| Trade Names | |
| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | C01EA01 G04BE01 |
| UNII | F5TD010360 |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID9022578 |
Structure
| InChI Key | GMVPRGQOIOIIMI-DWKJAMRDSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H34O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 354.49 |
| AlogP | 3.48 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 4.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 3.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 13.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 94.83 |
| Molecular species | ACID |
| Aromatic Rings | 0.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 25.0 |
Pharmacology
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Hydrolase
|
- | - | - | - | -1.69-16.57 | |
|
Membrane receptor
Family A G protein-coupled receptor
Small molecule receptor (family A GPCR)
Lipid-like ligand receptor (family A GPCR)
Prostanoid receptor
|
1.8-3.6 | - | - | 3.1-150 | - |
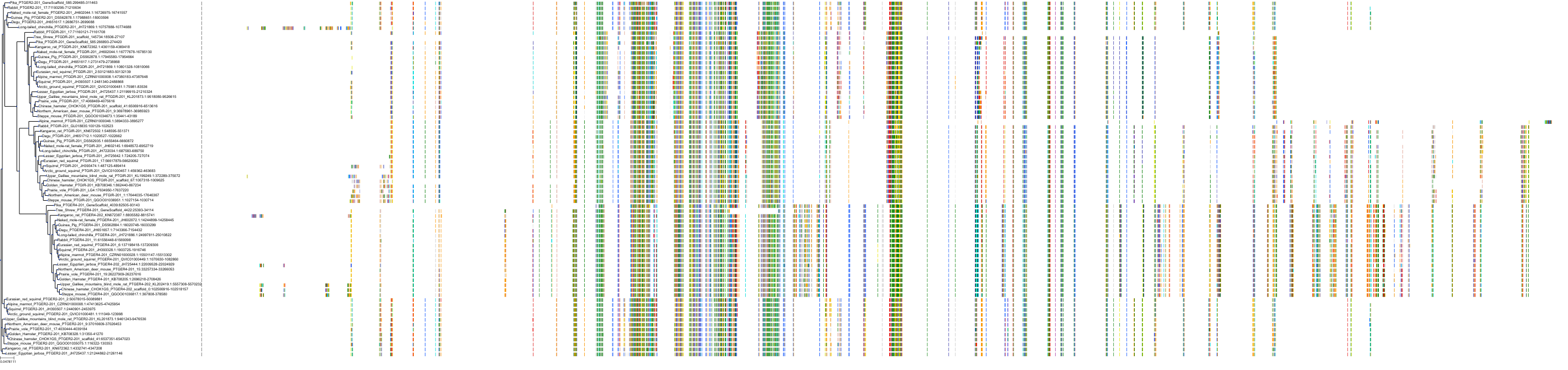
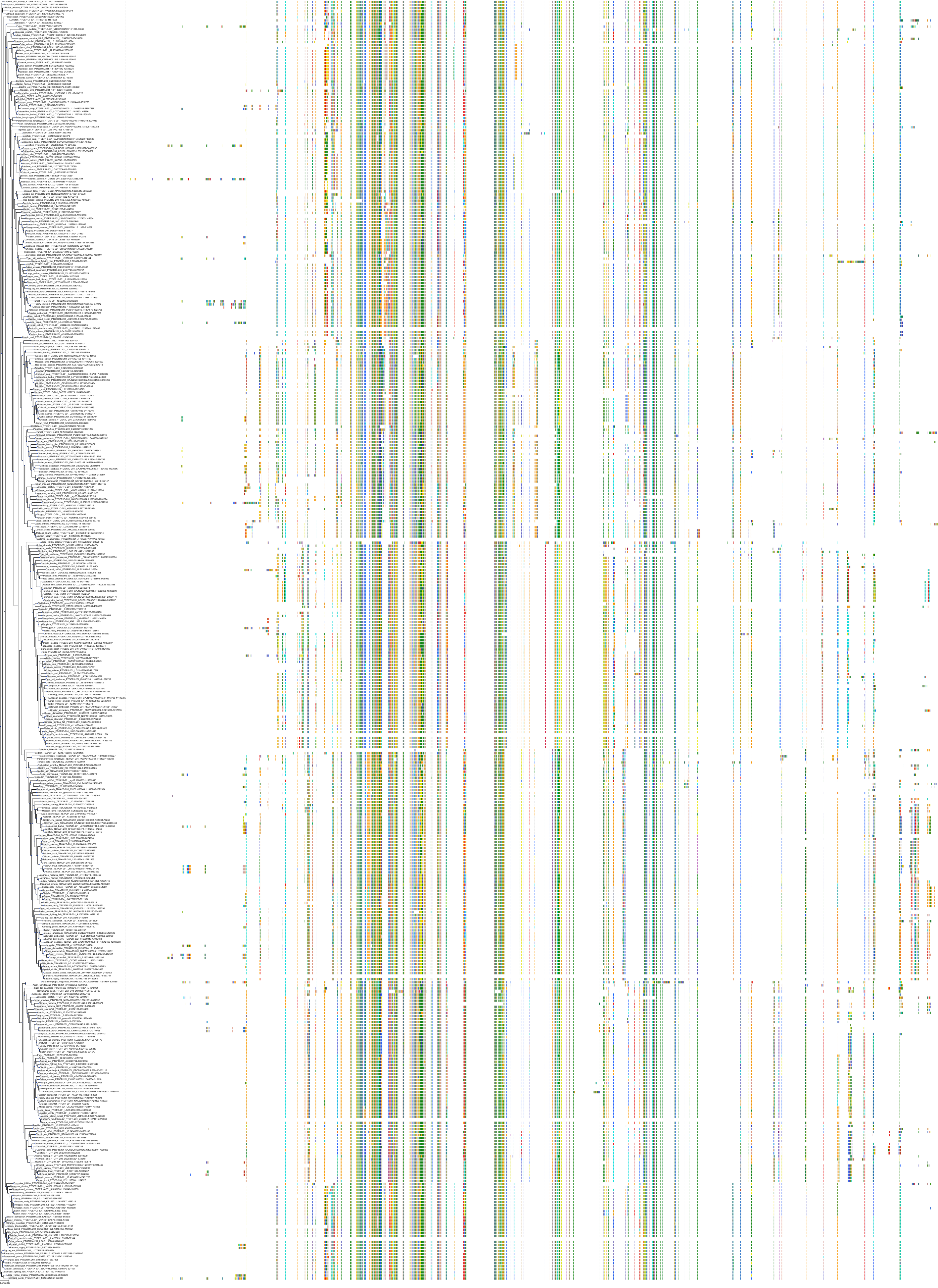
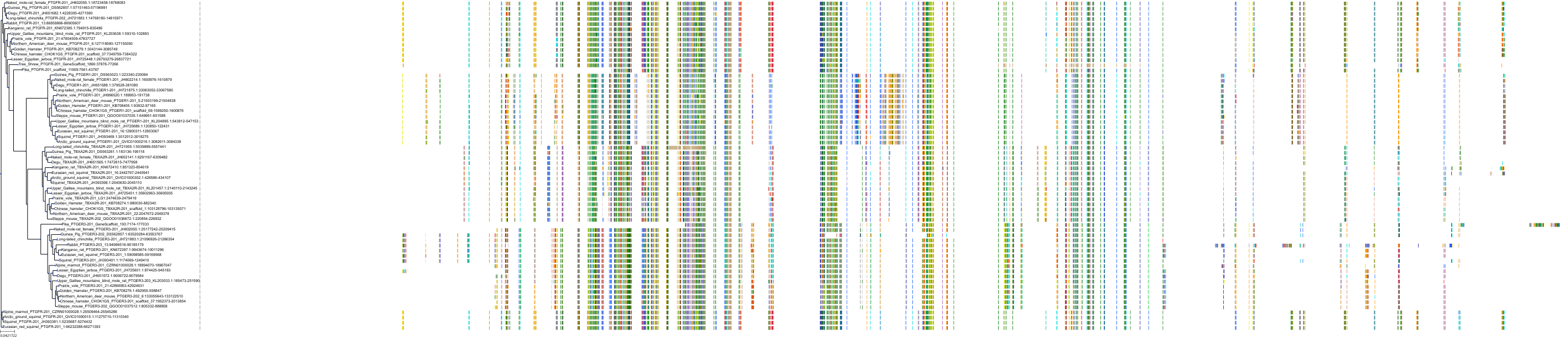
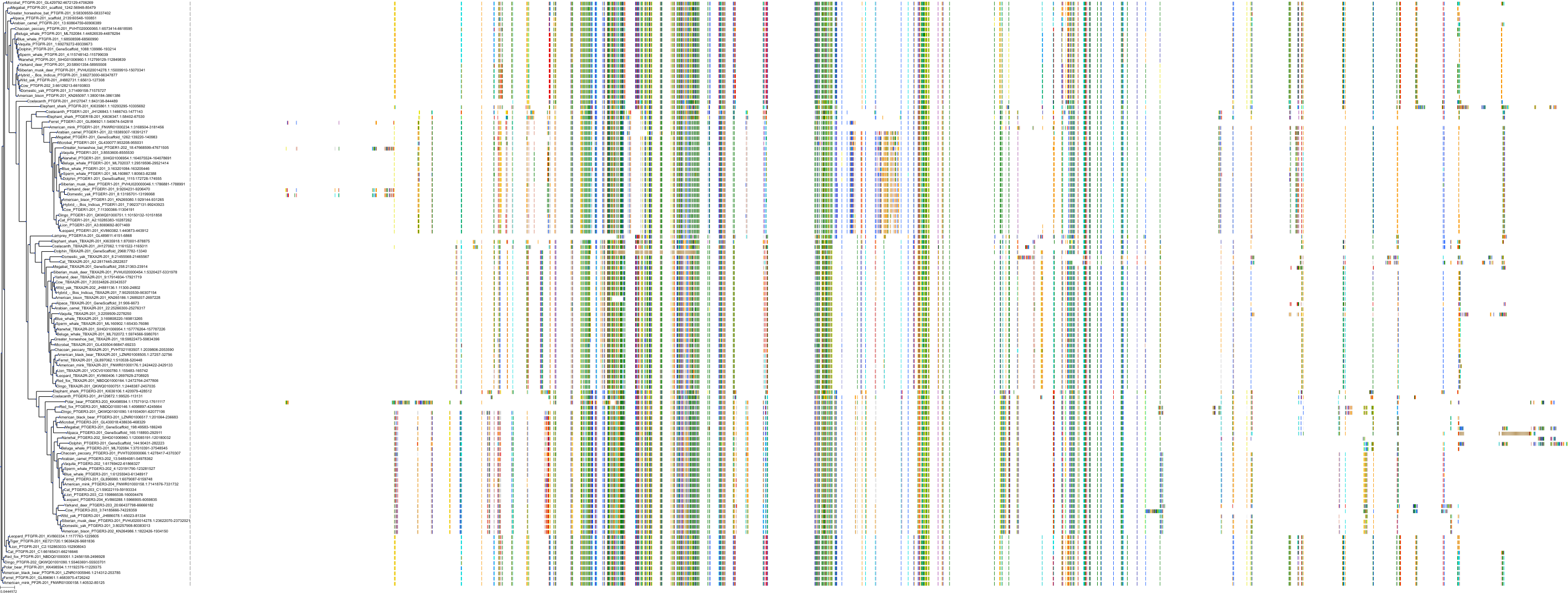
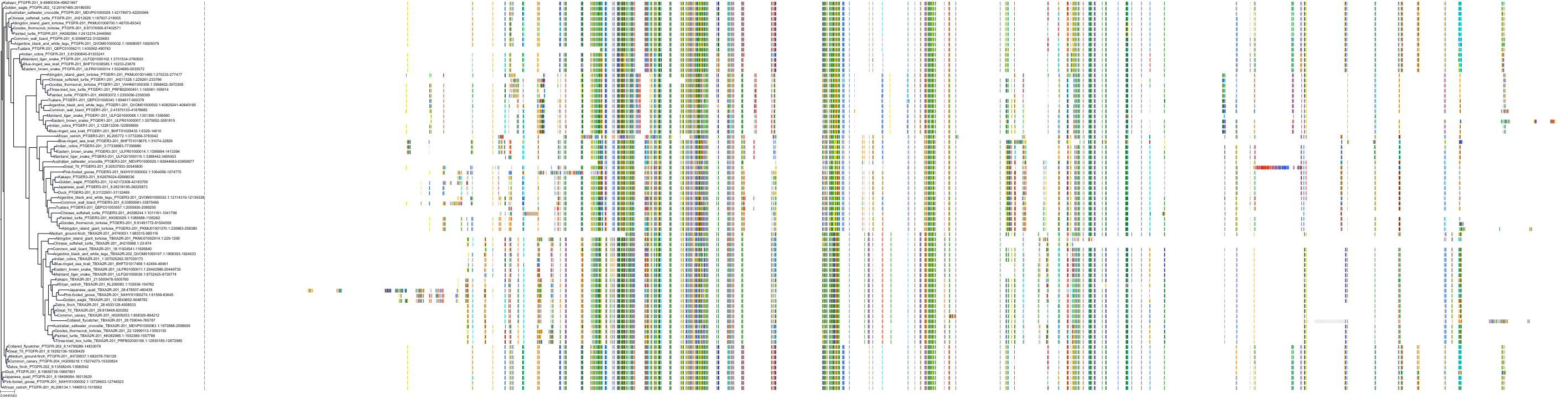
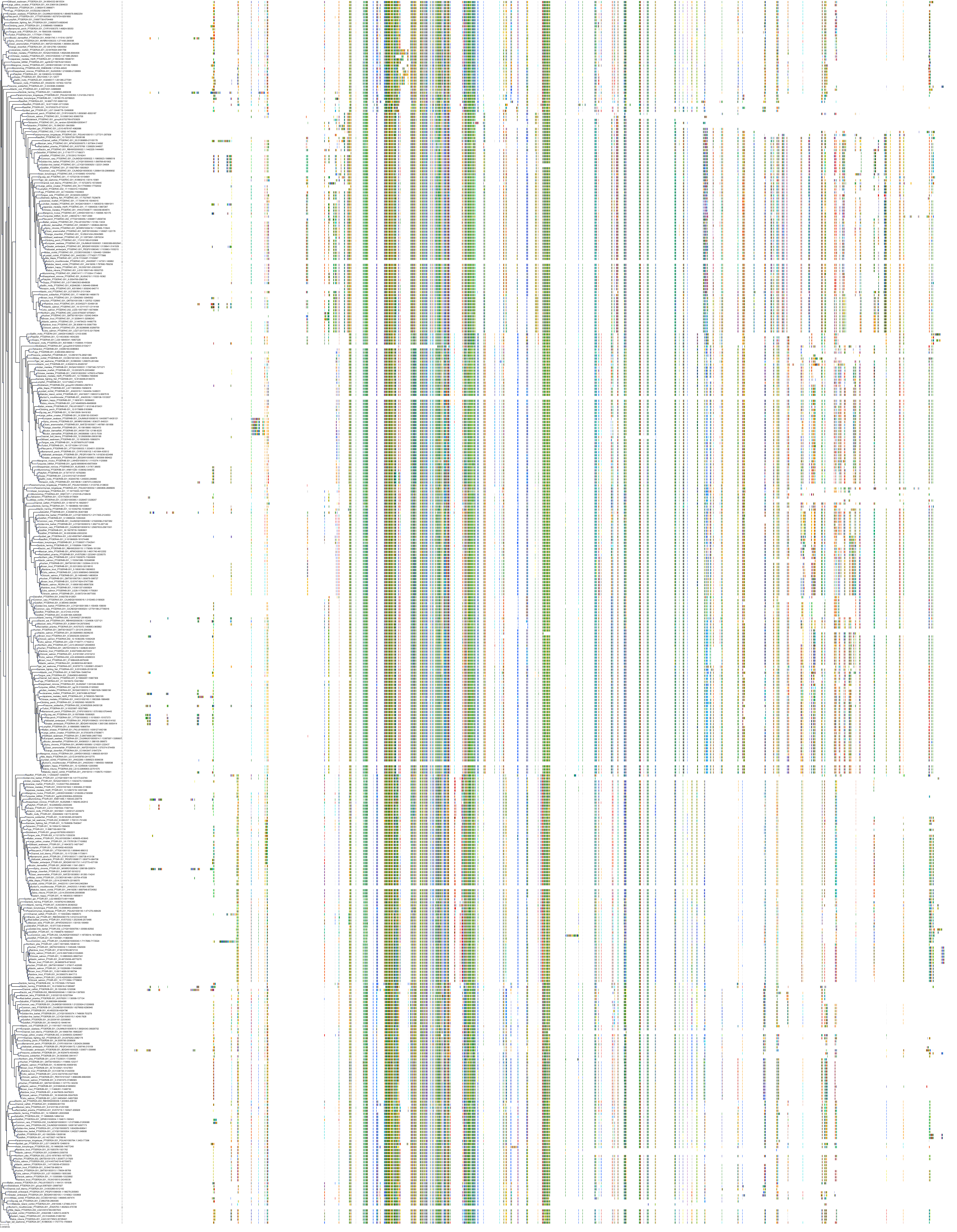
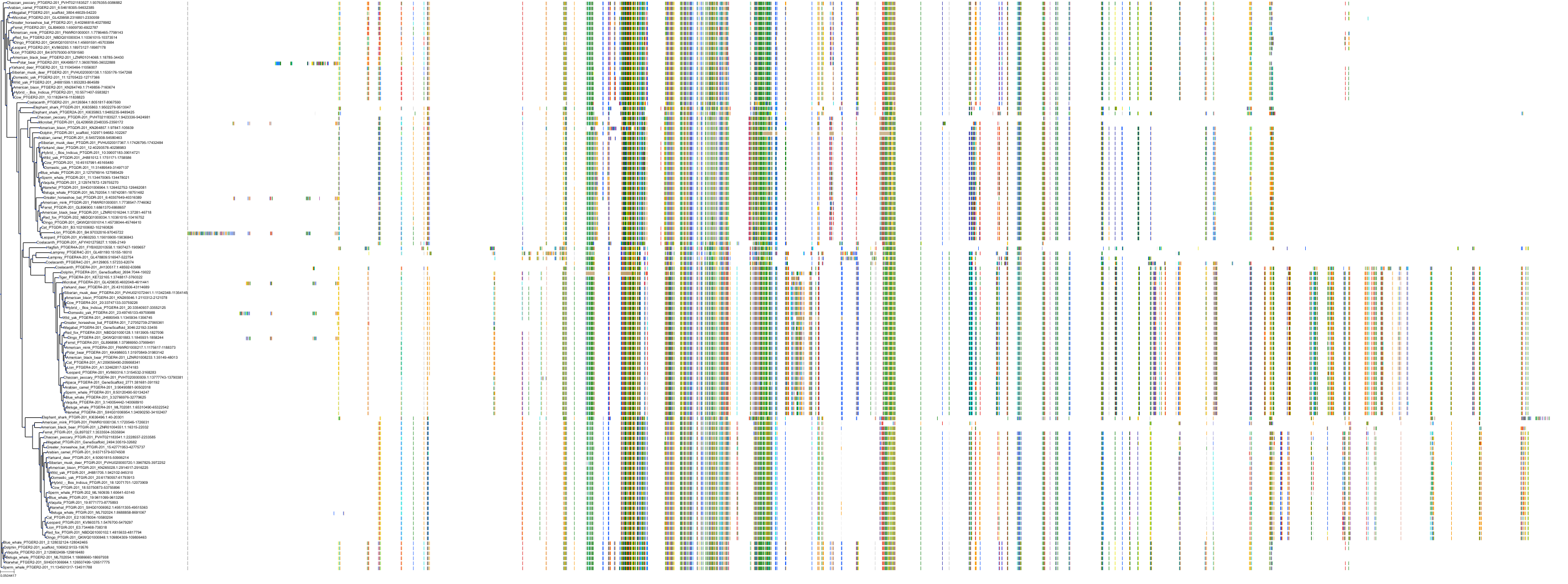
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Prostanoid EP1 receptor Description: Prostaglandin E2 receptor EP1 subtype Organism : Homo sapiens P34995 ENSG00000160951 |
||||
|
Protein: Prostanoid EP2 receptor Description: Prostaglandin E2 receptor EP2 subtype Organism : Homo sapiens P43116 ENSG00000125384 |
||||
Related Entries
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 15544 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL495 |
| DrugBank | DB00770 |
| DrugCentral | 138 |
| FDA SRS | F5TD010360 |
| Human Metabolome Database | HMDB0001442 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 1882 |
| KEGG | C04741 |
| PDB | XPG |
| PubChem | 5280723 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL33317 |
| ZINC | ZINC000003813088 |
 Electrophorus electricus
Electrophorus electricus
 Equus caballus
Equus caballus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus