| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | A10BH02 |
| UNII | I6B4B2U96P |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID80881091 |
Structure
| InChI Key | SYOKIDBDQMKNDQ-XWTIBIIYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H25N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 303.41 |
| AlogP | 1.17 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 4.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 2.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 3.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 76.36 |
| Molecular species | BASE |
| Aromatic Rings | 0.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 22.0 |
Pharmacology
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Protease
Serine protease
Serine protease SC clan
Serine protease S9B subfamily
|
- | 0.12-680 | 2.4-10.7 | 3-810 | 94.66 | |
|
Enzyme
Protease
Serine protease
|
- | 0.12-680 | 2.4-10.7 | 3-810 | 94.66 |
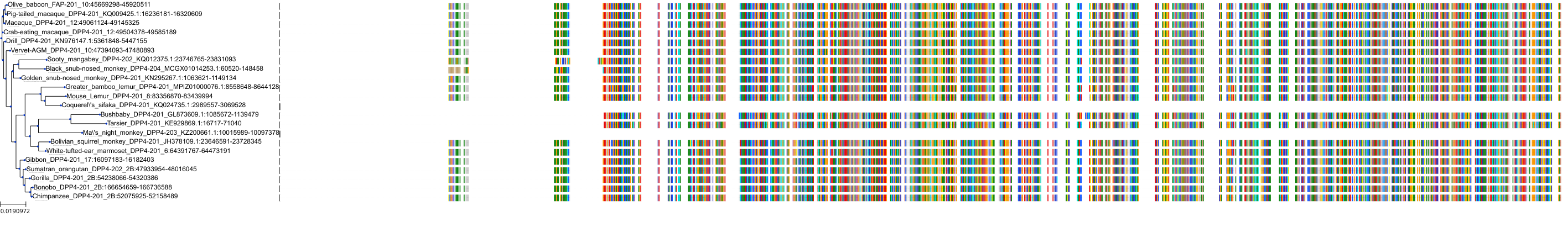
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Dipeptidyl peptidase IV Description: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 Organism : Homo sapiens P27487 ENSG00000197635 |
||||
Environmental Exposure
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 135285 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL142703 |
| DrugBank | DB04876 |
| DrugCentral | 3642 |
| FDA SRS | I6B4B2U96P |
| Human Metabolome Database | HMDB0015596 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 6310 |
| PharmGKB | PA165958346 |
| PubChem | 6918537 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL16579 |
 Bos taurus
Bos taurus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Porphyromonas gingivalis
Porphyromonas gingivalis
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus