| Trade Names | |
| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | L01XK01 |
| UNII | WOH1JD9AR8 |
Structure
| InChI Key | FDLYAMZZIXQODN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H23FN4O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 434.47 |
| AlogP | 2.35 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 4.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 4.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 86.37 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 3.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 32.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| PARP 1, 2 and 3 inhibitor | INHIBITOR | FDA |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Transferase
|
0.4-60 | 0.3981-410 | 0.24-0.31 | 0.787 | 7-100 |
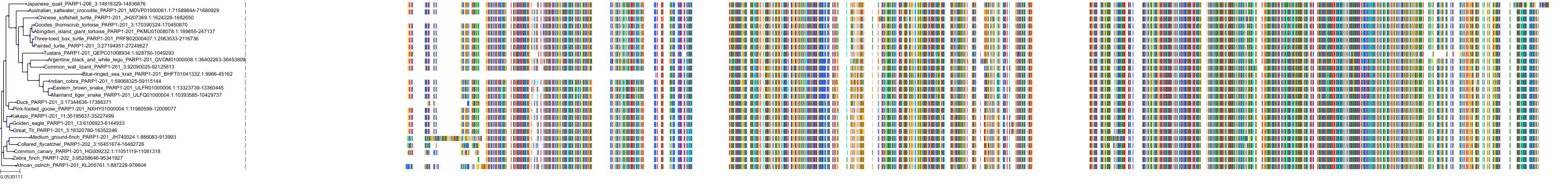
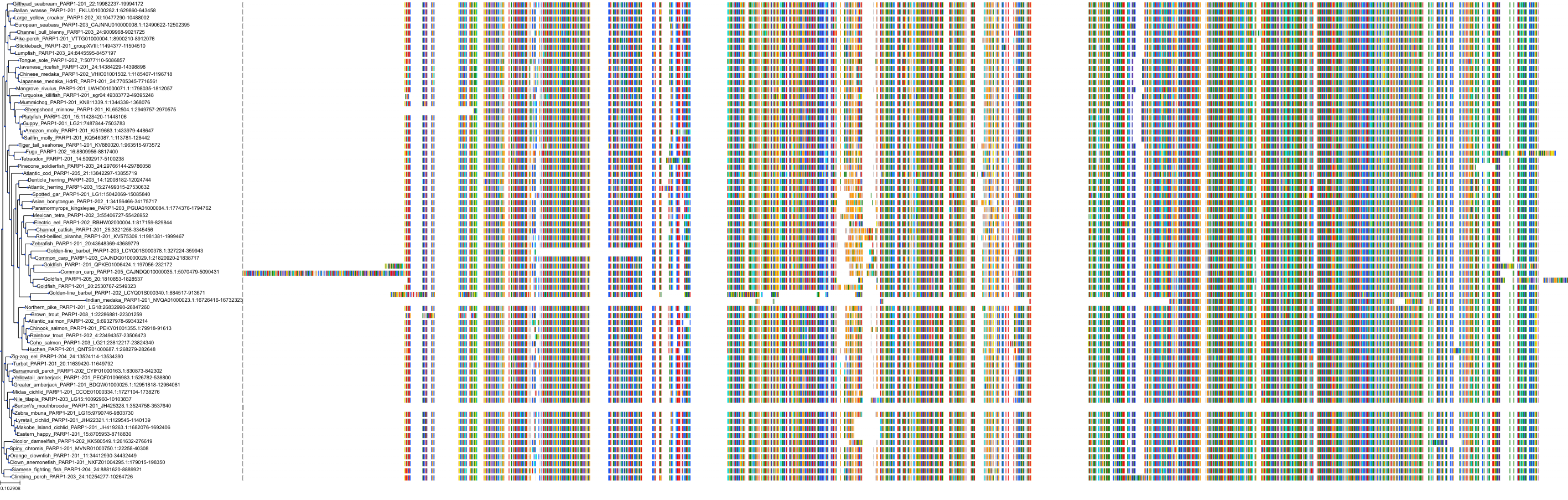
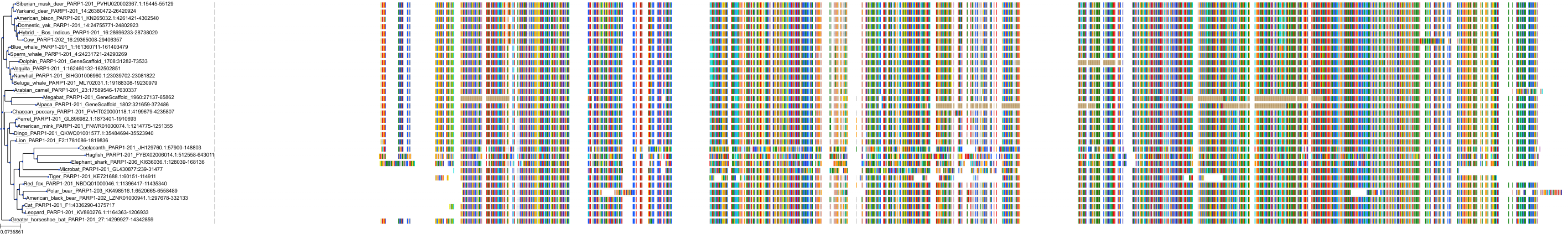
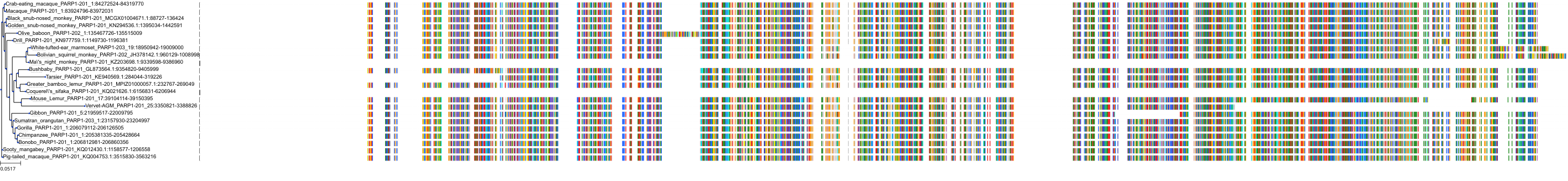
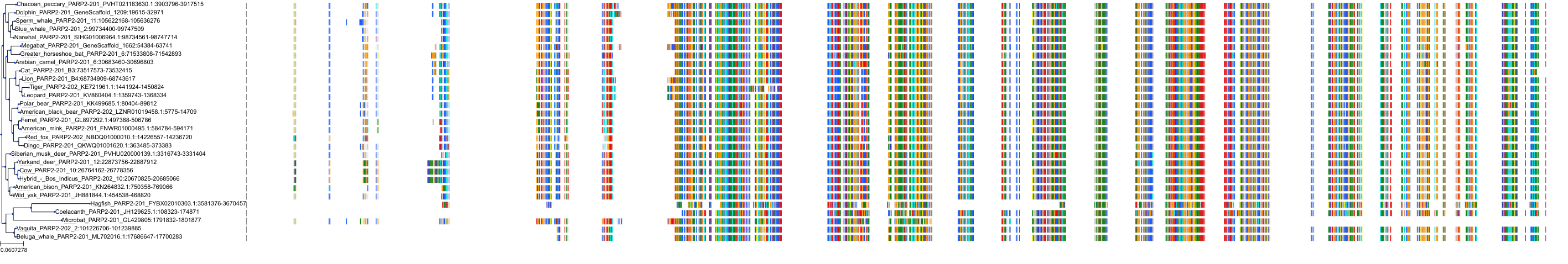
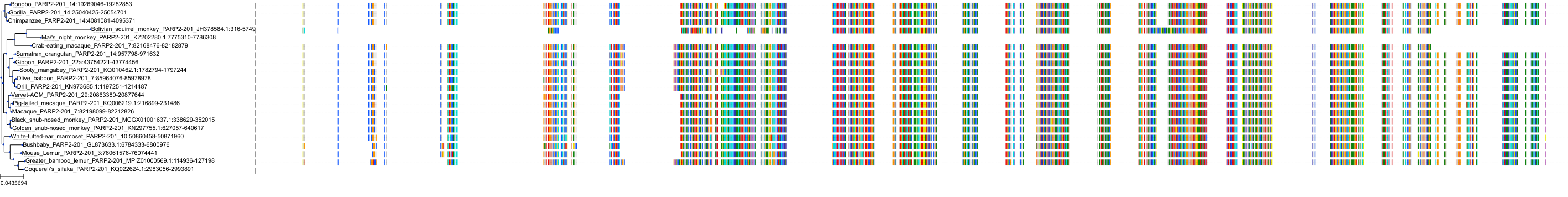
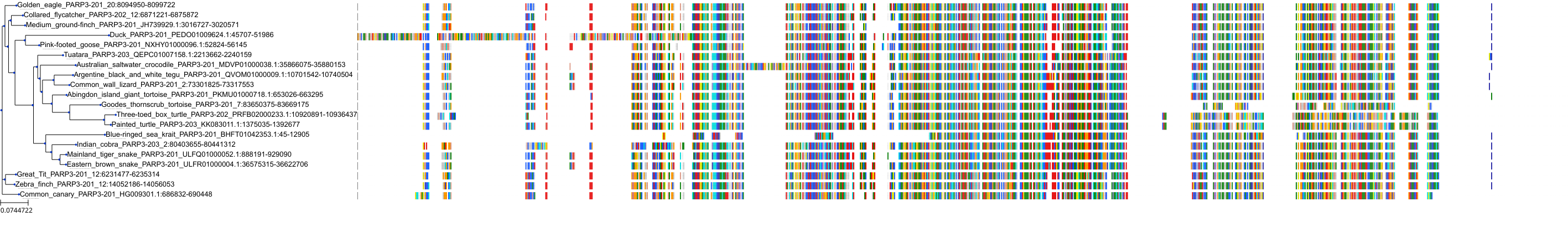
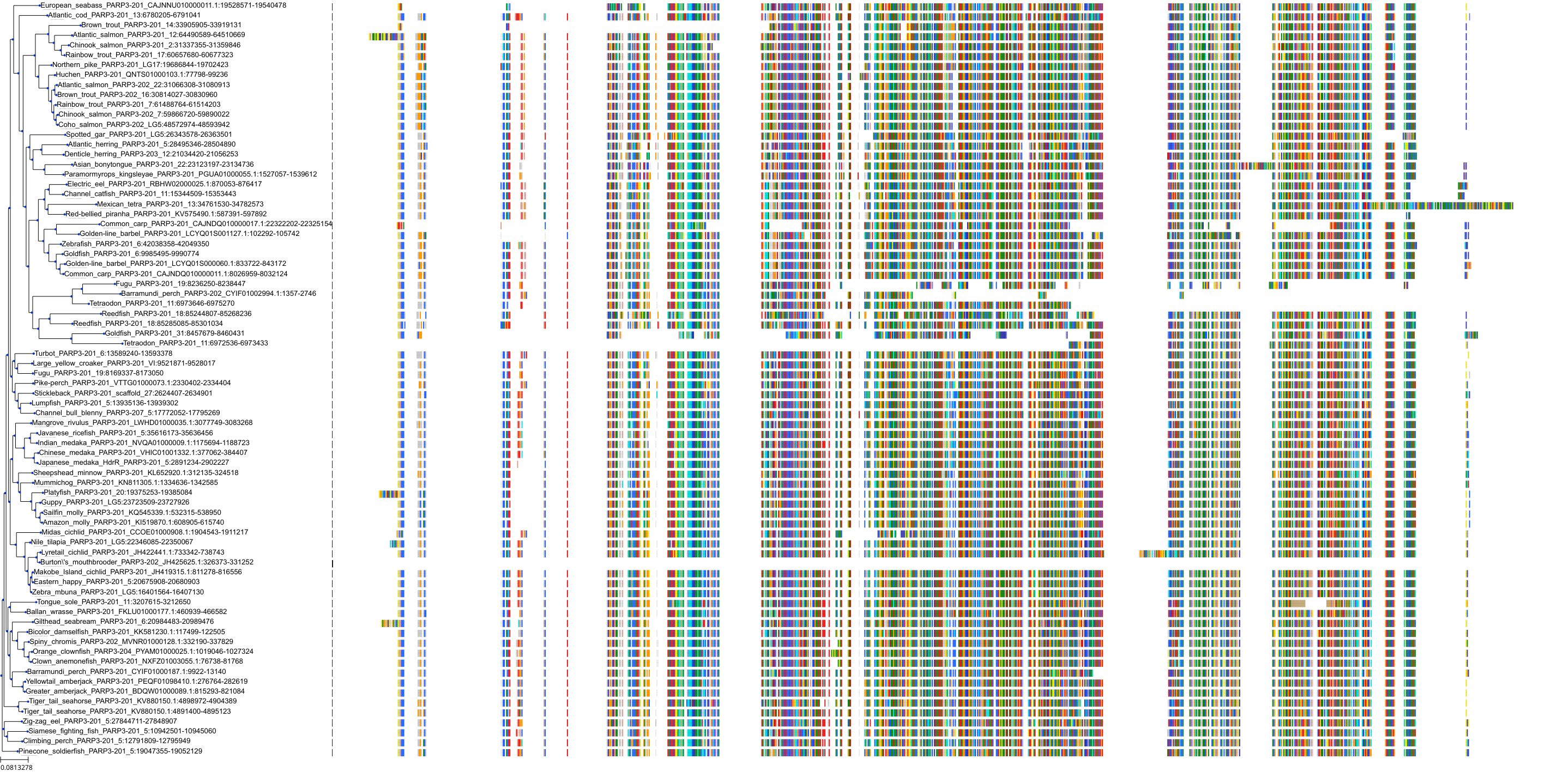
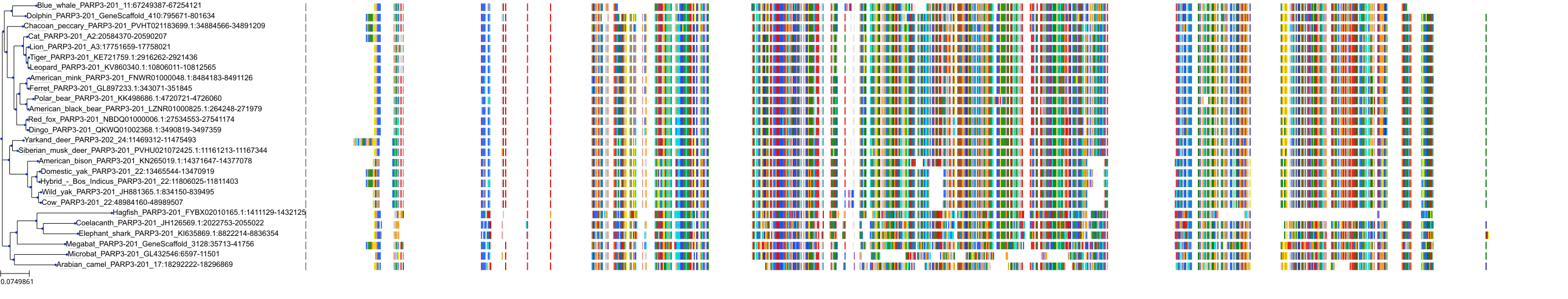
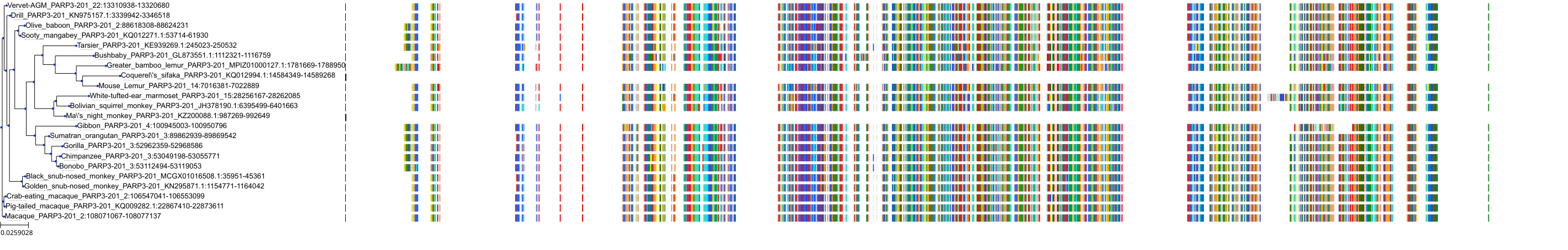
Target Conservation
|
Protein: PARP 1, 2 and 3 Description: Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 Organism : Homo sapiens P09874 ENSG00000143799 |
||||
|
Protein: PARP 1, 2 and 3 Description: Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 2 Organism : Homo sapiens Q9UGN5 ENSG00000129484 |
||||
|
Protein: PARP 1, 2 and 3 Description: Protein mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase PARP3 Organism : Homo sapiens Q9Y6F1 ENSG00000041880 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 83766 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL521686 |
| DrugBank | DB09074 |
| DrugCentral | 4907 |
| FDA SRS | WOH1JD9AR8 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 7519 |
| PDB | 09L |
| PubChem | 23725625 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL426568 |
| ZINC | ZINC000040430143 |
 Cricetulus griseus
Cricetulus griseus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens