| Trade Names | |
| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | N05AG02 |
| UNII | 1HIZ4DL86F |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID8023474 |
Structure
| InChI Key | YVUQSNJEYSNKRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C28H29F2N3O |
| Molecular Weight | 461.56 |
| AlogP | 5.86 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 3.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 7.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 41.03 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 4.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 34.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Dopamine receptor antagonist | ANTAGONIST | ISBN DailyMed Wikipedia |
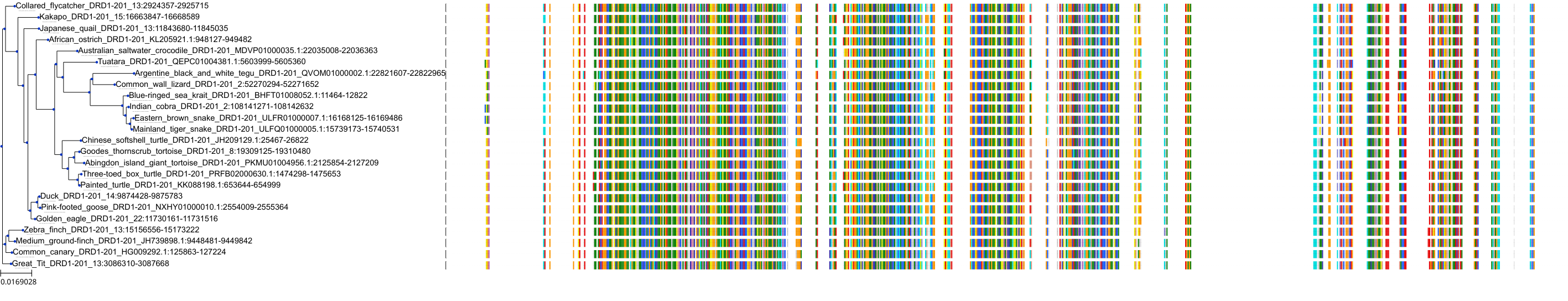
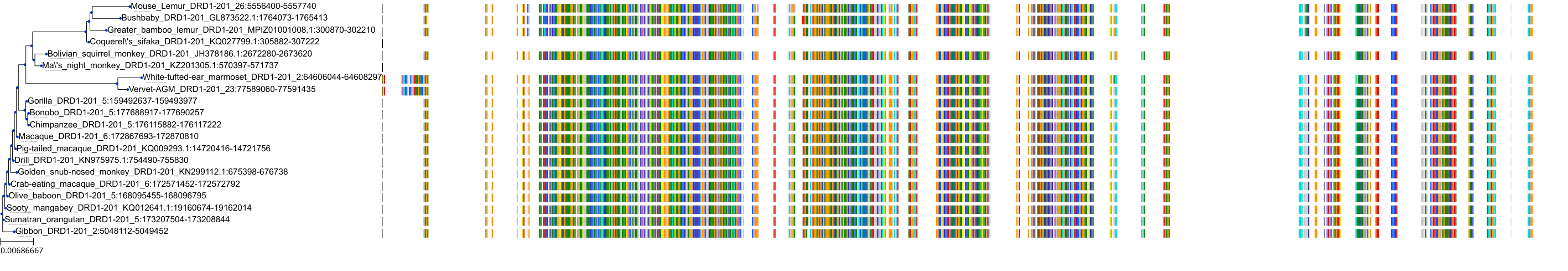
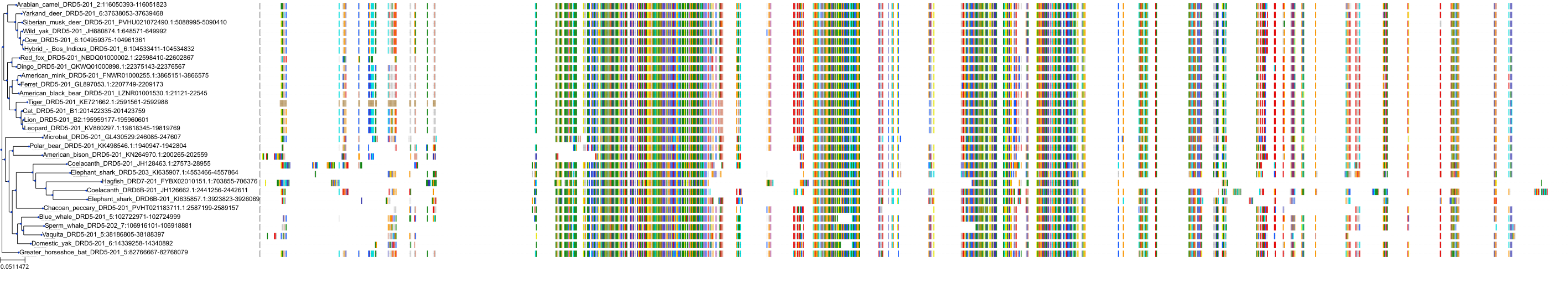
Target Conservation
|
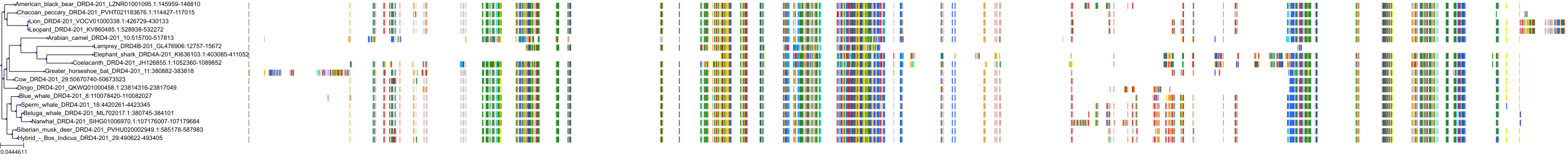
Protein: Dopamine receptor Description: D(2) dopamine receptor Organism : Homo sapiens P14416 ENSG00000149295 |
||||
|
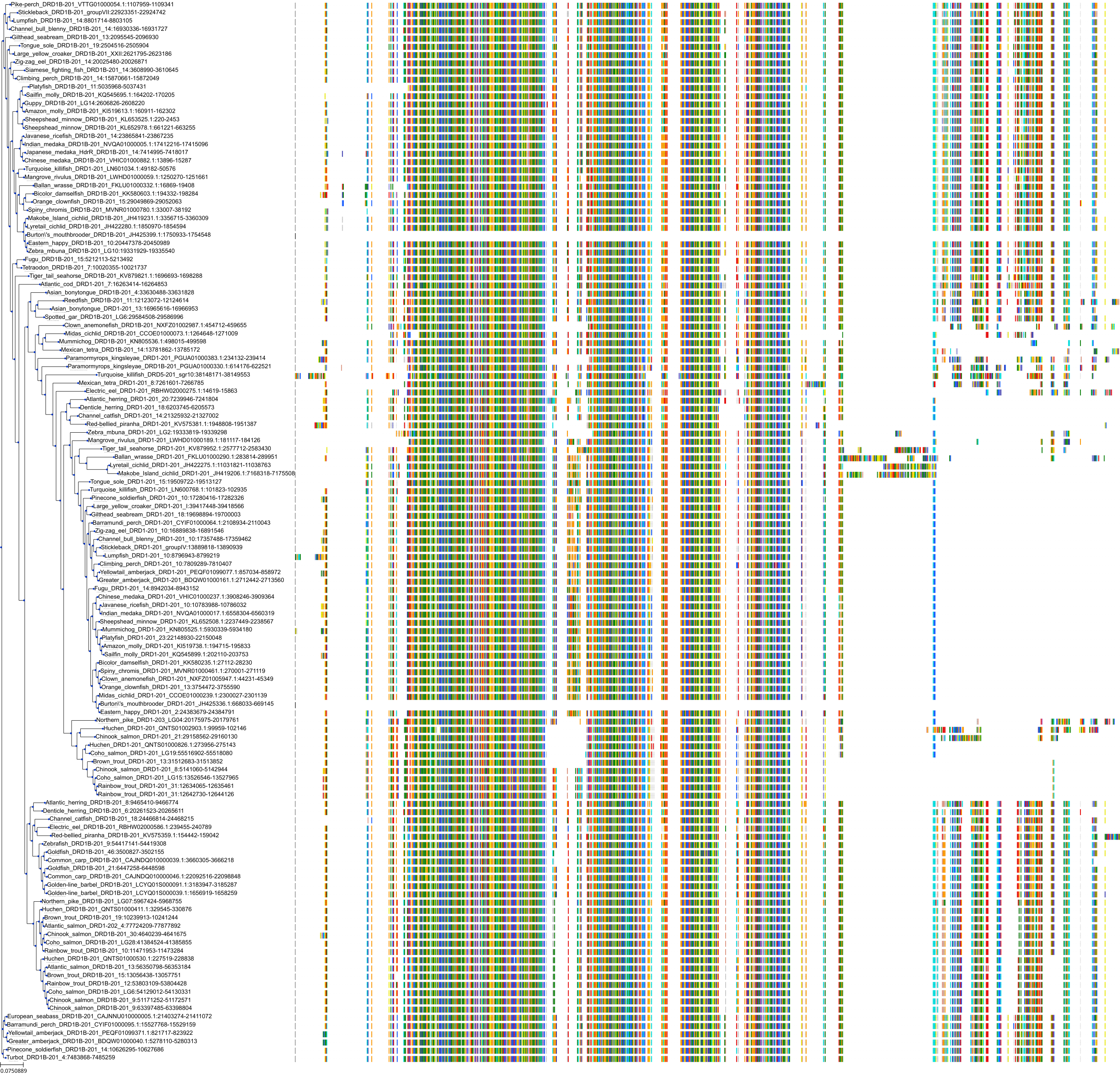
Protein: Dopamine receptor Description: D(1A) dopamine receptor Organism : Homo sapiens P21728 ENSG00000184845 |
||||
|
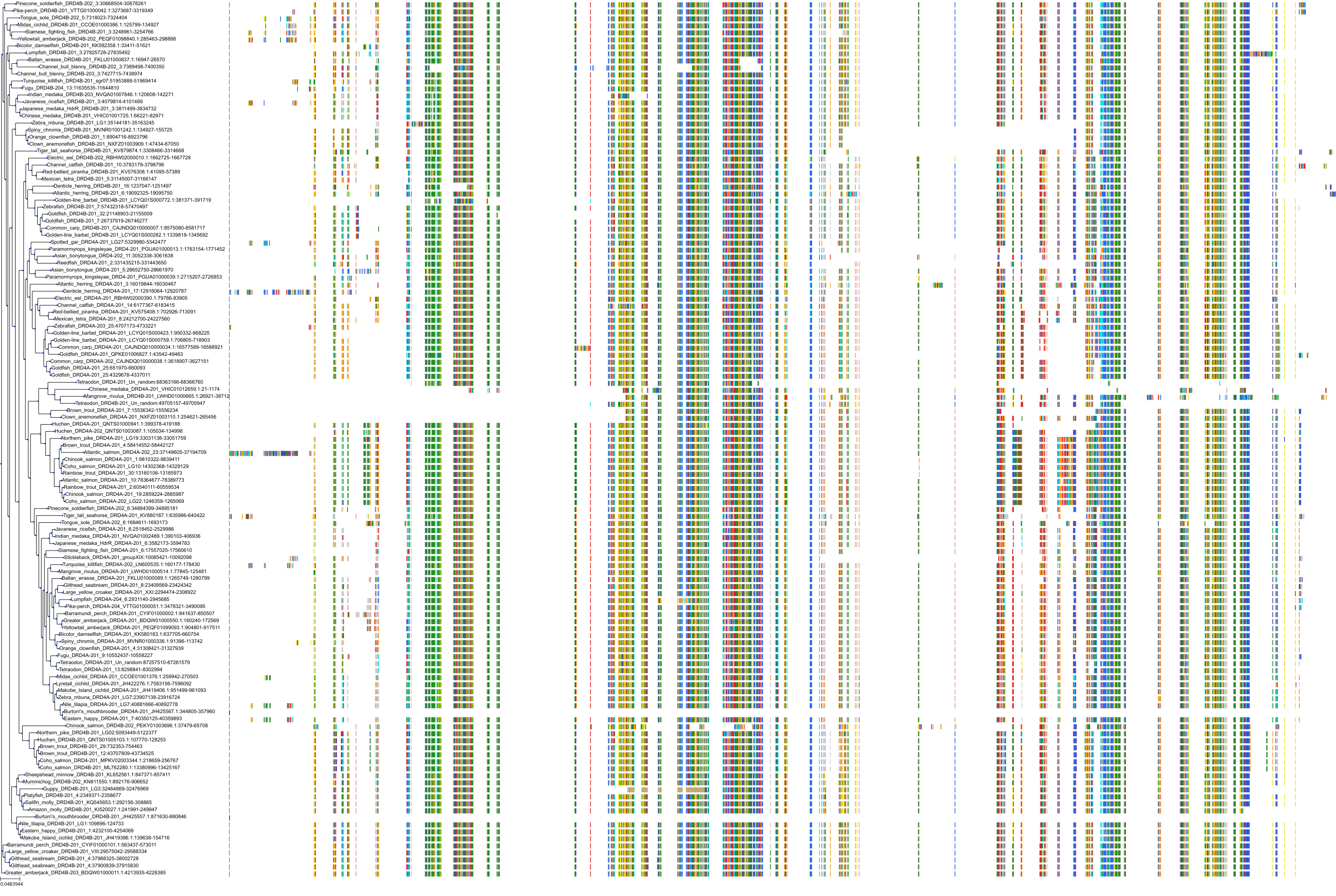
Protein: Dopamine receptor Description: D(4) dopamine receptor Organism : Homo sapiens P21917 ENSG00000069696 |
||||
|
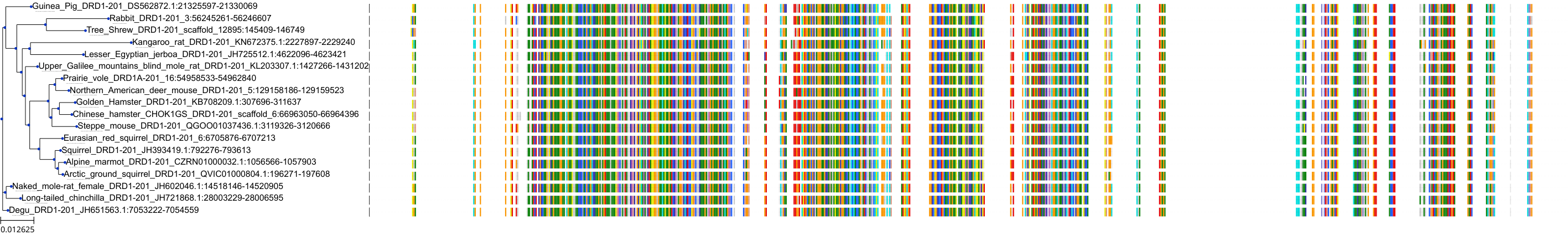
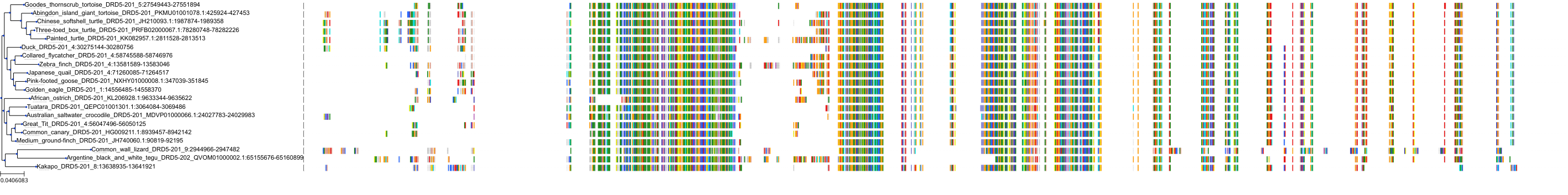
Protein: Dopamine receptor Description: D(1B) dopamine receptor Organism : Homo sapiens P21918 ENSG00000169676 |
||||
|
Protein: Serotonin 2a (5-HT2a) receptor Description: 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2A Organism : Homo sapiens P28223 ENSG00000102468 |
||||
|
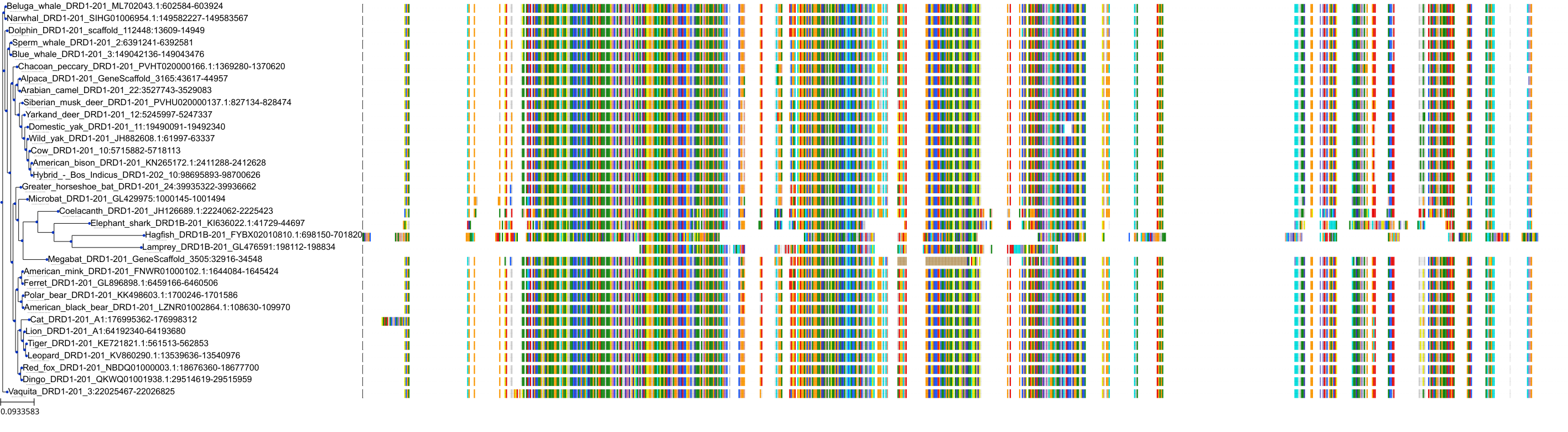
Protein: Dopamine receptor Description: D(3) dopamine receptor Organism : Homo sapiens P35462 ENSG00000151577 |
||||
Related Entries
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 8212 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1423 |
| DrugBank | DB01100 |
| DrugCentral | 2172 |
| FDA SRS | 1HIZ4DL86F |
| Human Metabolome Database | HMDB0015232 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 90 |
| KEGG | C07566 |
| PharmGKB | PA450965 |
| PubChem | 16362 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL41584 |
| ZINC | ZINC000004175630 |
 Bacillus subtilis
Bacillus subtilis
 Cricetulus griseus
Cricetulus griseus
 Escherichia coli K-12
Escherichia coli K-12
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Listeria monocytogenes
Listeria monocytogenes
 Listeria monocytogenes 10403S
Listeria monocytogenes 10403S
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus
 Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium
Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium