| Trade Names | |
| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | L02BG01 |
| UNII | 0O54ZQ14I9 |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID8022589 |
Structure
| InChI Key | ROBVIMPUHSLWNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C13H16N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 232.28 |
| AlogP | 1.35 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 3.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 2.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 2.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 72.19 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 1.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 17.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Cytochrome P450 11A1 inhibitor | INHIBITOR | FDA |
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Cytochrome P450
Cytochrome P450 family 11
Cytochrome P450 family 11A
Cytochrome P450 11A1
|
- | - | - | - | 14-85 | |
|
Enzyme
Cytochrome P450
Cytochrome P450 family 19
Cytochrome P450 family 19A
Cytochrome P450 19A1
|
260 | 5.2-270 | - | 470-680 | 32.5-90 | |
|
Transporter
Electrochemical transporter
SLC superfamily of solute carriers
SLC21/SLCO family of organic anion transporting polypeptides
|
- | - | - | - | 52.33-77 |
Target Conservation
|
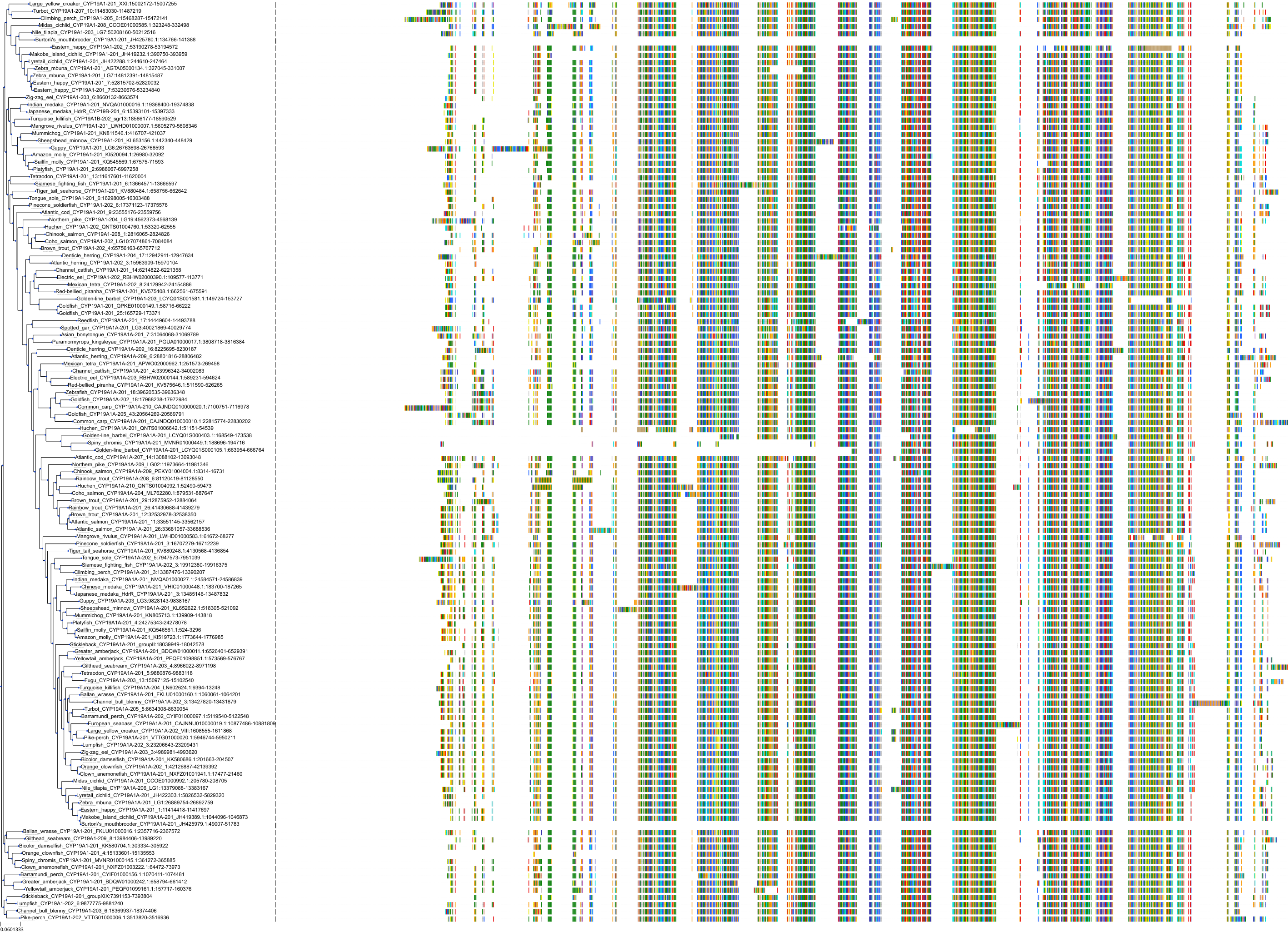
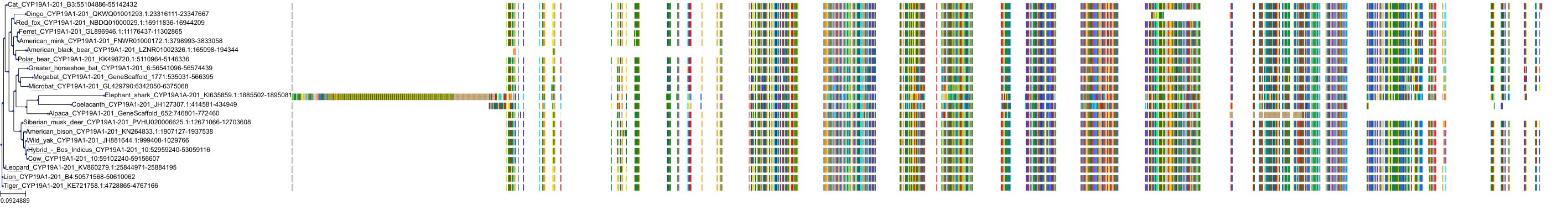
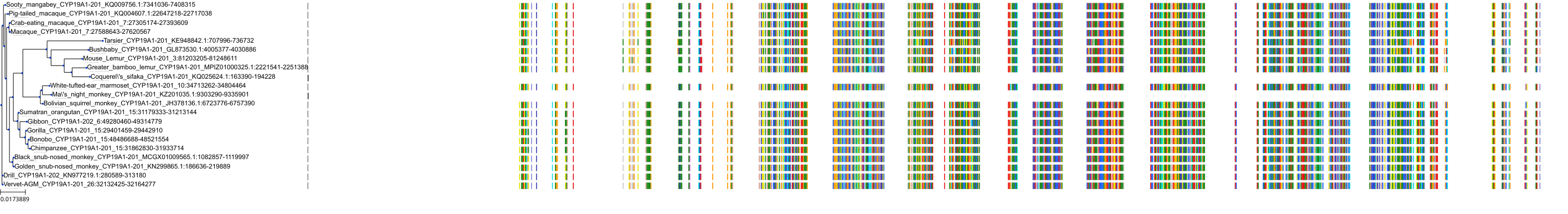
Protein: Cytochrome P450 19A1 Description: Aromatase Organism : Homo sapiens P11511 ENSG00000137869 |
||||
Related Entries
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 2654 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL488 |
| DrugBank | DB00357 |
| DrugCentral | 164 |
| FDA SRS | 0O54ZQ14I9 |
| Human Metabolome Database | HMDB0014501 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 7054 |
| KEGG | C07617 |
| PharmGKB | PA448375 |
| PubChem | 2145 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL4306 |
| ZINC | ZINC01530856 |
 Bos taurus
Bos taurus
 Cricetulus griseus
Cricetulus griseus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus