| Trade Names | |
| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | C01AA05 |
| UNII | 73K4184T59 |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID5022934 |
Structure
| InChI Key | LTMHDMANZUZIPE-PUGKRICDSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C41H64O14 |
| Molecular Weight | 780.95 |
| AlogP | 2.22 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 14.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 6.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 7.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 203.06 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 0.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 55.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase inhibitor | INHIBITOR | DailyMed Wikipedia |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Hydrolase
|
- | 5.5-500 | - | - | - | |
|
Ion channel
Other ion channel
Phospholemman family
|
- | 270-400 | - | - | - | |
|
Transcription factor
Nuclear receptor
Nuclear hormone receptor subfamily 1
Nuclear hormone receptor subfamily 1 group F
Nuclear hormone receptor subfamily 1 group F member 3
|
- | - | 109 | - | - | |
|
Transporter
Electrochemical transporter
SLC superfamily of solute carriers
SLC21/SLCO family of organic anion transporting polypeptides
|
- | - | - | - | -4.7-81.25 | |
|
Transporter
Electrochemical transporter
SLC superfamily of solute carriers
SLC22 family of organic cation and anion transporters
|
- | - | - | - | 46.9 | |
|
Transporter
Primary active transporter
ATP-binding cassette
ABCB subfamily
|
- | - | - | - | 1 | |
|
Transporter
Primary active transporter
P-type ATPase
Sodium potassium ATPase
|
- | 5.5-500 | - | - | - |
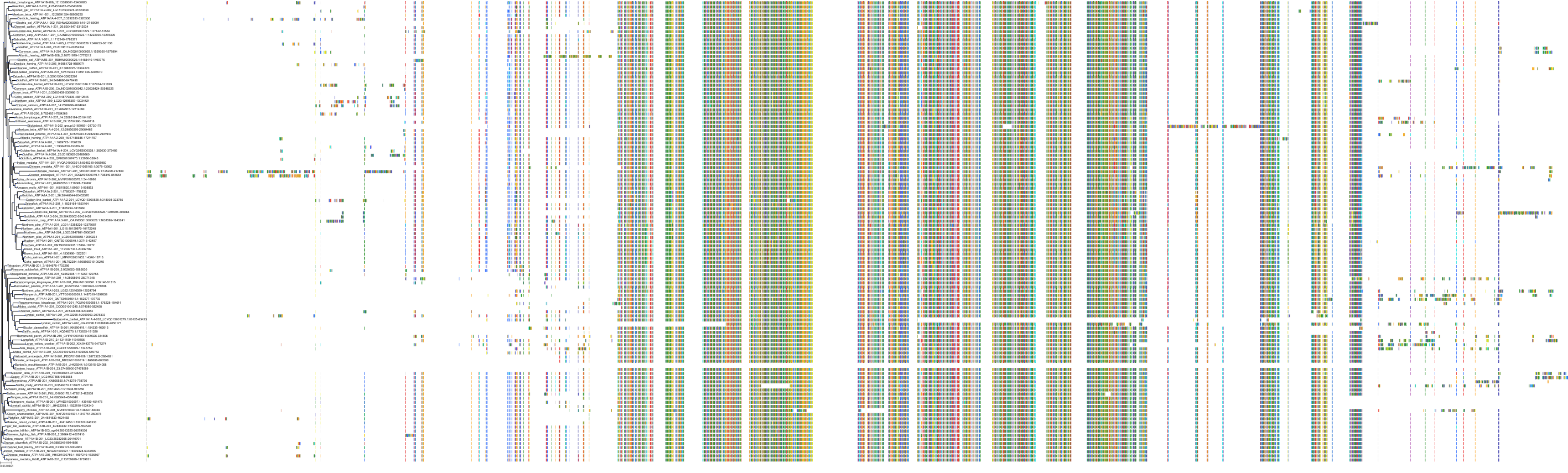
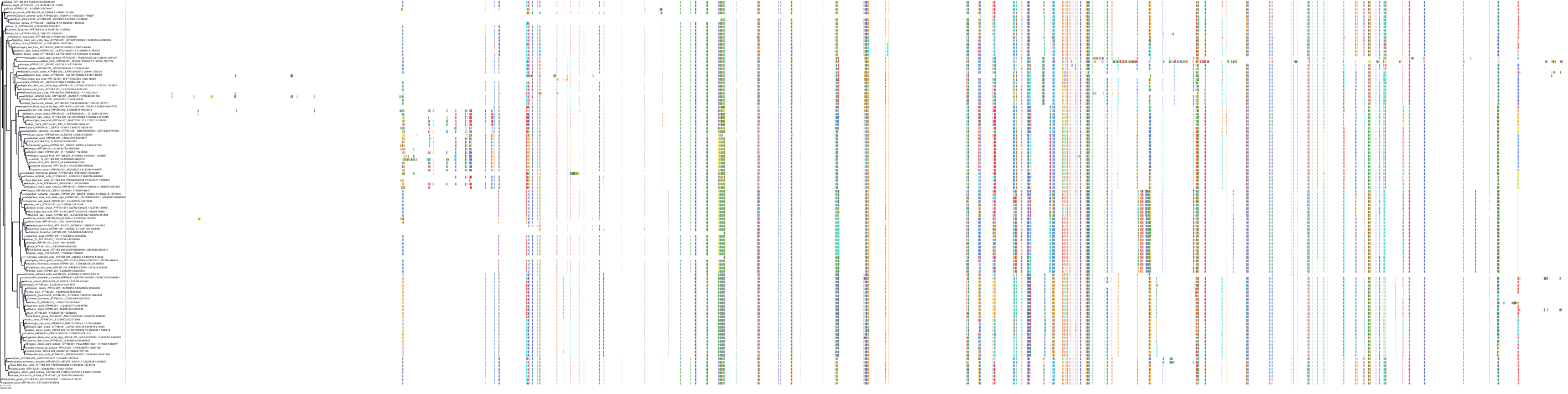
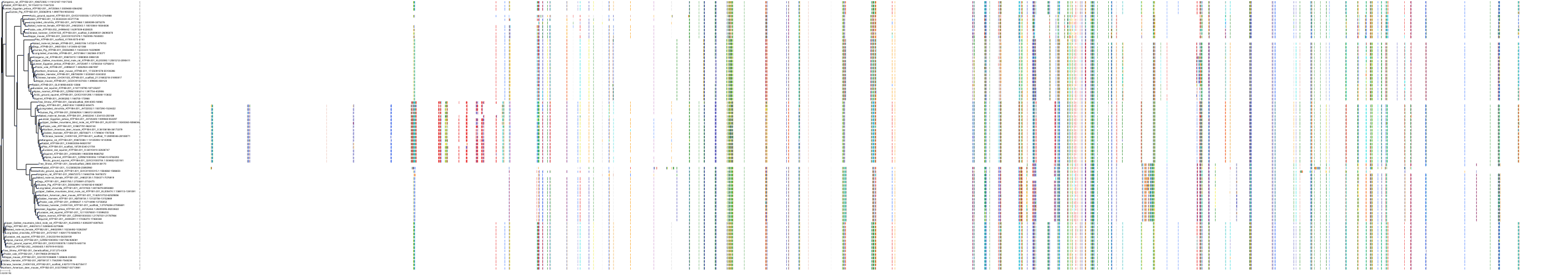
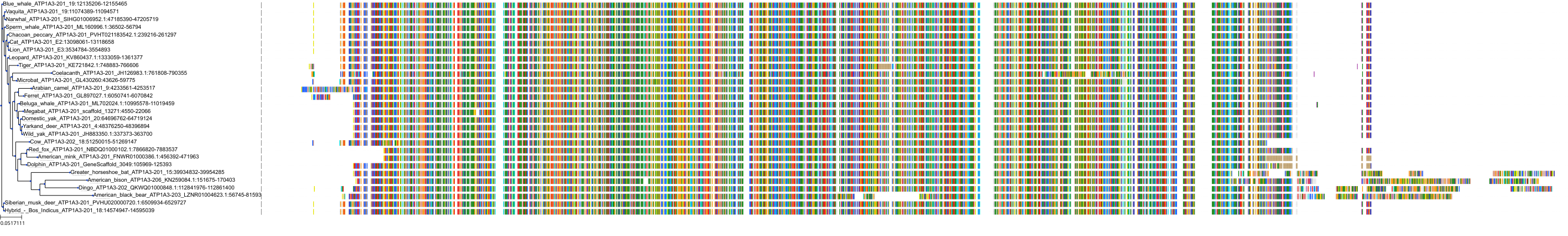
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase Description: Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-1 Organism : Homo sapiens P05023 ENSG00000163399 |
||||
|
Protein: Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase Description: Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit beta-1 Organism : Homo sapiens P05026 ENSG00000143153 |
||||
|
Protein: Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase Description: Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-3 Organism : Homo sapiens P13637 ENSG00000105409 |
||||
|
Protein: Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase Description: Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit beta-2 Organism : Homo sapiens P14415 ENSG00000129244 |
||||
|
Protein: Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase Description: Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-2 Organism : Homo sapiens P50993 ENSG00000018625 |
||||
|
Protein: Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase Description: Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-4 Organism : Homo sapiens Q13733 ENSG00000132681 |
||||
Related Entries
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 4551 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1751 |
| DrugBank | DB00390 |
| DrugCentral | 882 |
| FDA SRS | 73K4184T59 |
| Human Metabolome Database | HMDB0001917 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 4726 |
| KEGG | C06956 |
| PDB | DGX |
| PubChem | 2724385 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL20506 |
| ZINC | ZINC000242548690 |
 Canis lupus familiaris
Canis lupus familiaris
 Cavia porcellus
Cavia porcellus
 Cricetulus griseus
Cricetulus griseus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus
 Sus scrofa
Sus scrofa