG00000142627 |
||||
|
Protein: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Description: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 Organism : Homo sapiens P35916 ENSG00000037280 |
||||
|
Protein: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Description: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 Organism : Homo sapiens P35968 ENSG00000128052 |
||||
|
Protein: Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK Description: Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK Organism : Homo sapiens P42685 ENSG00000111816 |
||||
|
Protein: Tyrosine-protein kinase TIE-2 Description: Angiopoietin-1 receptor Organism : Homo sapiens Q02763 ENSG00000120156 |
||||
|
Protein: MAP kinase p38 beta Description: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 11 Organism : Homo sapiens Q15759 ENSG00000185386 |
||||
|
Protein: Discoidin domain-containing receptor 2 Description: Discoidin domain-containing receptor 2 Organism : Homo sapiens Q16832 ENSG00000162733 |
||||
Related Entries
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 68647 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1946170 |
| DrugBank | DB08896 |
| DrugCentral | 4654 |
| FDA SRS | 24T2A1DOYB |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 5891 |
| KEGG | D10138 |
| PubChem | 11167602 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL432230 |
| ZINC | ZINC000006745272 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus