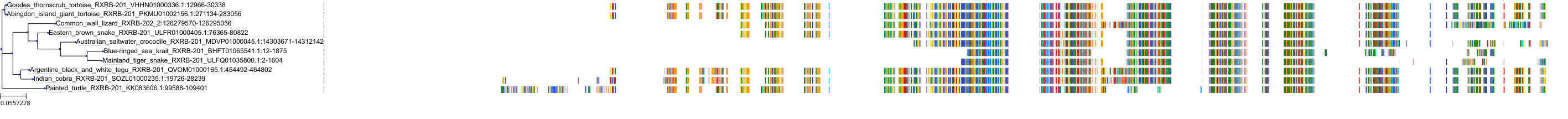| Trade Names | |
| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | L01XF03 |
| UNII | A61RXM4375 |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID1040619 |
Structure
| InChI Key | NAVMQTYZDKMPEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H28O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 348.49 |
| AlogP | 6.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 1.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 3.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 37.3 |
| Molecular species | ACID |
| Aromatic Rings | 2.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 26.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Retinoid X receptor agonist | AGONIST | FDA |
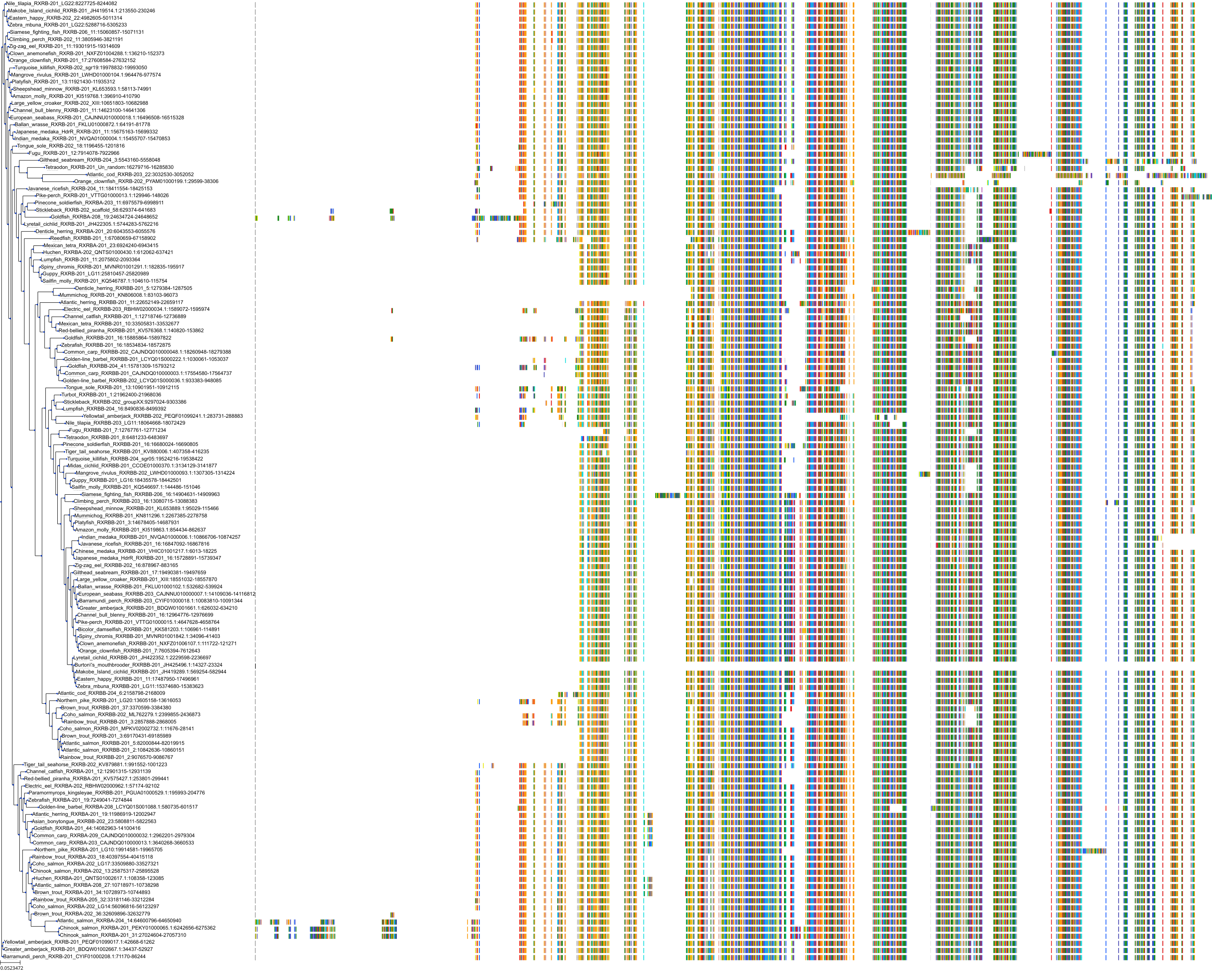
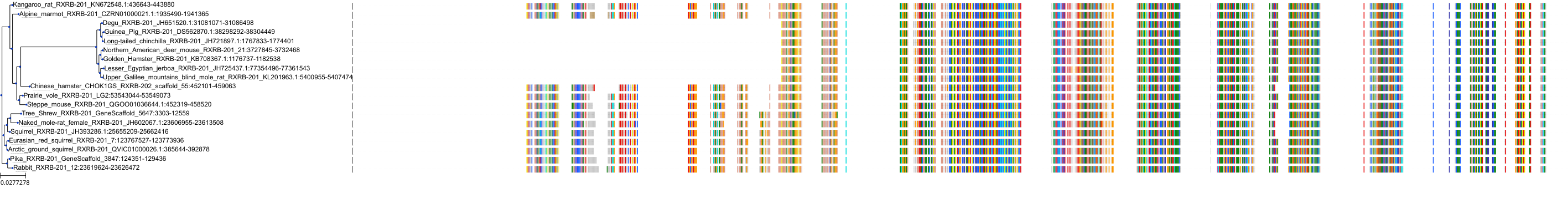
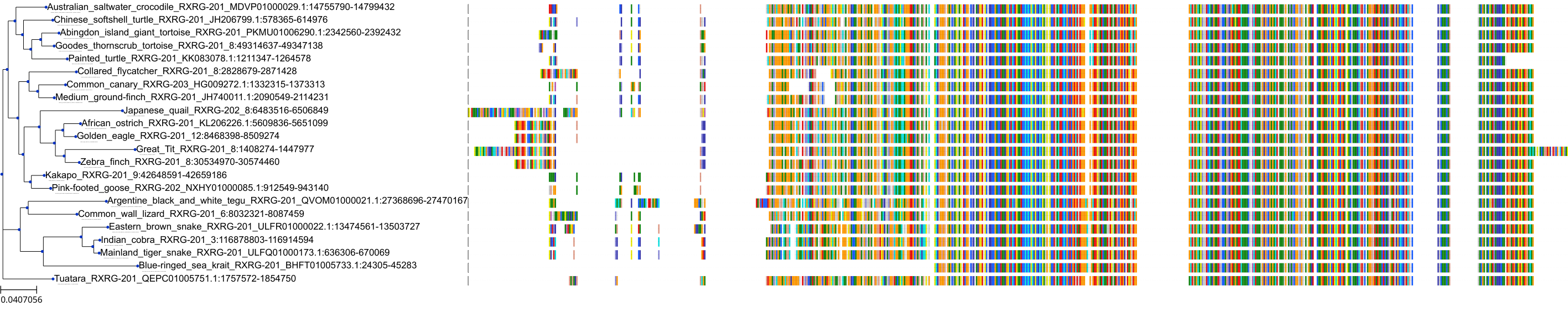
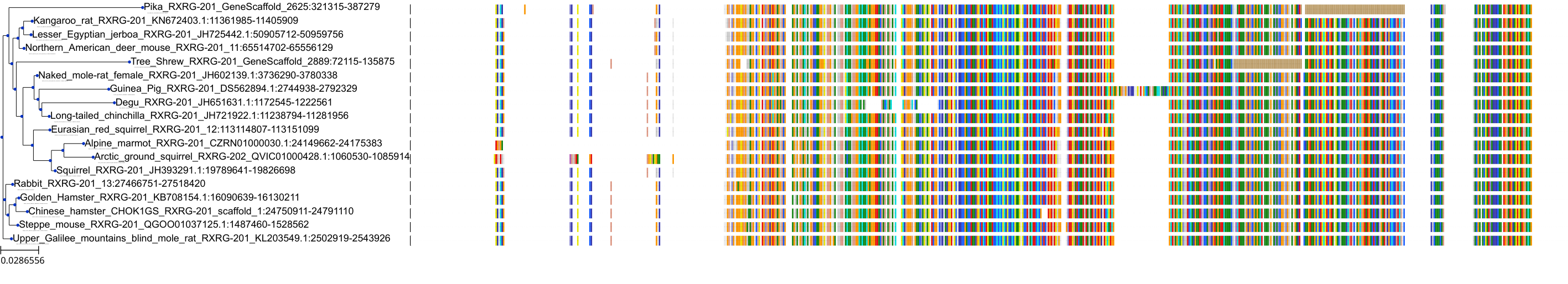
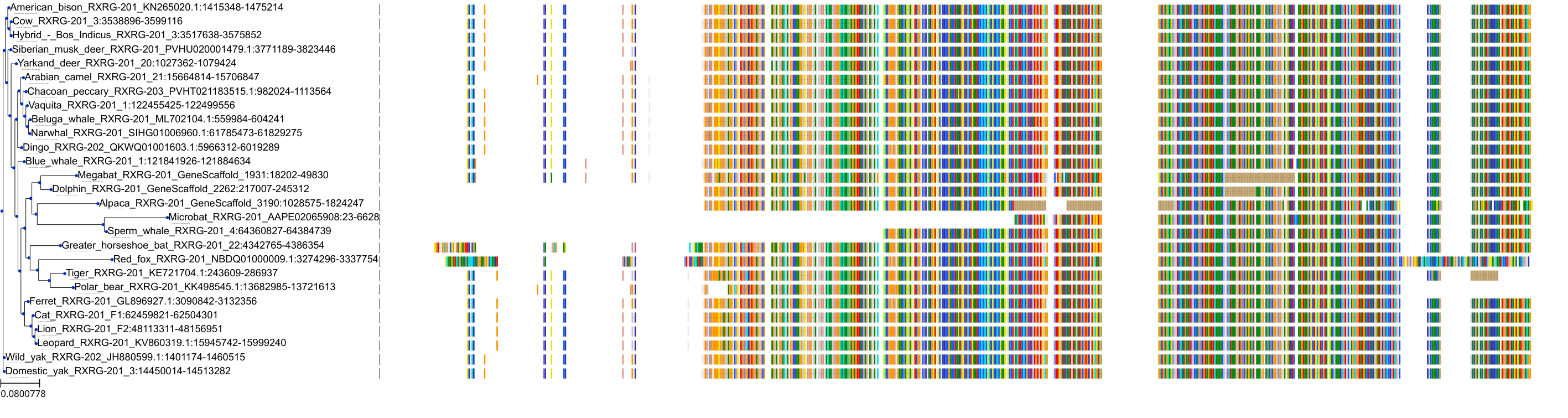
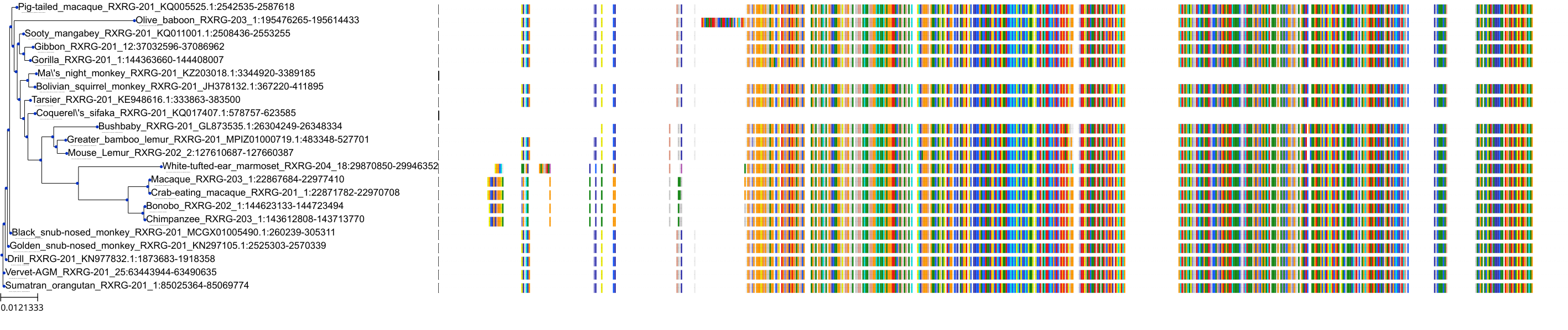
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Retinoid X receptor Description: Retinoic acid receptor RXR-alpha Organism : Homo sapiens P19793 ENSG00000186350 |
||||
|
Protein: Retinoid X receptor Description: Retinoic acid receptor RXR-beta Organism : Homo sapiens P28702 ENSG00000204231 |
||||
|
Protein: Retinoid X receptor Description: Retinoic acid receptor RXR-gamma Organism : Homo sapiens P48443 ENSG00000143171 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 50859 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1023 |
| DrugBank | DB00307 |
| DrugCentral | 361 |
| FDA SRS | A61RXM4375 |
| Human Metabolome Database | HMDB0014452 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 2807 |
| KEGG | D03106 |
| PDB | 9RA |
| PharmGKB | PA164752250 |
| PubChem | 82146 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL9025 |
| ZINC | ZINC000001539579 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus