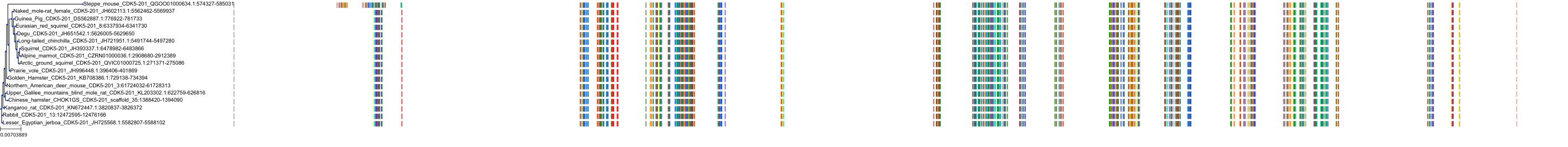Structure
| InChI Key | PIMQWRZWLQKKBJ-SFHVURJKSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H28N6O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 396.5 |
| AlogP | 2.28 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 7.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 2.0 |
| Number of Rotational Bond | 7.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 92.63 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 3.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 29.0 |
Pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 inhibitor | INHIBITOR | PubMed |
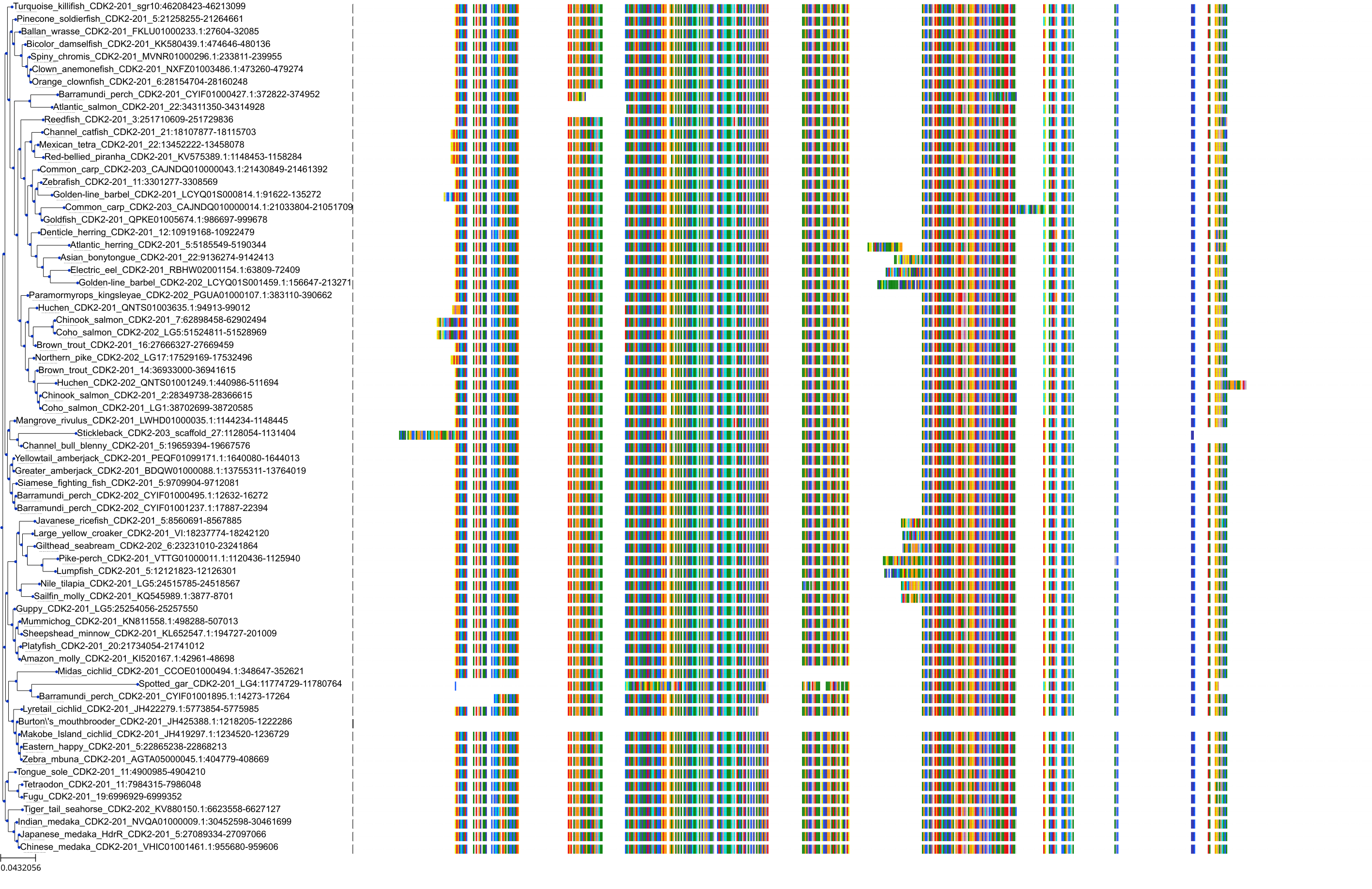
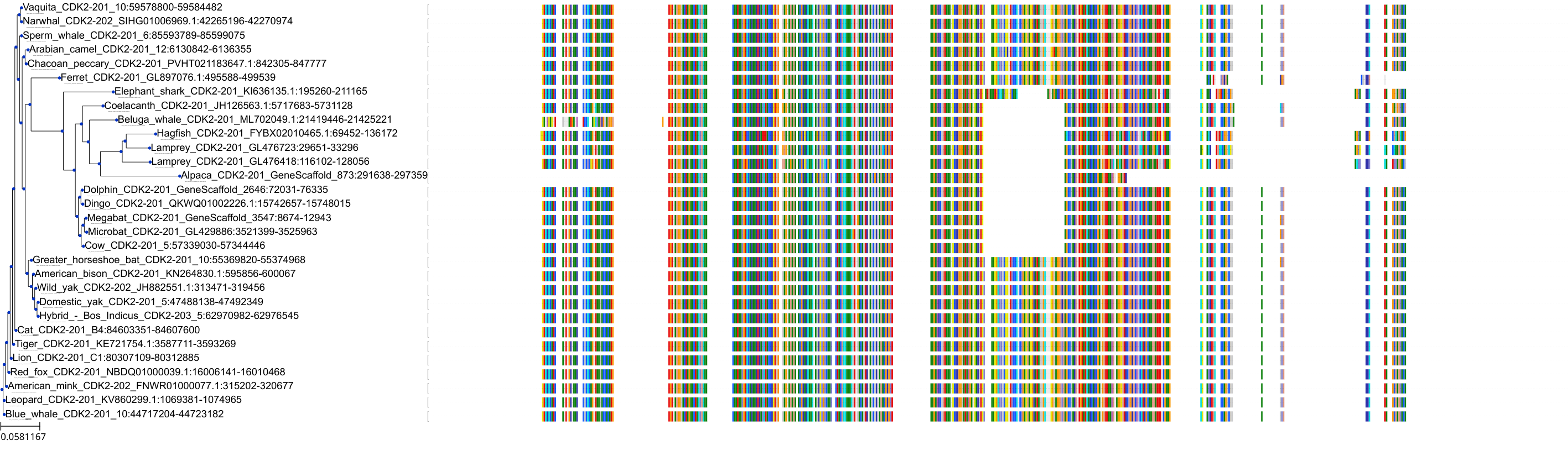
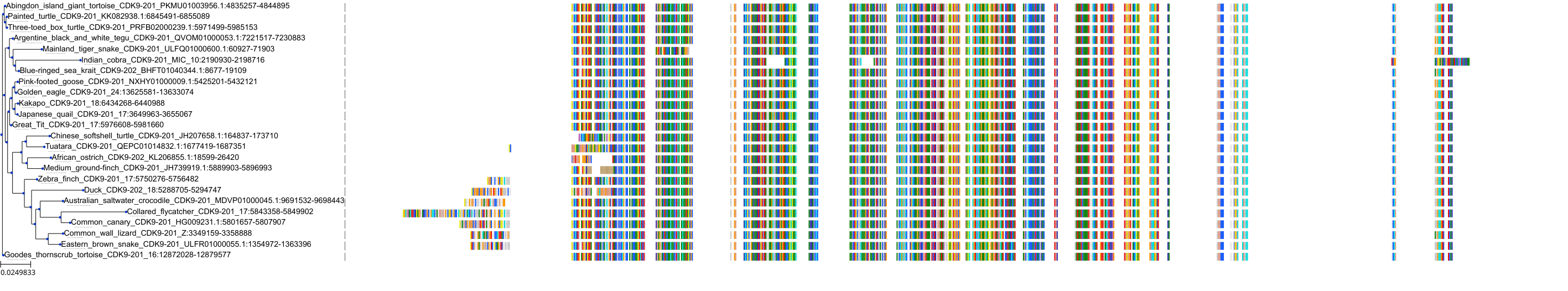
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 Description: Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 Organism : Homo sapiens P06493 ENSG00000170312 |
||||
|
Protein: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 Description: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 Organism : Homo sapiens P24941 ENSG00000123374 |
||||
|
Protein: Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 Description: Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 Organism : Homo sapiens P50750 ENSG00000136807 |
||||
|
Protein: Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 Description: Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 Organism : Homo sapiens Q00535 ENSG00000164885 |
||||
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 95060 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2103840 |
| DrugBank | DB12021 |
| FDA SRS | 4V8ECV0NBQ |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 7379 |
| PubChem | 46926350 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL12048446 |
| ZINC | ZINC000034894449 |
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Trypanosoma brucei
Trypanosoma brucei