| Trade Names | |
| Synonyms | |
| Status | |
| Molecule Category | Free-form |
| ATC | N03AF01 |
| UNII | 33CM23913M |
| EPA CompTox | DTXSID4022731 |
Structure
| InChI Key | FFGPTBGBLSHEPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|---|
| Smiles | |
| InChI |
|
Physicochemical Descriptors
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H12N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 236.27 |
| AlogP | 3.39 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 1.0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 1.0 |
| Polar Surface Area | 46.33 |
| Molecular species | NEUTRAL |
| Aromatic Rings | 2.0 |
| Heavy Atoms | 18.0 |
Pharmacology
| Targets | EC50(nM) | IC50(nM) | Kd(nM) | Ki(nM) | Inhibition(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enzyme
Oxidoreductase
|
- | - | - | - | 8 | |
|
Ion channel
Ligand-gated ion channel
P2X receptor
|
- | - | - | - | 35 | |
|
Ion channel
Voltage-gated ion channel
Voltage-gated sodium channel
|
- | - | - | - | 1.6-64.8 | |
|
Transporter
Electrochemical transporter
SLC superfamily of solute carriers
SLC21/SLCO family of organic anion transporting polypeptides
|
- | - | - | - | 13.3-121.62 | |
|
Transporter
Electrochemical transporter
SLC superfamily of solute carriers
SLC22 family of organic cation and anion transporters
|
- | - | - | - | 8.4 |
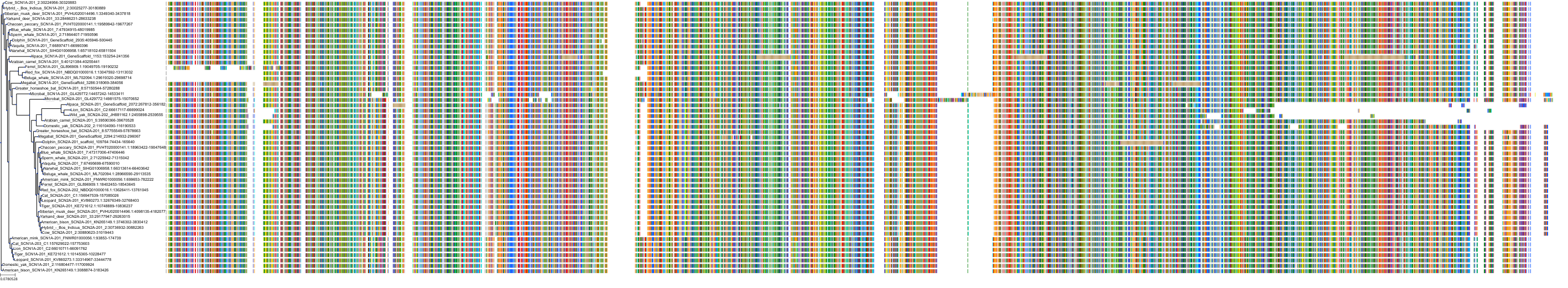
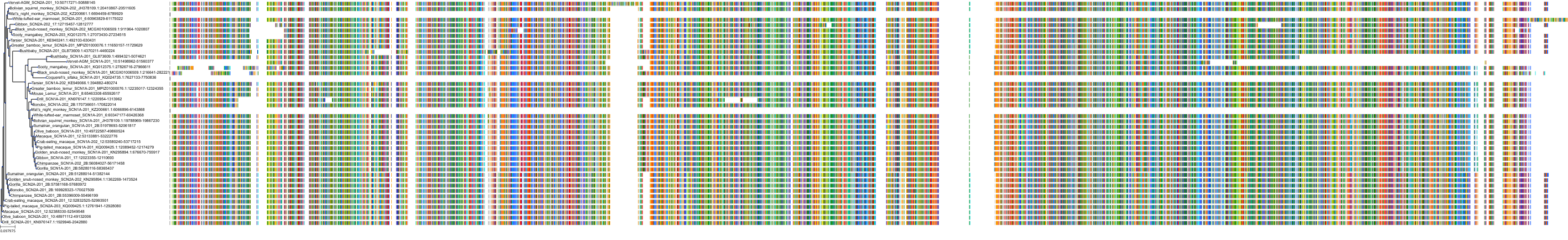
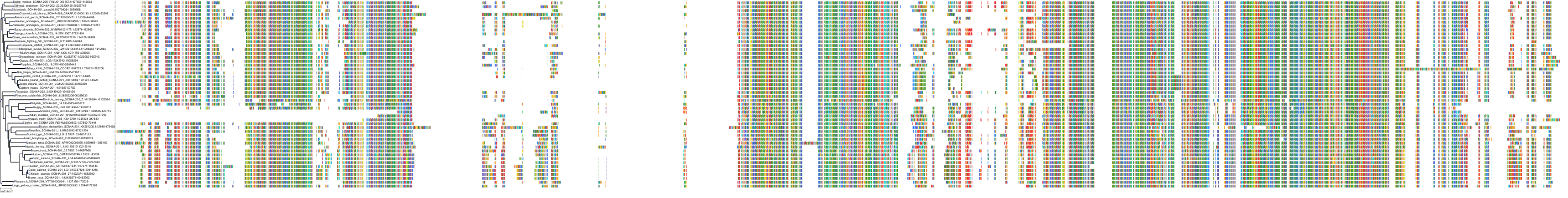
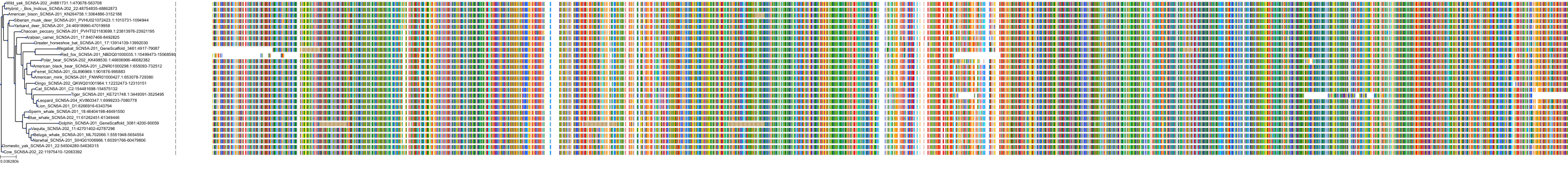
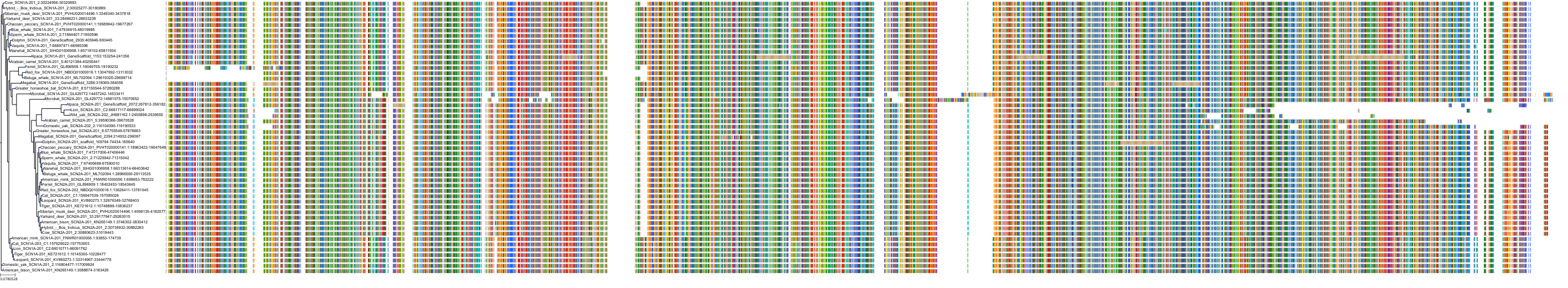
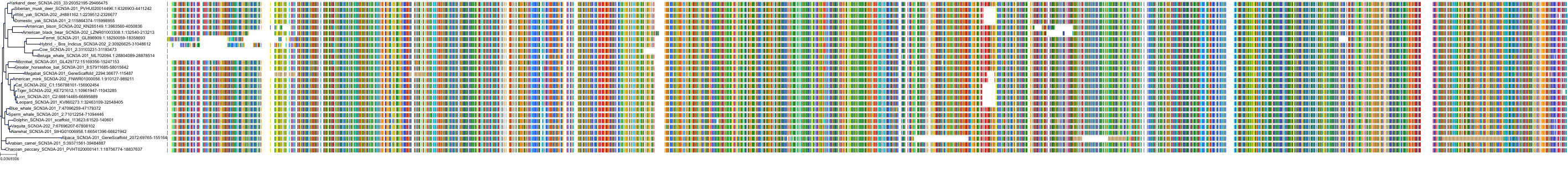
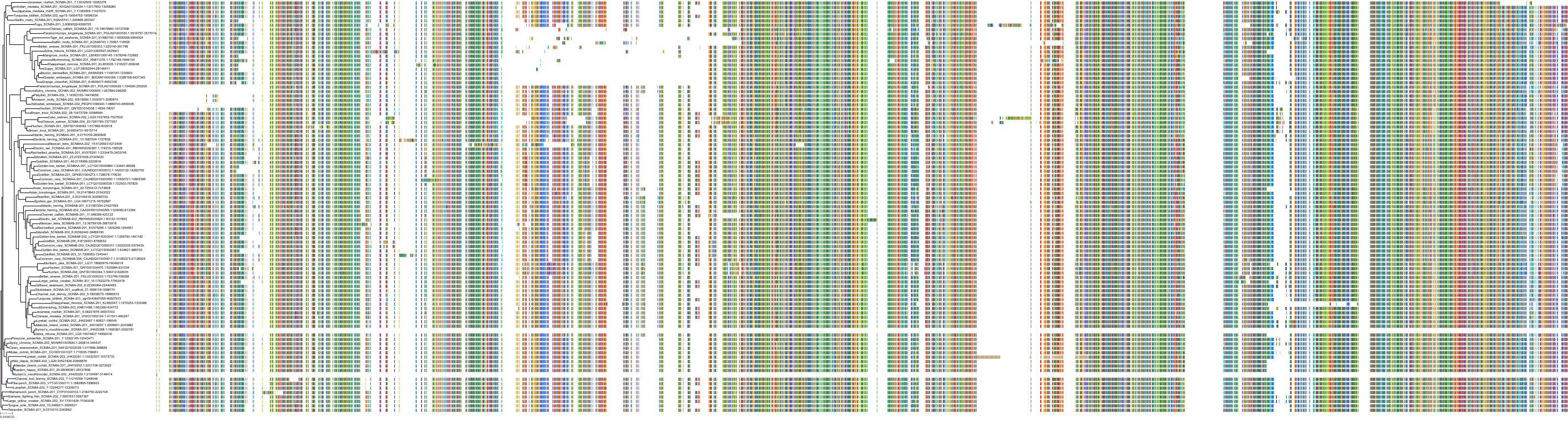
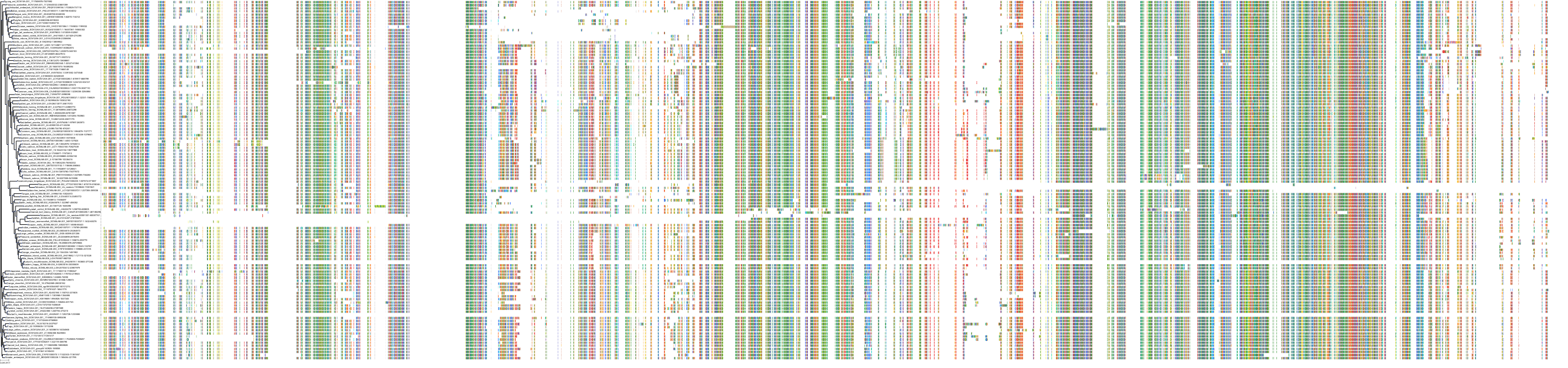
Target Conservation
|
Protein: Sodium channel alpha subunit Description: Sodium channel protein type 1 subunit alpha Organism : Homo sapiens P35498 ENSG00000144285 |
||||
|
Protein: Sodium channel alpha subunit Description: Sodium channel protein type 4 subunit alpha Organism : Homo sapiens P35499 ENSG00000007314 |
||||
|
Protein: Sodium channel alpha subunit Description: Sodium channel protein type 5 subunit alpha Organism : Homo sapiens Q14524 ENSG00000183873 |
||||
|
Protein: Sodium channel alpha subunit Description: Sodium channel protein type 9 subunit alpha Organism : Homo sapiens Q15858 ENSG00000169432 |
||||
|
Protein: Sodium channel alpha subunit Description: Sodium channel protein type 2 subunit alpha Organism : Homo sapiens Q99250 ENSG00000136531 |
||||
|
Protein: Sodium channel alpha subunit Description: Sodium channel protein type 3 subunit alpha Organism : Homo sapiens Q9NY46 ENSG00000153253 |
||||
|
Protein: Sodium channel alpha subunit Description: Sodium channel protein type 11 subunit alpha Organism : Homo sapiens Q9UI33 ENSG00000168356 |
||||
|
Protein: Sodium channel alpha subunit Description: Sodium channel protein type 8 subunit alpha Organism : Homo sapiens Q9UQD0 ENSG00000196876 |
||||
|
Protein: Sodium channel alpha subunit Description: Sodium channel protein type 10 subunit alpha Organism : Homo sapiens Q9Y5Y9 ENSG00000185313 |
||||
Environmental Exposure
Cross References
| Resources | Reference |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | 3387 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL108 |
| DrugBank | DB00564 |
| DrugCentral | 489 |
| FDA SRS | 33CM23913M |
| Human Metabolome Database | HMDB0014704 |
| Guide to Pharmacology | 5339 |
| KEGG | C06868 |
| PDB | N6W |
| PharmGKB | PA448785 |
| PubChem | 2554 |
| SureChEMBL | SCHEMBL21639 |
| ZINC | ZINC000000004785 |
 Cavia porcellus
Cavia porcellus
 Cricetulus griseus
Cricetulus griseus
 Homo sapiens
Homo sapiens
 Mus musculus
Mus musculus
 Rattus norvegicus
Rattus norvegicus