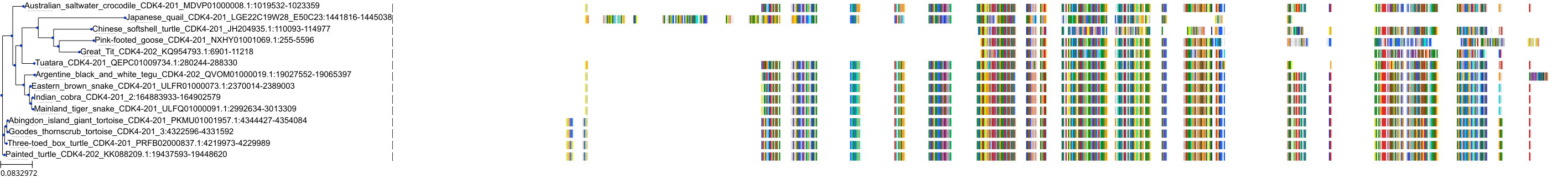| Trade Names | |
| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | L01EF01 |
| UNII | G9ZF61LE7G |
Structure
| InChI Key | AHJRHEGDXFFMBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H29N7O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 447.54 |
| AlogP | 2.97 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 9.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 2.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 5.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 105.04 |
| Molecular species | BASE |
| Aromatic Rings | 3.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 33.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| CDK6/cyclin D1 inhibitor | INHIBITOR | FDA |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
CMGC protein kinase group
CMGC protein kinase CDK family
CMGC protein kinase CDC2 subfamily
|
- | 230-230 | - | - | 5-42 | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
CMGC protein kinase group
CMGC protein kinase CDK family
CMGC protein kinase CDK9 subfamily
|
- | 794.33-892 | - | 364 | ||
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
CMGC protein kinase group
|
- | 2-100 | - | 3-27 | -97-104.7 | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase JakA family
|
- | 63.1 | - | - | - | |
|
Enzyme
Kinase
Protein Kinase
TK protein kinase group
Tyrosine protein kinase JakB family
|
- | 63.1 | - | - | - | |
|
Other cytosolic protein
|
- | 2-230 | - | 3-364 | -97-104.7 |
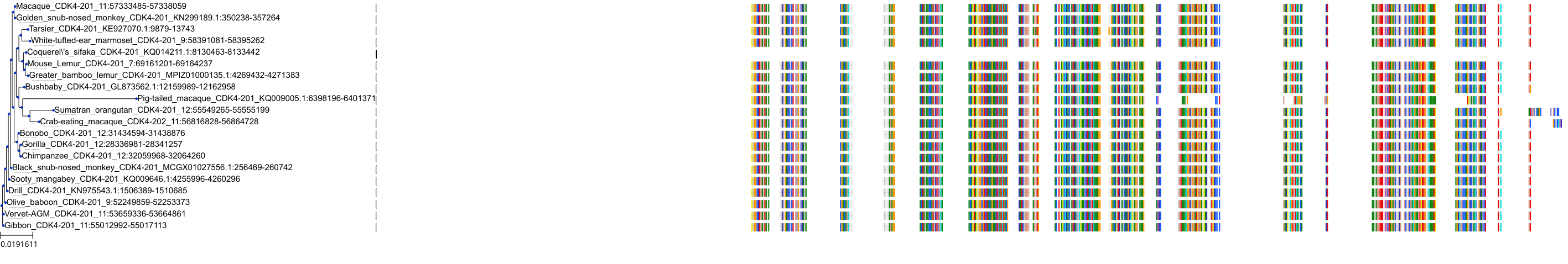
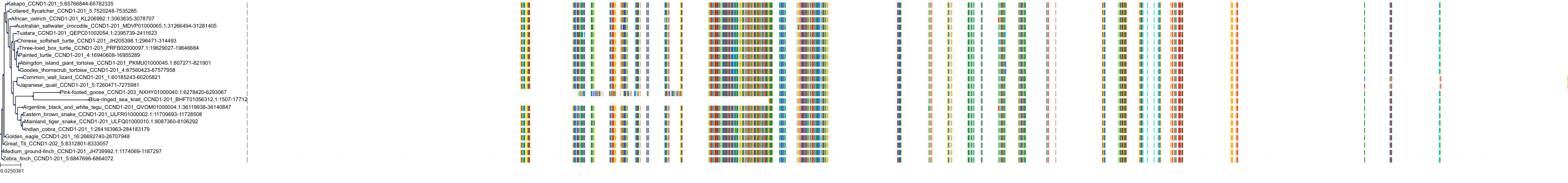
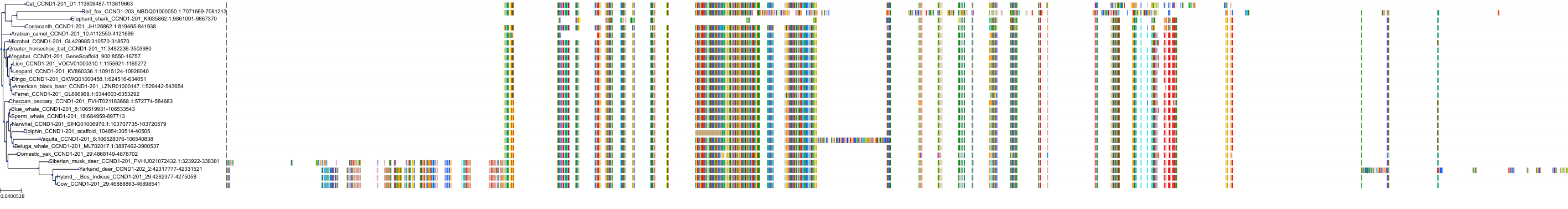
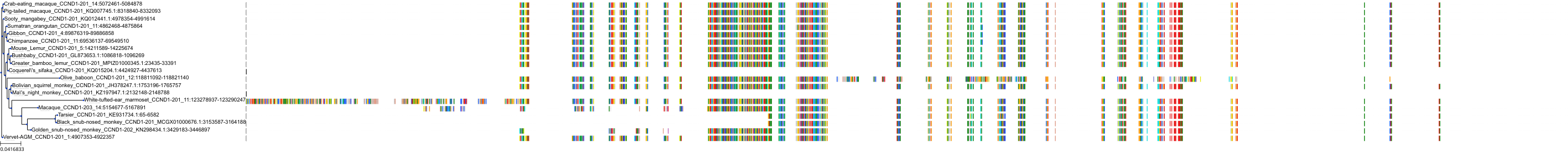
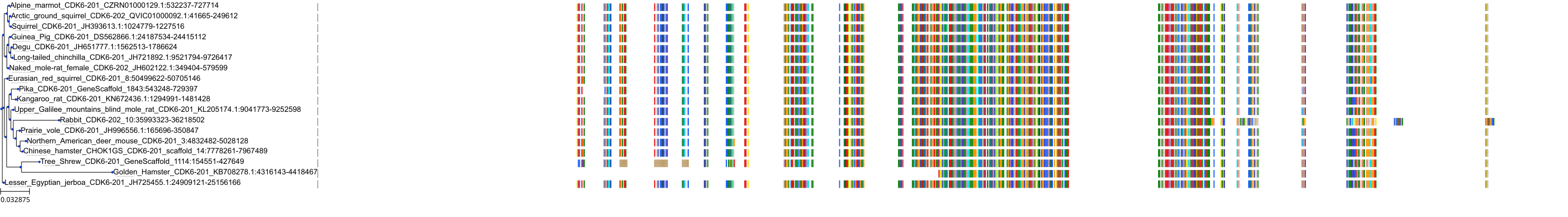
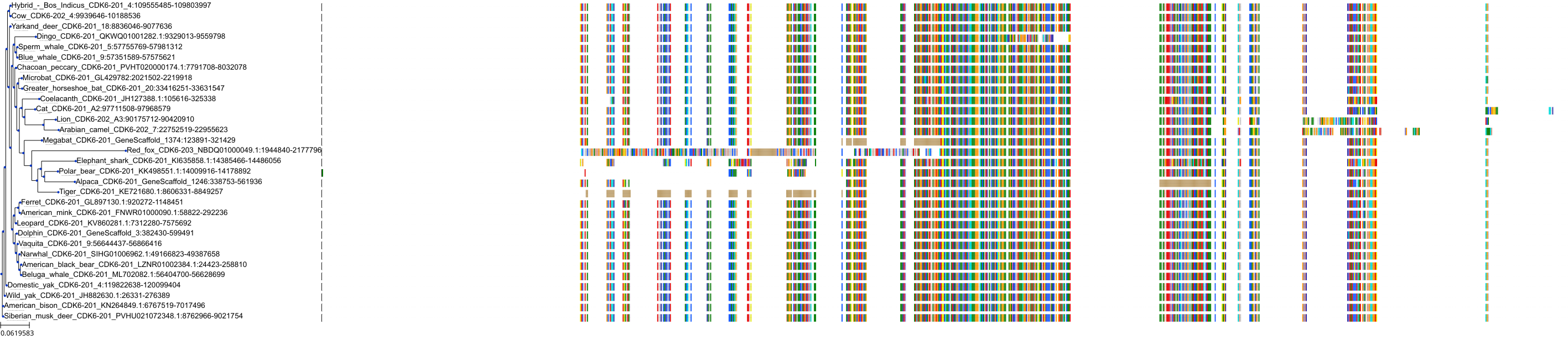
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/cyclin D1 Description: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 Organism : Homo sapiens P11802 ENSG00000135446 |
||||
|
Protein: CDK6/cyclin D1 Description: G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 Organism : Homo sapiens P24385 ENSG00000110092 |
||||
|
Protein: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/cyclin D1 Description: G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 Organism : Homo sapiens P24385 ENSG00000110092 |
||||
|
Protein: CDK6/cyclin D1 Description: Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 Organism : Homo sapiens Q00534 ENSG00000105810 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 85993 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL189963 |
| DrugBank | DB09073 |
| DrugCentral | 4941 |
| FDA SRS | G9ZF61LE7G |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 7380 |
| PDB | LQQ |
| PharmGKB | PA166153469 |
| PubChem | 5330286 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL462630 |
| ZINC | ZINC000003938686 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens