Structure
| InChI Key | JYGXADMDTFJGBT-VWUMJDOOSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H30O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 362.47 |
| AlogP | 1.78 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 5.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 3.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 2.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 94.83 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 0.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 26.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Glucocorticoid receptor agonist | AGONIST | PubMed PubMed PubMed PubMed |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Oxidoreductase
|
- | - | - | - | 10.3 | |
|
Secreted protein
|
- | - | 630.96 | 13.18 | - | |
|
Transcription factor
Nuclear receptor
Nuclear hormone receptor subfamily 3
Nuclear hormone receptor subfamily 3 group C
Nuclear hormone receptor subfamily 3 group C member 1
|
- | 25.12 | 43 | - | -23-69 | |
|
Transcription factor
Nuclear receptor
Nuclear hormone receptor subfamily 3
Nuclear hormone receptor subfamily 3 group C
Nuclear hormone receptor subfamily 3 group C member 2
|
- | - | 0.5 | - | - | |
|
Transporter
Electrochemical transporter
SLC superfamily of solute carriers
SLC21/SLCO family of organic anion transporting polypeptides
|
- | - | - | - | 98.24-113.79 | |
|
Transporter
Primary active transporter
ATP-binding cassette
ABCB subfamily
|
- | - | - | - | 0 |
Target Conservation
|
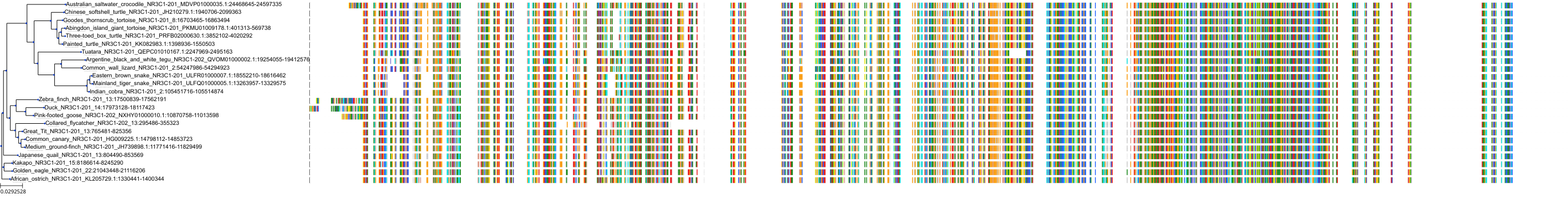
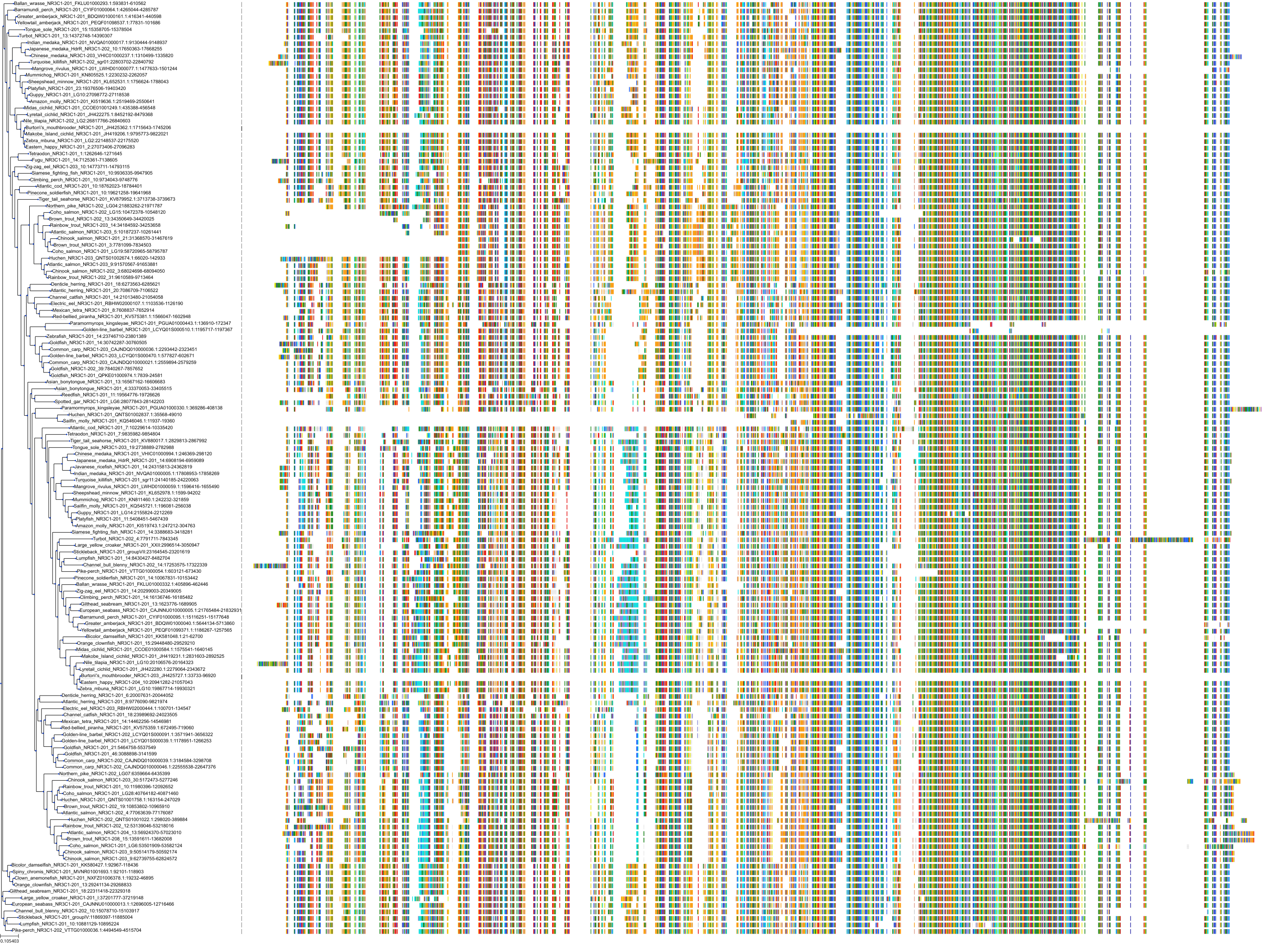
Protein: Glucocorticoid receptor Description: Glucocorticoid receptor Organism : Homo sapiens P04150 ENSG00000113580 |
||||
Related Entries
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 17650 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL389621 |
| DrugBank | DB00741 |
| DrugCentral | 1388 |
| FDA SRS | WI4X0X7BPJ |
| Human Metabolome Database | HMDB0000063 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 2868 |
| KEGG | C08176 |
| PDB | HCY |
| PharmGKB | PA449905 |
| PubChem | 5754 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL4148 |
| ZINC | ZINC000013540519 |
 Cricetulus griseus
Cricetulus griseus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus